Cresyl violet
| Cresyl violet | ||
|---|---|---|
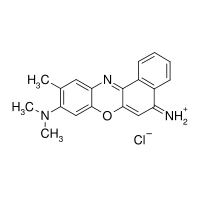 | ||
| IUPAC name (9-dimethylamino-10-methyl-benzo[a]phenoxazin-5-ylidene)ammonium chloride | ||
| Other names 9-(Dimethylamino)-5-imino-10-methyl-5H-benzo(a)phenoxazine hydrochloride; Cresole Violet | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| ChemSpider | 27064 | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Cl-].N=1c4c(OC=3C=1c2ccccc2\C(=[NH2+])\C=3)cc(c(c4)C)N(C)C|Image 1 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C19H18ClN3O | |
| Molar mass | 339.8187 | |
| Hazards | ||
| Flash point | 245.5 °C; 473.9 °F; 518.6 K | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Cresyl violet is an organic compound with the chemical formula C19H18ClN3O. It is used in biology and medicine as a histological stain. Cresyl violet is an effective and reliable stain used for light microscopy sections. Initially, tissue sections are "defatted" by passing through graded dilutions of ethanol. Then, rehydrated by passing back through decreasing concentrations of ethanol. Lastly, back into water. The ethanol solutions act to differentiate the stain, causing myelin and other components to lose color whereas perikarya retain the color.