Coniferin
| Coniferin | |
|---|---|
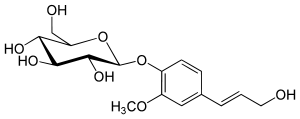 | |
| IUPAC name (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-[4-[(E)-3-hydroxyprop-1-enyl]-2-methoxyphenoxy]oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Other names • β-D-Glucopyranoside 4-(3-hydroxy-1-propenyl)-2-methoxyphenyl | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 531-29-3 |
| PubChem | 5280372 |
| ChemSpider | 4444067 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O(c1c(OC)cc(/C=C/CO)cc1)[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C16H22O8 |
| Molar mass | 342.35 g/mol |
| Melting point | 186 °C; 367 °F; 459 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Coniferin is a glucoside of coniferyl alcohol. This white crystalline solid is a metabolite in conifers, serving as an intermediate in cell wall lignification, as well as having other biological roles. It can also be found in the water root extract of Angelica archangelica subsp. litoralis.[1]
Vanillin was first synthesized from coniferin by chemists Ferdinand Tiemann and Wilhelm Haarmann.
References
- ↑ Dihydrofurocoumarin glucosides from Angelica archangelica and Angelica silvestris. John Lemmich, Svend Havelund and Ole Thastrup, Phytochemistry, 1983, Volume 22, Issue 2, Pages 553–555, doi:10.1016/0031-9422(83)83044-1
| ||||||||