Cruciform eminence
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Cruciform eminence | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Human skull. Position of cruciform eminence is shown in red. | |
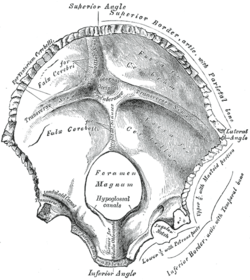 | |
| Occipital bone. Inner surface. | |
| Latin | Eminentia cruciformis |
| Gray's | p.130 |
The internal surface of the occipital bone is deeply concave and divided into four fossae by a cruciform eminence (or cruciate eminence).
- The superior two fossae, called cerebral fossa, are triangular and lodge the occipital lobes of the cerebrum.
- The inferior two fossae, called cerebellar fossa, are quadrilateral and accommodate the hemispheres of the cerebellum.
The superior and inferior fossae are separated by a transverse groove. At the point of intersection between all four fossae is the internal occipital protuberance.
Additional images
-

Occipital bone. Position of cruciform eminence is shown in red. Animation.
-

Human skull. Position of cruciform eminence is shown in red. Animation.
-

Occipital bone. Inner surface.
-

Cerebral fossa (shown in red)
-

Cerebellar fossa (shown in red)
See also
References
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cruciform eminence. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.