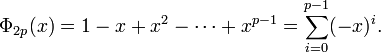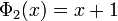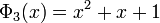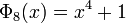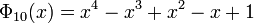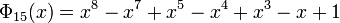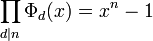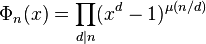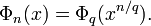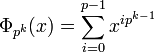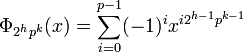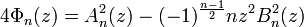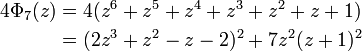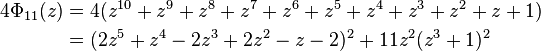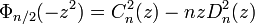Cyclotomic polynomial
In algebra, the nth cyclotomic polynomial, for any positive integer n, is the unique irreducible polynomial with integer coefficients, which is a divisor of  and is not a divisor of
and is not a divisor of  for any k < n. Its roots are the nth primitive roots of unity
for any k < n. Its roots are the nth primitive roots of unity
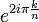 , where k runs over the integers lower than n and coprime to n. In other words, the nth cyclotomic polynomial is equal to
, where k runs over the integers lower than n and coprime to n. In other words, the nth cyclotomic polynomial is equal to
It may also be defined as the monic polynomial with integer coefficients, which is the minimal polynomial over the field of the rational numbers of any primitive nth-root of unity ( is such a primitive root).
is such a primitive root).
Examples
If n is a prime number then
If n=2p where p is an odd prime number then
For n up to 10 we have:
For n up to 20, the cyclotomic polynomials not covered by above formulas are:
The case of 105 is interesting because it is the first integer that is the product of three distinct odd prime numbers and the 105th cyclotomic polynomial is the first one that has a coefficient of magnitude greater than 1:
Properties
Fundamental tools
The cyclotomic polynomials are monic polynomials with integer coefficients that are irreducible over the field of the rational numbers. Except for n equal to 1 or 2, they are palindromic polynomials of even degree.
The degree of  , or in other words the number of nth primitive roots of unity, is
, or in other words the number of nth primitive roots of unity, is  , where
, where  is Euler's totient function.
is Euler's totient function.
The fact that  is an irreducible polynomial of degree
is an irreducible polynomial of degree  in the ring
in the ring ![{\mathbb {Z}}[x]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/7/2/0/1720d8ed9c2582abffc3c0685c1ddb77.png) is a nontrivial result due to Gauss.[1] Depending on the chosen definition, it is either the value of the degree or the irreducibility which is a nontrivial result. The case of prime n is easier to prove than the general case, thanks to Eisenstein's criterion.
is a nontrivial result due to Gauss.[1] Depending on the chosen definition, it is either the value of the degree or the irreducibility which is a nontrivial result. The case of prime n is easier to prove than the general case, thanks to Eisenstein's criterion.
A fundamental relation involving cyclotomic polynomials is
which means that each n-th root of unity is a primitive d-th root of unity for a unique d dividing n.
The Möbius inversion formula allows the expression of 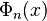 as an explicit rational fraction:
as an explicit rational fraction:
The cyclotomic polynomial  may be computed by (exactly) dividing
may be computed by (exactly) dividing  by the cyclotomic polynomials of the proper divisors of n previously computed recursively by the same method:
by the cyclotomic polynomials of the proper divisors of n previously computed recursively by the same method:
(Recall that 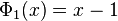 ).
).
This formula allows to compute 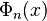 on a computer for any n, as soon as integer factorization and division of polynomials are available. Many computer algebra systems have a built in function to compute the cyclotomic polynomials. For example in Maple,
on a computer for any n, as soon as integer factorization and division of polynomials are available. Many computer algebra systems have a built in function to compute the cyclotomic polynomials. For example in Maple, 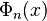 may be computed by typing "numtheory[cyclotomic](n,x);".
may be computed by typing "numtheory[cyclotomic](n,x);".
Easy cases for the computation
As noted above, if n is a prime number then
If n is an odd integer greater than one, then
 .
.
In particular, if n=2p is twice an odd prime then (as noted above)
If n=pm is a prime power (where p is prime), then
More generally, if n=qmr with m>1 then
 [citation needed]
[citation needed]
This formula may be iterated to get a simple expression of any cyclotomic polynomial 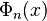 in term of a cyclotomic polynomial of square free index: If q is the product of the prime divisors of n (its radical), then
in term of a cyclotomic polynomial of square free index: If q is the product of the prime divisors of n (its radical), then
This allows to give formulas for the nth cyclotomic polynomial when n has at most one odd prime factor: If p is an odd prime number, and h and k are positive integers, then:
For the other values of n, the computation of the nth cyclotomic polynomial is similarly reduced to that of  where q is the product of the distinct odd prime divisors of n.
where q is the product of the distinct odd prime divisors of n.
Integers appearing as coefficients
The problem of bounding the magnitude of the coefficients of the cyclotomic polynomials has been the object of a number of research papers.
If n has at most two distinct odd prime factors, then Migotti showed that the coefficients of  are all in the set {1, −1, 0}.[2]
are all in the set {1, −1, 0}.[2]
The first cyclotomic polynomial for a product of 3 different odd prime factors is 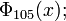 it has a coefficient −2 (see its expression above). The converse isn't true:
it has a coefficient −2 (see its expression above). The converse isn't true:  =
= 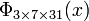 only has coefficients in {1, −1, 0}.
only has coefficients in {1, −1, 0}.
If n is a product of more odd different prime factors, the coefficients may increase to very high values. E.g., 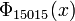 =
=  has coefficients running from −22 to 22,
has coefficients running from −22 to 22, 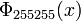 =
= 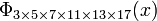 , the smallest n with 6 different odd primes, has coefficients up to ±532.
, the smallest n with 6 different odd primes, has coefficients up to ±532.
Let A(n) denote the maximum absolute value of the coefficients of Φn. It is known that for any positive k, the number of n up to x with A(n) > nk is at least c(k)⋅x for a positive c(k) depending on k and x sufficiently large. In the opposite direction, for any function ψ(n) tending to infinity with n we have A(n) bounded above by nψ(n) for almost all n.[3]
Gauss's formula
Let n be odd, square-free, and greater than 3. Then[4][5]
where both An(z) and Bn(z) have integer coefficients, An(z) has degree φ(n)/2, and Bn(z) has degree φ(n)/2 − 2. Furthermore, An(z) is palindromic when its degree is even; if its degree is odd it is antipalindromic. Similarly, Bn(z) is palindromic unless n is composite and ≡ 3 (mod 4), in which case it is antipalindromic.
The first few cases are
Lucas's formula
Let n be odd, square-free and greater than 3. Then[6]
where both Un(z) and Vn(z) have integer coefficients, Un(z) has degree φ(n)/2, and Vn(z) has degree φ(n)/2 − 1. This can also be written
If n is even, square-free and greater than 2 (this forces n to be ≡ 2 (mod 4)),
where both Cn(z) and Dn(z) have integer coefficients, Cn(z) has degree φ(n), and Dn(z) has degree φ(n) − 1. Cn(z) and Dn(z) are both palindromic.
The first few cases are:
Applications
Using the fact that  is irreducible, one can prove the infinitude of primes congruent to 1 modulo n,[7] which is a special case of Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions.
is irreducible, one can prove the infinitude of primes congruent to 1 modulo n,[7] which is a special case of Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Lang, Serge (2002), Algebra, Graduate Texts in Mathematics 211 (Revised third ed.), New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-95385-4, MR 1878556
- ↑ Isaacs, Martin (2009). Algebra: A Graduate Course. AMS Bookstore. p. 310. ISBN 978-0-8218-4799-2.
- ↑ Meier (2008)
- ↑ Gauss, DA, Articles 356-357
- ↑ Riesel, pp. 315-316, p. 436
- ↑ Riesel, pp. 309-315, p. 443
- ↑ S. Shirali. Number Theory. Orient Blackswan, 2004. p. 67. ISBN 81-7371-454-1
References
The Disquisitiones Arithmeticae has been translated from Latin into English and German. The German edition includes all of his papers on number theory: all the proofs of quadratic reciprocity, the determination of the sign of the Gauss sum, the investigations into biquadratic reciprocity, and unpublished notes.
- Gauss, Carl Friedrich; Clarke, Arthur A. (translator into English) (1986), Disquisitiones Arithemeticae (Second, corrected edition), New York: Springer, ISBN 0387962549
- Gauss, Carl Friedrich; Maser, H. (translator into German) (1965), Untersuchungen uber hohere Arithmetik (Disquisitiones Arithemeticae & other papers on number theory) (Second edition), New York: Chelsea, ISBN 0-8284-0191-8
- Lemmermeyer, Franz (2000), Reciprocity Laws: from Euler to Eisenstein, Berlin: Springer, doi:10.1007/978-3-662-12893-0, ISBN 978-3-642-08628-1
- Maier, Helmut (2008), "Anatomy of integers and cyclotomic polynomials", in De Koninck, Jean-Marie; Granville, Andrew; Luca, Florian, Anatomy of integers. Based on the CRM workshop, Montreal, Canada, March 13--17, 2006, CRM Proceedings and Lecture Notes 46, Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, pp. 89–95, ISBN 978-0-8218-4406-9, Zbl 1186.11010
- Riesel, Hans (1994), Prime Numbers and Computer Methods for Factorization (second edition), Boston: Birkhäuser, ISBN 0-8176-3743-5
External links
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Cyclotomic polynomials", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- "Sloane's A013594 : Smallest order of cyclotomic polynomial containing n or −n as a coefficient", The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.