Cyclohexene
| Cyclohexene | |
|---|---|
 | |
| | |
| IUPAC name Cyclohexene | |
| Other names Tetrahydrobenzene, 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydrobenzene, Benzenetetrahydride, Cyclohex-1-ene, Hexanaphthylene, UN 2256 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 110-83-8 |
| PubChem | 8079 |
| ChemSpider | 7788 |
| EC number | 203-807-8 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:36404 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL16396 |
| RTECS number | GW2500000 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C6H10 |
| Molar mass | 82.143 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Odor | sweet |
| Density | 0.8110 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −103.5 °C; −154.3 °F; 169.7 K |
| Boiling point | 82.98 °C; 181.36 °F; 356.13 K |
| Solubility in water | 2.13 g/100 mL |
| Solubility | miscible with organic solvents |
| Vapor pressure | 8.93 kPa (20 °C)
11.9 kPa (25 °C) |
| kH | 0.022 mol·kg−1·bar−1 |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4465 |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R11, R19, R21/22 |
| S-phrases | S16, S23, S24, S25, S33 |
| NFPA 704 |
 3
1
0
|
| Flash point | −12 °C; 10 °F; 261 K |
| Autoignition temperature | 244 °C; 471 °F; 517 K |
| Explosive limits | 0.8–5 % |
| LD50 | 1946 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula C6H10. This cycloalkene is a colorless liquid with a sharp smell. It is an intermediate in various industrial processes. Cyclohexene is not very stable upon long term storage with exposure to light and air because it forms peroxides.
Production and uses
Cyclohexene is produced by the partial hydrogenation of benzene, a process developed by Asahi Chemical Company. It is converted to cyclohexanol, which is dehydrogenated to give cyclohexanone, a precursor to caprolactam.[1] Cyclohexene is also a precursor to adipic acid, maleic acid, dicyclohexyladipate, and cyclohexeneoxide. Furthermore, it is used as a solvent.
Laboratory experiments
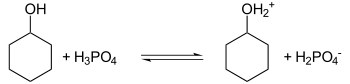
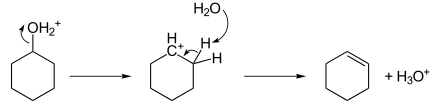
A common experiment for beginning organic chemistry students is the acid catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol with distillative removal of the resulting cyclohexene from the reaction mixture:
- Critical temperature: 287.2 °C (560.4 K)
See also
- Diels-Alder reaction
- Benzene
- Cyclohexane
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 1054
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards 0167
- Material Safety Data Sheet for cyclohexene
- Safety MSDS data
- Reaction of Cyclohexene with Bromine and Potassium Permanganate
- Cyclohexene synthesis
- Data sheet at inchem.org
References
- ↑ Michael T. Musser "Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_217
| |||||||||||