Creosol
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Not to be confused with cresol.
| Creosol | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| IUPAC name 2-Methoxy-4-methylphenol | |
| Other names 4-Methylguaiacol; Valspice | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 93-51-6 |
| PubChem | 7144 |
| ChemSpider | 21105936 |
| UNII | W9GW1KZG6N |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C8H10O2 |
| Molar mass | 138.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless to yellowish aromatic liquid |
| Density | 1.092 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 5.5 °C; 41.9 °F; 278.6 K |
| Boiling point | 220 °C; 428 °F; 493 K |
| Solubility in water | Slightly soluble |
| Solubility in ethanol, ether, benzene | Miscible |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Creosol is an ingredient of creosote. Compared with phenol, creosol is a less toxic disinfectant.
Sources
- Coal tar creosote
- Wood creosote
- Reduction product of vanillin using zinc powder in strong hydrochloric acid
- Found as glycosides in green vanilla beans[1]
- It is also found in tequila.[2]
Reactions
Creosol reacts with hydrogen halide to give a catechol.
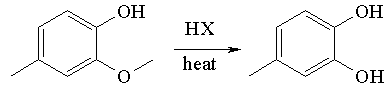
See also
References
- ↑ Dignum, Mark J.W.; Van Der Heijden, Rob; Kerler, Josef; Winkel, Chris; Verpoorte, Rob (2004). "Identification of glucosides in green beans of Vanilla planifolia Andrews and kinetics of vanilla β-glucosidase". Food Chemistry 85 (2): 199–205. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00293-0.
- ↑ Characterization of volatile compounds from ethnic Agave alcoholic beverages by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. León-Rodríguez, A. de, Escalante-Minakata, P., Jiménez-García, M. I., Ordoñez-Acevedo, L. G., Flores Flores, J. L. and Barba de la Rosa, A. P., Food Technology and Biotechnology, 2008, Volume 46, Number 4, pages 448-455 (abstract)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.