Cyclobutyne
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Cyclobutyne | |
|---|---|
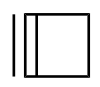 | |
| IUPAC name Cyclobutyne | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 1191-94-2 |
| ChemSpider | 10637133 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C4H4 |
| Molar mass | 52.07 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Cyclobutyne (C4H4) is a hydrocarbon molecule containing a triple bond within a four carbon atom ring.[1] This cycloalkyne is very unstable due to its high ring strain and has not been isolated in the pure state. However, osmium coordination complexes containing cyclobutyne have been synthesized.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Hopf, Henning; Grunenberg, Jrg (2009). Angle-Strained Cycloalkynes. p. 375. doi:10.1002/9783527627134.ch7.
- ↑ Adams, Richard D.; Qu, Xiaosu (1996). "The Chemistry of Cyclobutyne and Cyclobutenyl Ligands in Metal Cluster Complexes". Synlett 1996 (06): 493. doi:10.1055/s-1996-5466.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.