Costovertebral angle tenderness
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
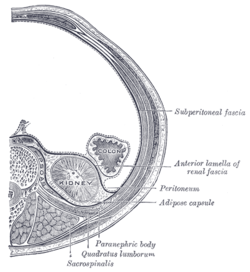
Transverse section, showing the relations of the capsule of the kidney.

Image of a human back
Costovertebral angle tenderness (CVAT), also known as Murphy's punch sign (Latin: succusio renalis), is a medical test in which pain is elicited by percussion of the area of the back overlying the kidney (the costovertebral angle, an angle made by the vertebral column and the costal margin). The test is positive in people with an infection around the kidney (perinephric abscess), pyelonephritis or renal stone. Because the kidney lies directly below this area, known as the costovertebral angle, tapping disturbs the inflamed tissue, causing pain.
This medical test was first described by the American surgeon John Benjamin Murphy.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ Oh, Timothy T.; Schmitz, Robert L. (1993). The Remarkable surgical practice of John Benjamin Murphy. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. ISBN 0-252-01958-X.
- ↑ Musana KA, Yale SH (August 2005). "Murphy's Sign". Clin Med Res 3 (3): 132. PMC 1237152. PMID 16160065.
- ↑ Musana K, Yale SH (May 2005). "John Benjamin Murphy (1857 - 1916)". Clin Med Res 3 (2): 110–2. PMC 1183442. PMID 16012130.
| |||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.