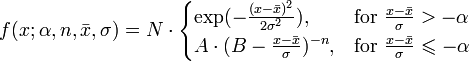Crystal Ball function
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
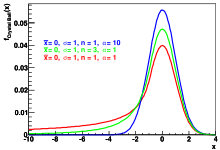
Examples of the Crystal Ball function.
The Crystal Ball function, named after the Crystal Ball Collaboration (hence the capitalized initial letters), is a probability density function commonly used to model various lossy processes in high-energy physics. It consists of a Gaussian core portion and a power-law low-end tail, below a certain threshold. The function itself and its first derivative are both continuous.
The Crystal Ball function is given by:
where
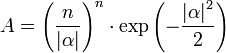 ,
, ,
,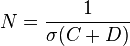
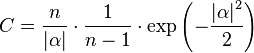

 (Skwarnicki 1986) is a normalization factor and
(Skwarnicki 1986) is a normalization factor and  ,
,  ,
, 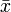 and
and 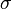 are parameters which are fitted with the data. erf is the error function.
are parameters which are fitted with the data. erf is the error function.
External links
- J. E. Gaiser, Appendix-F Charmonium Spectroscopy from Radiative Decays of the J/Psi and Psi-Prime, Ph.D. Thesis, SLAC-R-255 (1982). (This is a 205 page document in .pdf form – the function is defined on p. 178.)
- M. J. Oreglia, A Study of the Reactions psi prime --> gamma gamma psi, Ph.D. Thesis, SLAC-R-236 (1980), Appendix D.
- T. Skwarnicki, A study of the radiative CASCADE transitions between the Upsilon-Prime and Upsilon resonances, Ph.D Thesis, DESY F31-86-02(1986), Appendix E.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.