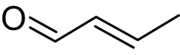
Crotonaldehyde
| Crotonaldehyde[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| IUPAC name (2E)-but-2-enal | |
| Other names Crotonaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 4170-30-3 |
| PubChem | 447466 |
| ChemSpider | 394562 |
| EC number | 204-647-1 |
| DrugBank | DB04381 |
| KEGG | C19377 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:41607 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1086445 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C4H6O |
| Molar mass | 70.09 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Odor | pungent, suffocating odor |
| Density | 0.846 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −76.5 °C; −105.7 °F; 196.7 K |
| Boiling point | 104.0 °C; 219.2 °F; 377.1 K |
| Solubility | very soluble in ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone soluble in chloroform miscible in benzene |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4362 |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R11 R24/25 R26 R37/38 R41 R48/22 R50 R68 |
| S-phrases | S26 S28 S36/37/39 S45 S61 |
| NFPA 704 |
 3
4
2
|
| Flash point | 13 °C; 55 °F; 286 K |
| Autoignition temperature | 207 °C; 405 °F; 480 K |
| Explosive limits | 2.95-15.5% |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkenals | Acrolein cis-3-hexenal |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.[2]
Production and uses
Crotonaldehyde is produced by the aldol condensation of acetaldehyde:
- 2 CH3CHO → CH3CH=CHCHO + H2O
Its main application is as a precursor to fine chemicals. Sorbic acid, a food preservative, and trimethylhydroquinone, a precursor to the vitamin E, are prepared from crotonaldehyde. Other derivatives include crotonic acid and 3-methoxybutanol.[2]
Crotonaldehyde is a multifunctional molecule that exhibits diverse reactivity. It is an excellent prochiral dienophile.[3] It is a Michael acceptor. Addition of methylmagnesium chloride affords 3-penten-2-ol.[4]
Safety
Crotonaldehyde is an irritant. It is listed as an "extremely hazardous substance" as defined by the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. It occurs widely in nature.
See also
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2599
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 R. P. Schulz, J. Blumenstein, C. Kohlpaintner "Crotonaldehyde and Crotonic Acid" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim: 2005. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_083
- ↑ Longley, Jr., R. I..; Emerson, W. S.; Blardinelli, A. J. (1963), "3,4-Dihydro-2-methoxy-4-methyl-2H-pyran", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 4: 311
- ↑ Coburn, E. R. (1955), "3-Penten-2-ol", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 3: 696