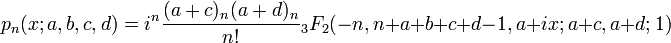Continuous Hahn polynomials
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, the continuous Hahn polynomials are a family of orthogonal polynomials in the Askey scheme of hypergeometric orthogonal polynomials. They are defined in terms of generalized hypergeometric functions by
Roelof Koekoek, Peter A. Lesky, and René F. Swarttouw (2010, 14) give a detailed list of their properties.
Closely related polynomials include the dual Hahn polynomials Rn(x;γ,δ,N), the Hahn polynomials, and the continuous dual Hahn polynomials Sn(x;a,b,c). These polynomials all have q-analogs with an extra parameter q, such as the q-Hahn polynomials Qn(x;α,β, N;q), and so on.
Orthogonality
Recurrence and difference relations
Rodrigues formula
Generating function
Relation to other polynomials
- Wilson polynomials, a generalization of continuous Hahn polynomials
References
- Hahn, Wolfgang (1949), "Über Orthogonalpolynome, die q-Differenzengleichungen genügen", Mathematische Nachrichten 2: 4–34, doi:10.1002/mana.19490020103, ISSN 0025-584X, MR 0030647
- Koekoek, Roelof; Lesky, Peter A.; Swarttouw, René F. (2010), Hypergeometric orthogonal polynomials and their q-analogues, Springer Monographs in Mathematics, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-05014-5, ISBN 978-3-642-05013-8, MR 2656096
- Koornwinder, Tom H.; Wong, Roderick S. C.; Koekoek, Roelof; Swarttouw, René F. (2010), "Hahn Class: Definitions", in Olver, Frank W. J.; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F.; Clark, Charles W., NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521192255, MR 2723248
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.