Congo–Ocean Railway
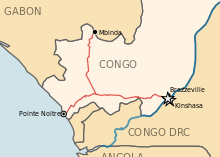
The Congo–Ocean Railway (COR; French: Chemin de fer Congo-Océan, CFCO) links the Atlantic port of Pointe-Noire (now in the Republic of Congo) with Brazzaville, a distance of 502 kilometres (312 mi). It bypasses the rapids on the lower Congo River; from Brazzaville river boats are able to ascend the Congo River and its major tributaries, including the Oubangui River to Bangui.
History



Under French colonial administration, in 1921 they contracted Société de Construction des Batignolles to construct the railway using forced labour, recruited from what is now southern Chad and the Central African Republic. Like Spain and Portugal, France did not ratify the International Labour Organisation Forced Labour Convention of 1930, No. 29.[1] Disdain among the native population towards this conscripted labour and other forms of oppression lead to the Kongo-Wara rebellion in between 1928 and 1931. Through the period of construction until 1934 there was a continual heavy cost in human lives, with total deaths estimated in excess of 17,000 of the construction workers, from a combination of both industrial accidents and diseases including malaria.[2] In 1946, France ratified ILO No.29, in light of a permanent state of emergency, due to indigenous revolt.
In 1962, a branch was constructed to Mbinda near the border with Gabon, to connect with the COMILOG Cableway and thus carry manganese ore to Pointe-Noire. The Cableway closed in 1986 when neighbouring Gabon built its own railway to haul this traffic. The branch line remains active nonetheless.
The Congo–Ocean Railway was a user of the Golwé locomotive. Motive power is now provided by diesel locomotives.
From the start of the civil war in 1997, the line was closed for six years.
Present
COR a state-owned enterprise whose privatization was planned as part of the commitments made by the Congolese government to the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund. Among the candidates were several consortia, including Congo-Rail (Bolloré Investments, Maersk, SNCF), and the South African consortium Sheltam Mvela.
Operations restarted in 2004, but in August 2007 BBC News reported that COR was in a "decrepit state, with the majority of trains now broken", after UNICEF had organised a train to distribute malaria nets.[3] In 2007, a Korean-led consortium CMKC Group signed a deal to build railway extensions to Ouesso and Djambala mainly for timber traffic.[4]
On 22 June 2010, a train of the Congo–Ocean Railroad was involved in a major incident, in which at least 60 people were killed. The train is believed to have derailed as it went round a curve in a remote area between Bilinga and Tchitondi, throwing four carriages into a ravine. The dead and wounded were taken to hospitals and morgues in Pointe-Noire.[5]
In 2011, it was announced that Africa Iron was close to concluding a 25-year ore transport deal with Congo–Ocean.[6]
In the media
The Congo–Ocean Railway has featured in a recent episode of Channel 5 Television's series Chris Tarrant's Extreme Railways.
Stations served
| Congo–Ocean Railway Chemin de fer Congo-Océan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line length: | 512 km / 318 mi | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge: | 1067 mm / 3 ft 6 in | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COMILOG-Line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line length: | 285 km / 177 mi | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge: | 1067 mm / 3 ft 6 in | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Specifications
- Rail gauge : 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) Cape gauge (Jane's 69/70)
- Brake (railway): Vacuum brake (Jane's 69/70)
- Coupler: SA3 coupler (Jane's 69/70)
See also
- Congo Railway
- Matadi-Kinshasa Railway in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Railway stations in Congo
References
- ↑ ILO Forced Labour Convention, 1930 (No. 29)
- ↑ "In pictures: Malaria train, Mayomba forest". news.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2009-12-09.
- ↑ "In pictures: Malaria train, Train engine". news.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2009-12-09.
- ↑ "Korea to build railroad in Congo". Korean Consortium. Retrieved 2009-12-09.
- ↑ "60 reported dead in Congo train crash". Wikinews. 23 June 2010. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ↑ "Railway Gazette: News in Brief". 2011-04-16. Retrieved 2011-04-16.
- ↑ http://www.cfco.cg/FileUpload/pics/Cartes/cfco_carte.jpg
- ↑ http://www.cfco.cg/FileUpload/pics/Cartes/cfco_carte.jpg
- André Gide, Voyage au Congo (1926)
- Albert Londres, Terre d'Ébène (1929)
- Gilles Sautter, "Notes sur la construction du chemin de fer Congo-Océan (1921-1934)," Cahiers d'Études africaines 7:219-299 (1967)
- Jane's World Railways 69/70, pages 542/543