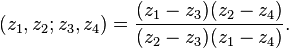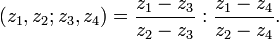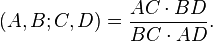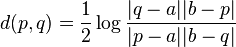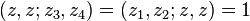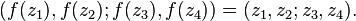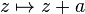Cross-ratio

In geometry, the cross-ratio, also called double ratio and anharmonic ratio, is a special number associated with an ordered quadruple of collinear points, particularly points on a projective line. Variants of this concept exist for a quadruple of concurrent lines on the projective plane and a quadruple of points on the Riemann sphere.
The cross-ratio is preserved by the fractional linear transformations and it is essentially the only projective invariant of a quadruple of points, which underlies its importance for projective geometry. In the Cayley–Klein model of hyperbolic geometry, the distance between points is expressed in terms of a certain cross-ratio.
Cross-ratio had been defined in deep antiquity, possibly already by Euclid, and was considered by Pappus, who noted its key invariance property. It was extensively studied in the 19th century.[1]
Definition
The cross-ratio of a 4-tuple of distinct points on the real line with coordinates z1, z2, z3, z4 is given by
It can also be written as a "double ratio" of two division ratios of triples of points:
The same formulas can be applied to four different complex numbers or, more generally, to elements of any field and can also be extended to the case when one of them is the symbol ∞, by removing the corresponding two differences from the formula.
The formula shows that cross-ratio is a function of four points, generally four numbers  taken from a field.
taken from a field.
In geometry, if A, B, C and D are collinear points, then the cross ratio is defined similarly as
where each of the distances is signed according to a fixed orientation of the line.
Terminology and history
Pappus of Alexandria made implicit use of concepts equivalent to the cross-ratio in his Collection: Book VII. Early users of Pappus included Isaac Newton, Michel Chasles, and Robert Simson. In 1986 Alexander Jones made a translation of the original by Pappus, then wrote a commentary on how the lemmas of Pappus relate to modern terminology.
Modern use of the cross ratio in projective geometry began with Lazare Carnot in 1803 with his book Géométrie de Position. The term used was le rapport anharmonique (Fr: anharmonic ratio). German geometers call it das Doppelverhältnis (Ger: double ratio). However, in 1847 Karl von Staudt introduced the term Throw (Wurf) to avoid the metrical implication of a ratio. His construction of the Algebra of Throws provides an approach to numerical propositions, usually taken as axioms, but proven in projective geometry.
The English term "cross-ratio" was introduced in 1878 by William Kingdon Clifford.[2]
Projective geometry

Cross-ratio is a projective invariant in the sense that it is preserved by the projective transformations of a projective line. In particular, if four points lie on a straight line L in R2 then their cross-ratio is a well-defined quantity, because any choice of the origin and even of the scale on the line will yield the same value of the cross-ratio. Furthermore, let {Li, 1 ≤ i ≤ 4}, be four distinct lines in the plane passing through the same point Q. Then any line L not passing through Q intersects these lines in four distinct points Pi (if L is parallel to Li then the corresponding intersection point is "at infinity"). It turns out that the cross-ratio of these points (taken in a fixed order) does not depend on the choice of a line L, and hence it is an invariant of the 4-tuple of lines {Li}. This can be understood as follows: if L and L′ are two lines not passing through Q then the perspective transformation from L to L′ with the center Q is a projective transformation that takes the quadruple {Pi} of points on L into the quadruple {Pi′} of points on L′. Therefore, the invariance of the cross-ratio under projective automorphisms of the line implies (in fact, is equivalent to) the independence of the cross-ratio of the four collinear points {Pi} on the lines {Li} from the choice of the line that contains them.
Definition in homogeneous coordinates
If the four points are represented in homogeneous coordinates by vectors a,b,c,d such that c=a+b and d=ka+b, then their cross-ratio is k.
Role in non-Euclidean geometry
Arthur Cayley and Felix Klein found an application of the cross-ratio to non-Euclidean geometry. Given a nonsingular conic C in the real projective plane, its stabilizer GC in the projective group G = PGL(3,R) acts transitively on the points in the interior of C. However, there is an invariant for the action of GC on pairs of points. In fact, every such invariant is expressible as a function of the appropriate cross ratio.[citation needed]
Explicitly, let the conic be the unit circle. For any two points in the unit disk, p, q, the line connecting them intersects the circle in two points, a and b. The points are, in order, a, p, q, b. Then the distance between p and q in the Cayley–Klein model of the plane hyperbolic geometry can be expressed as
(the factor one half is needed to make the curvature −1). Since the cross-ratio is invariant under projective transformations, it follows that the hyperbolic distance is invariant under the projective transformations that preserve the conic C. Conversely, the group G acts transitively on the set of pairs of points (p,q) in the unit disk at a fixed hyperbolic distance.
Six cross-ratios
There is a number of definitions of the cross-ratio. However, they all differ from each other by a suitable permutation of the coordinates. In general, there are six possible different values the cross-ratio  can take depending on the order in which the points zi are given.
can take depending on the order in which the points zi are given.
Action of symmetric group
Since there are 24 possible permutations of the four coordinates, some permutations must leave the cross-ratio unaltered. In fact, exchanging any two pairs of coordinates preserves the cross-ratio:
Using these symmetries, there can then be 6 possible values of the cross-ratio, depending on the order in which the points are given. These are:
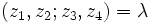 |
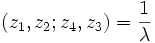 | |
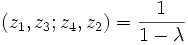 | 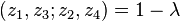 | |
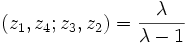 | 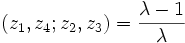 |
Six cross-ratios as Möbius transformations
Viewed as Möbius transformations, the six cross-ratios listed above represent torsion elements of PGL(2,Z). Namely,  ,
, 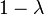 , and
, and 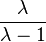 are of order 2 in PGL(2,Z), with fixed points, respectively, −1, 1/2, and 2 (namely, the orbit of the harmonic cross-ratio). Meanwhile, elements
are of order 2 in PGL(2,Z), with fixed points, respectively, −1, 1/2, and 2 (namely, the orbit of the harmonic cross-ratio). Meanwhile, elements
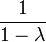 and
and  are of order 3 in PGL(2,Z) – in fact in PSL(2,Z). Each of them fixes both values
are of order 3 in PGL(2,Z) – in fact in PSL(2,Z). Each of them fixes both values 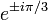 of the "most symmetric" cross-ratio.
of the "most symmetric" cross-ratio.
The anharmonic group is the group of order 6 generated by λ→1/λ and λ→1−λ. It is abstractly isomorphic to S3 and may be realised as the six Möbius transformations mentioned.[3]
Role of Klein four-group
In the language of group theory, the symmetric group S4 acts on the cross-ratio by permuting coordinates. The kernel of this action is isomorphic to the Klein four-group K. This group consists of 2-cycle permutations of type 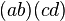 (in addition to the identity), which preserve the cross-ratio. The effective symmetry group is then the quotient group
(in addition to the identity), which preserve the cross-ratio. The effective symmetry group is then the quotient group 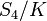 , which is isomorphic to S3.
, which is isomorphic to S3.
Exceptional orbits
For certain values of λ there will be an enhanced symmetry and therefore fewer than six possible values for the cross-ratio. These values of λ correspond to fixed points of the action of S3 on the Riemann sphere (given by the above six functions); or, equivalently, those points with a non-trivial stabilizer in this permutation group.
The first set of fixed points is {0, 1, ∞}. However, the cross-ratio can never take on these values if the points {zi} are all distinct. These values are limit values as one pair of coordinates approach each other:
The second set of fixed points is {−1, 1/2, 2}. This situation is what is classically called the harmonic cross-ratio, and arises in projective harmonic conjugates. In the real case, there are no other exceptional orbits.
The most symmetric cross-ratio occurs when  . These are then the only two possible values of the cross-ratio.
. These are then the only two possible values of the cross-ratio.
Transformational approach
The cross-ratio is invariant under the projective transformations of the line. In the case of a complex projective line, or the Riemann sphere, these transformation are known as Möbius transformations. A general Möbius transformation has the form
These transformations form a group acting on the Riemann sphere, the Möbius group.
The projective invariance of the cross-ratio means that
The cross-ratio is real if and only if the four points are either collinear or concyclic, reflecting the fact that every Möbius transformation maps generalized circles to generalized circles.
The action of the Möbius group is simply transitive on the set of triples of distinct points of the Riemann sphere: given any ordered triple of distinct points, (z2,z3,z4), there is a unique Möbius transformation f(z) that maps it to the triple (1,0,∞). This transformation can be conveniently described using the cross-ratio: since (z,z2,z3,z4) must equal (f(z),1;0,∞) which in turn equals f(z), we obtain
An alternative explanation for the invariance of the cross-ratio is based on the fact that the group of projective transformations of a line is generated by the translations, the homotheties, and the multiplicative inversion. The differences zj - zk are invariant under the translations
where a is a constant in the ground field F. Furthermore, the division ratios are invariant under a homothety
for a non-zero constant b in F. Therefore, the cross-ratio is invariant under the affine transformations.
In order to obtain a well-defined inversion mapping
the affine line needs to be augmented by the point at infinity, denoted ∞, forming the projective line P1(F). Each affine mapping f: F → F can be uniquely extended to a mapping of P1(F) into itself that fixes the point at infinity. The map T swaps 0 and ∞. The projective group is generated by T and the affine mappings extended to P1(F). In the case F = C, the complex plane, this results in the Möbius group. Since the cross-ratio is also invariant under T, it is invariant under any projective mapping of P1(F) into itself.
Differential-geometric point of view
The theory takes on a differential calculus aspect as the four points are brought into proximity. This leads to the theory of the Schwarzian derivative, and more generally of projective connections.
Higher-dimensional generalizations
The cross-ratio does not generalize in a simple manner to higher dimensions, due to other geometric properties of configurations of points, notably collinearity – configuration spaces are more complicated, and distinct k-tuples of points are not in general position.
While the projective linear group of the plane is 3-transitive (any three distinct points can be mapped to any other three points), and indeed simply 3-transitive (there is a unique projective map taking any triple to another triple), with the cross ratio thus being the unique projective invariant of a set of four points, there are basic geometric invariants in higher dimension. The projective linear group of n-space 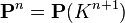 has (n + 1)2 − 1 dimensions (because it is
has (n + 1)2 − 1 dimensions (because it is 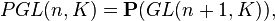 projectivization removing one dimension), but in other dimensions the projective linear group is only 2-transitive – because three collinear points must be mapped to three collinear points (which is not a restriction in the projective line) – and thus there is not a "generalized cross ratio" providing the unique invariant of n2 points.
projectivization removing one dimension), but in other dimensions the projective linear group is only 2-transitive – because three collinear points must be mapped to three collinear points (which is not a restriction in the projective line) – and thus there is not a "generalized cross ratio" providing the unique invariant of n2 points.
Collinearity is not the only geometric property of configurations of points that must be maintained – for example, five points determine a conic, but six general points do not lie on a conic, so whether any 6-tuple of points lies on a conic is also a projective invariant. One can study orbits of points in general position – in the line "general position" is equivalent to being distinct, while in higher dimensions it requires geometric considerations, as discussed – but, as the above indicates, this is more complicated and less informative.
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ A theorem on the anharmonic ratio of lines appeared in the work of Pappus, but Michel Chasles, who devoted considerable efforts to reconstructing lost works of Euclid, asserted that it had earlier appeared in his book Porisms.
- ↑ W.K. Clifford (1878) Elements of Dynamic, page 42, London: MacMillan & Co; online presentation from Cornell University Historical Mathematical Monographs
- ↑ Chandrasekharan, K. (1985). Elliptic Functions. Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften 281. Springer-Verlag. p. 120. ISBN 3-540-15295-4. Zbl 0575.33001.
- Lars Ahlfors (1953,1966,1979) Complex Analysis, 1st edition, page 25; 2nd & 3rd editions, page 78, McGraw-Hill ISBN 0-07-000657-1 .
- Viktor Blåsjö (2009) "Jakob Steiner’s Systematische Entwickelung: The Culmination of Classical Geometry", Mathematical Intelligencer 31(1): 21–9.
- Alexander Jones (1986) Book 7 of the Collection, part 1: introduction, text, translation ISBN 0-387-96257-3, part 2: commentary, index, figures ISBN 3-540-96257-3, Springer-Verlag .
- John J. Milne (1911) An Elementary Treatise on Cross-Ratio Geometry with Historical Notes, Cambridge University Press.
- Dirk Struik (1953) Lectures on Analytic and Projective Geometry, page 7, Addison-Wesley.
- I. R. Shafarevich & A. O. Remizov (2012) Linear Algebra and Geometry, Springer ISBN 978-3-642-30993-9.
External links
- MathPages - Kevin Brown explains the cross-ratio in his article about Pascal's Mystic Hexagram
- Java Applet demonstrating the invariance of the cross ratio under a bilinear transformation
- Cross-Ratio at cut-the-knot
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Cross-ratio", MathWorld.