Cumene hydroperoxide
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Cumene hydroperoxide[1] | |
|---|---|
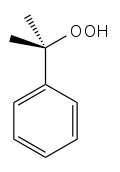 | |
| IUPAC name 2-hydroperoxypropan-2-ylbenzene | |
| Other names Cumyl Hydroperoxide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 80-15-9 |
| PubChem | 6629 |
| ChemSpider | 6377 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C9H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 152.19 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless to pale yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.02 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −9 °C; 16 °F; 264 K |
| Boiling point | 153 °C |
| Solubility in water | 1.5 g / 100 mL |
| Vapor pressure | 14 mmHg at 20 °C |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | sigmaaldrich.com |
| GHS pictograms |      |
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| GHS hazard statements | H242, H302, H312, H314, H331, H373, H411 |
| GHS precautionary statements | P220, P261, P273, P280, P305+351+338, P310 |
| NFPA 704 |
 2
1
4
|
| Flash point | 57 °C; 135 °F; 330 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Cumene hydroperoxide is an intermediate in the cumene process for developing phenol and acetone from benzene and propylene. It is typically used as an oxidizing agent.[2] Products of decomposition of cumene hydroperoxide are methylstyrene, acetophenone and cumyl alcohol.[3] Its formula is C6H5C(CH3)2OOH.
One of the key uses for the material is as a free radical initiator for acrylate and methacrylates monomers.
References
- ↑ University, Safety Officer in Physical Chemistry at Oxford (2005). "Safety (MSDS) data for cumene hydroperoxide". Retrieved 2009-05-13
- ↑ Richard J. Lewis, Richard J. Lewis (Sr.), Hazardous chemicals desk reference, Publisher Wiley-Interscience, 2008, ISBN 0-470-18024-2, ISBN 978-0-470-18024-2, 1953 pages (page 799)
- ↑ Cumene Hydroperoxide at the Organic Chemistry Portal
Related terms
External links
- Cumene hydroperoxide
- Cumene hydroperoxide at International Chemical Safety Cards
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.