Cyclone Martin
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
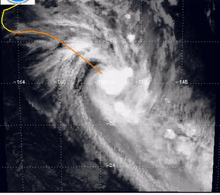 Cyclone Martin near its peak intensity | |||||
| Formed | October 20, 1997 | ||||
| Dissipated | November 5, 1997 | ||||
| Highest winds |
10-minute sustained: 155 km/h (100 mph) 1-minute sustained: 185 km/h (115 mph) | ||||
| Lowest pressure | 945 mbar (hPa); 27.91 inHg | ||||
| Fatalities | 28 | ||||
| Areas affected | Cook Islands, French Polynesia | ||||
| Part of the 1997–98 South Pacific cyclone season | |||||
Severe Tropical Cyclone Martin was the deadliest tropical cyclone of the 1997–98 South Pacific cyclone season.
Meteorological history
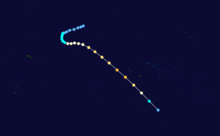
On October 27, 1997 the Fiji Meteorological Service's Regional Specialized Meteorological Center in Nadi, Fiji (RSMC Nadi) started to monitor a weak tropical disturbance that had developed to the north of the Northern Cook Islands.[1] Over the next few days atmospheric convection surrounding the system remained disorganised, as the system moved to the southwest and was affected by strong upper-level north-easterly winds and moderate to strong vertical wind shear.[2][3] Late on October 30, the United States Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (NPMOC) designated the disturbance as Tropical Cyclone 04P, as it had become a tropical depression.[2][4][5] During the next day the system started to show a marked improvement in organisation and began rapidly developing, before RSMC Nadi named it Martin at 1500 UTC after it had developed into a category 1 tropical cyclone on the Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale.[1] When it was named, Martin was located about 500 km (310 mi) to the west of Manihiki Atoll in the Northern Cook Islands and had started to re-curve and move towards the south-east during that day.[1][6][7] Early on November 1, RSMC Nadi reported that the system had become a category 2 tropical cyclone on the Australian scale, before the NPMOC reported that Martin had become equivalent to a category one hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).[6][8] During that day as the cyclone season officially started, Martin continued to intensify and became a category 3 severe tropical cyclone on the Australian scale, as it passed about 150 km (95 mi) to the south of Manihiki.[3][6][9]
During November 2, the system continued to intensify as it moved towards the southeast and became equivalent to a category 2 hurricane on the SSHWS, as it moved towards the French Polynesian Society Islands of Bellingshausen, Mopelia and Scilly.[3][6][8] During the next day, Martin passed near the Society Islands as it developed an 17 km (10 mi) eye, before RSMC Nadi reported at 06:00 UTC that the system had peaked as a category 3 severe tropical cyclone with 10-minute sustained wind speeds of 155 km/h (100 mph).[3][10][11] The NPMOC also reported at around that time that Martin had peaked with 1-minute sustained windspeeds of 185 km/h (115 mph), which made it equivalent to a category 3 hurricane on the SSHWS.[8][11] After peaking in intensity Martin started to weaken, as it interacted with a frontal system and started to accelerate towards the south-southeast.[1][12] During November 4, Martin passed within 250 km (160 mi) of Tahiti as it became a category 2 tropical cyclone and started to transition into an extratropical cyclone.[1][10][13] Later that day, the NPMOC issued their final advisory on system as it had become equivalent to a tropical depression, vertically sheared with its surface center dislocated about 110 km (70 mi) from its upper level center.[8][14] Early on November 5, RSMC Nadi reported that Martin had become a category 1 tropical cyclone on the Australian scale before passing the primary warning responsibility for the system to the Tropical Cyclone Warning Center in Wellington, New Zealand.[1] Later that day TCWC Wellington reported that Martin had weakened below tropical cyclone intensity, before it was last noted on November 8 in the Southeastern Pacific ocean over 1,800 km (1,120 mi) to the southeast of Adamstown in the Pitcairn Islands.[6]
Preparations, impact and aftermath
While it was active Cyclone Martin affected both the Cook Islands and French Polynesia, and was responsible for 28 deaths. Due to the impact of this storm, the name Martin was retired from the lists of tropical cyclone names.[9]
Cook Islands
Martin was quite destructive at Manihiki Atoll. When the centre was closest to the island, the automatic weather station reported a lowest pressure of 994hPa, sustained winds of 20 m/s, and a highest gust of 29 m/s.[3] However, this was the last meteorological report from the station before it was destroyed by storm surge.[3] There were 10 fatalities recorded on Manihiki with 10 more persons reported missing and presumed drowned by the Cook Islands Coroner.[3][15] Almost every building on the island was destroyed by the storm surge.[3] Within the Cook Islands, Martin was the deadliest known tropical cyclone to affect the Cook Islands in over a century, after it caused 19 deaths within the Islands.[16][17]
French Polynesia
At its peak intensity, Martin passed near the western-most islands of the Socitey group (Bellingshausan, Mopelia, and Scilly) where 8 deaths were reported.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 RSMC Nadi - Tropical Cyclone Center. Tropical Cyclone Season Summary 1997–98. Fiji Meteorological Service. Archived from the original on August 1, 2010. http://www.pacificdisaster.net/pdnadmin/data/original/TC_Seasonal_Summary_97-98.pdf. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Padgett, Gary (1997). "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary October 1997". Archived from the original on June 5, 2011. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Chappel Lori-Carmen; Bate Peter W (June 2, 2000). "The South Pacific and Southeast Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclone Season 1997–98". Australian Meteorological Magazine (Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Journal) (Bureau of Meteorology) 49: 121–138. Archived from the original on June 5, 2011. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ↑ Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (October 30, 1997). Tropical Cyclone 04P Warning 1 October 30, 1997 21z. United States Navy, United States Air Force. Archived from the original on January 15, 2012. http://www.nrlmry.navy.mil/atcf_web/docs/warnings/1998/sh041998.97103018.wrn. Retrieved August 9, 2012.
- ↑ Joint Typhoon Warning Center; Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (1998). Chapter 4 Summary of South Pacific and South Indian Tropical Cyclones (1998 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report). United States Navy, United States Airforce. pp. 128. Archived from the original on July 23, 2013. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1998atcr.pdf. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 RSMC Nadi — Tropical Cyclone Centre, TCWC Brisbane, TCWC Wellington (May 22, 2009). "TCWC Wellington Best Track Data 1967–2006". Fiji Meteorological Service, Meteorological Service of New Zealand Limited, Australian Bureau of Meteorology. United States: International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship.
- ↑ Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (November 1, 1997). Tropical Cyclone 04P (Martin) Warning 4 November 1, 1997 09z. United States Navy, United States Air Force. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. http://www.nrlmry.navy.mil/atcf_web/docs/warnings/1998/sh041998.97110106.wrn. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center; Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical Cyclone 04P (Martin) best track analysis. United States Navy, United States Air Force. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/best_tracks/1998/1998s-bsh/bsh041998.txt. Retrieved July 23, 2013.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 RA V Tropical Cyclone Committee (December 12, 2012) (PDF). Tropical Cyclone Operational Plan for the South-East Indian Ocean and the Southern Pacific Ocean 2012 (Report). World Meteorological Organization. pp. 2B-1 - 2B-4 (23 - 26). Archived from the original on April 1, 2013. http://www.wmo.int/pages/prog/www/tcp/documents/TCP24_RAVOpPlan_2012.pdf. Retrieved December 14, 2012.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 RSMC Nadi — Tropical Cyclone Centre; TCWC Brisbane; TCWC Wellington (May 22, 2009). "RSMC Nadi — Tropical Cyclone Centre Best Track Data for 1997/98 Cyclone Season". Fiji Meteorological Service, Meteorological Service of New Zealand Limited, Australian Bureau of Meteorology. United States: International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (November 3, 1997). Tropical Cyclone 04P (Martin) Warning 8 November 3, 1997 09z. United States Navy, United States Air Force. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. http://www.nrlmry.navy.mil/atcf_web/docs/warnings/1998/sh041998.97110306.wrn. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (November 3, 1997). Tropical Cyclone 04P (Martin) Warning 9 November 3, 1997 21z. United States Navy, United States Air Force. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. http://www.nrlmry.navy.mil/atcf_web/docs/warnings/1998/sh041998.97110318.wrn. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (November 4, 1997). Tropical Cyclone 04P (Martin) Warning 10 November 4, 1997 03z. United States Navy, United States Air Force. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. http://www.nrlmry.navy.mil/atcf_web/docs/warnings/1998/sh041998.97110406.wrn. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (November 4, 1997). Tropical Cyclone 04P (Martin) Warning 11 November 4, 1997 21z. United States Navy, United States Air Force. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. http://www.nrlmry.navy.mil/atcf_web/docs/warnings/1998/sh041998.97110418.wrn. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ Cook Islands Government (June 20, 2007). "Coroner confirms Cyclone Martin Victims". Archived from the original on August 1, 2010. Retrieved April 30, 2010.
- ↑ De Scally, Fes (2008). "Insights provided by a historical database of tropical cyclones and their impacts in the Cook Islands". Island Climate Update (National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research) (88): 6.
- ↑ De Scally, Fes (2008). "Historical Tropical Cyclone Activity and Impacts in the Cook Islands". Pacific Science (University of Hawai'i Press) 62 (4): 443–459. doi:10.2984/1534-6188(2008)62[443:HTCAAI]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0030-8870.
External links
- World Meteorological Organization
- Fiji Meteorological Service
- Meteorological Service of New Zealand
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||