Cyclooctatetraenide anion
The cyclooctatetraenide dianion is an aromatic organic anion with the structure C8H82-. It is planar and aromatic, like the cyclopentadienide anion, and, like cyclopentadienide, easily forms compounds with metals.
Compounds
The salt potassium cyclooctatetraenide is easily formed by the reaction of cyclooctatetraene with potassium metal. It has the structure K2C8H8, or K2(COT).
Cyclooctatetraenic acid is a hypothetical acid with the structure H2C8H8, or H2(COT).
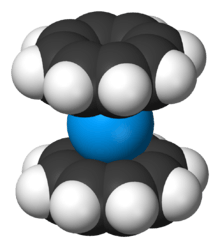
Several sandwich compounds involving the cyclooctatetraenide anion are known, the most notable of which are the actinocenes, such as uranocene, U(C8H8)2 or U(COT)2, thorocene, Th(C8H8)2 or Th(COT)2, and plutonocene, Pu(C8H8)2; ferricene (not to be confused with ferrocene), Fe(C8H8)2, is also known. Since the actinides can also exist in the (III) oxidation stade, they can also exist in the form (where A is any actinide) AC5H5C8H8, or A(Cp)(COT), as the cyclopentadienide-cyclooctatetraenide. An example of this is UC5H5C8H8, or uranium cyclopentadienide-cyclooctatetraenide.