Cycle rank
In graph theory, the cycle rank of a directed graph is a digraph connectivity measure proposed first by Eggan and Büchi (Eggan 1963). Intuitively, this concept measures how close a digraph is to a directed acyclic graph (DAG), in the sense that a DAG has cycle rank zero, while a complete digraph of order n with a self-loop at each vertex has cycle rank n. The cycle rank of a directed graph is closely related to the tree-depth of an undirected graph and to the star height of a regular language. It has also found use in sparse matrix computations (see Bodlaender et al. 1995) and logic (Rossman 2008).
Definition
The cycle rank r(G) of a digraph G = (V, E) is inductively defined as follows:
- If G is acyclic, then r(G) = 0.
- If G is strongly connected and E is nonempty, then
 where G - v is the digraph resulting from deletion of vertex v and all edges beginning or ending at v.
where G - v is the digraph resulting from deletion of vertex v and all edges beginning or ending at v.
- If G is not strongly connected, then r(G) is equal to the maximum cycle rank among all strongly connected components of G.
History
Cycle rank was introduced by Eggan (1963) in the context of star height of regular languages. It was rediscovered by (Eisenstat & Liu 2005) as a generalization of undirected tree-depth, which had been developed beginning in the 1980s and applied to sparse matrix computations (Schreiber 1982).
Examples
The cycle rank of a directed acyclic graph is 0, while a complete digraph of order n with a self-loop at
each vertex has cycle rank n. Apart from these, the cycle rank of a few other digraphs is known: the undirected path 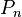 of order n, which possesses a symmetric edge relation and no self-loops, has cycle rank
of order n, which possesses a symmetric edge relation and no self-loops, has cycle rank  (McNaughton 1969). For the directed
(McNaughton 1969). For the directed 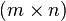 -torus
-torus 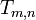 , i.e., the cartesian product of two directed circuits of lengths m and n, we have
, i.e., the cartesian product of two directed circuits of lengths m and n, we have
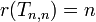 and
and 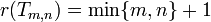 for m ≠ n (Eggan 1963, Gruber & Holzer 2008).
for m ≠ n (Eggan 1963, Gruber & Holzer 2008).
Computing the cycle rank
Computing the cycle rank is computationally hard: Gruber (2012) proves that the corresponding decision problem is NP-complete, even for sparse digraphs of maximum outdegree at most 2. On the positive side, the problem is solvable in time  on digraphs of maximum outdegree at most 2, and in time
on digraphs of maximum outdegree at most 2, and in time 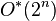 on general digraphs. There is an approximation algorithm with approximation ratio
on general digraphs. There is an approximation algorithm with approximation ratio 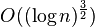 .
.
Applications
Star height of regular languages
The very first application of cycle rank was in formal language theory, for studying the star height of regular languages. Eggan (1963) established a relation between the theories of regular expressions, finite automata, and of directed graphs. In subsequent years, this relation became known as Eggan's theorem, cf. Sakarovitch (2009). In automata theory, a nondeterministic finite automaton with ε-moves (ε-NFA) is defined as a 5-tuple, (Q, Σ, δ, q0, F), consisting of
- a finite set of states Q
- a finite set of input symbols Σ
- a set of labeled edges δ, referred to as transition relation: Q × (Σ ∪{ε}) × Q. Here ε denotes the empty word.
- an initial state q0 ∈ Q
- a set of states F distinguished as accepting states F ⊆ Q.
A word w ∈ Σ* is accepted by the ε-NFA if there exists a directed path from the initial state q0 to some final state in F using edges from δ, such that the concatenation of all labels visited along the path yields the word w. The set of all words over Σ* accepted by the automaton is the language accepted by the automaton A.
When speaking of digraph properties of a nondeterministic finite automaton A with state set Q, we naturally address the digraph with vertex set Q induced by its transition relation. Now the theorem is stated as follows.
- Eggan's Theorem: The star height of a regular language L equals the minimum cycle rank among all nondeterministic finite automata with ε-moves accepting L.
Proofs of this theorem are given by Eggan (1963), and more recently by Sakarovitch (2009).
Cholesky factorization in sparse matrix computations
Another application of this concept lies in sparse matrix computations, namely for using nested dissection to compute the Cholesky factorization of a (symmetric) matrix in parallel. A given sparse 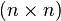 -matrix M may be interpreted as the adjacency matrix of some symmetric digraph G on n vertices, in a way such that the non-zero entries of the matrix are in one-to-one correspondence with the edges of G. If the cycle rank of the digraph G is at most k, then the Cholesky factorization of M can be computed in at most k steps on a parallel computer with
-matrix M may be interpreted as the adjacency matrix of some symmetric digraph G on n vertices, in a way such that the non-zero entries of the matrix are in one-to-one correspondence with the edges of G. If the cycle rank of the digraph G is at most k, then the Cholesky factorization of M can be computed in at most k steps on a parallel computer with  processors (Dereniowski & Kubale 2004).
processors (Dereniowski & Kubale 2004).
See also
References
- Bodlaender, Hans L.; Gilbert, John R.; Hafsteinsson, Hjálmtýr; Kloks, Ton (1995), "Approximating treewidth, pathwidth, frontsize, and shortest elimination tree", Journal of Algorithms 18 (2): 238–255, doi:10.1006/jagm.1995.1009, Zbl 0818.68118.
- Dereniowski, Dariusz; Kubale, Marek (2004), "Cholesky Factorization of Matrices in Parallel and Ranking of Graphs", 5th International Conference on Parallel Processing and Applied Mathematics, Lecture Notes on Computer Science 3019, Springer-Verlag, pp. 985–992, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-24669-5_127, Zbl 1128.68544.
- Eggan, Lawrence C. (1963), "Transition graphs and the star-height of regular events", Michigan Mathematical Journal 10 (4): 385–397, doi:10.1307/mmj/1028998975, Zbl 0173.01504.
- Eisenstat, Stanley C.; Liu, Joseph W. H. (2005), "The theory of elimination trees for sparse unsymmetric matrices", SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications 26 (3): 686–705, doi:10.1137/S089547980240563X.
- Gruber, Hermann (2012), "Digraph Complexity Measures and Applications in Formal Language Theory", Discrete Mathematics & Theoretical Computer Science 14 (2): 189–204.
- Gruber, Hermann; Holzer, Markus (2008), "Finite automata, digraph connectivity, and regular expression size", Proc. 35th International Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Programming, Lecture Notes on Computer Science 5126, Springer-Verlag, pp. 39–50, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-70583-3_4.
- McNaughton, Robert (1969), "The loop complexity of regular events", Information Sciences 1 (3): 305–328, doi:10.1016/S0020-0255(69)80016-2.
- Rossman, Benjamin (2008), "Homomorphism preservation theorems", Journal of the ACM 55 (3): Article 15, doi:10.1145/1379759.1379763.
- Sakarovitch, Jacques (2009), Elements of Automata Theory, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-84425-8
- Schreiber, Robert (1982), "A new implementation of sparse Gaussian elimination", ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 8 (3): 256–276, doi:10.1145/356004.356006.