Condyle (anatomy)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Condyle (anatomy) | |
|---|---|
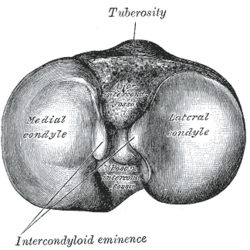 | |
| Upper surface of right tibia. | |
| Latin | condylus |
A condyle (/ˈkɒndəl/ or /ˈkɒndaɪl/;[1][2] Latin: condylus, from Greek: kondylos; knuckle) is the round prominence at the end of a bone, most often part of a joint - an articulation with another bone. It is one of the markings/features of bones, and can refer to:
- On the femur, in the knee joint:
- On the tibia, in the knee joint:
- On the mandible, in the temporomandibular joint:
- Mandibular condyle
- On the occipital bone, in the atlanto-occipital joint:
- Occipital condyles
Although not generally termed condyles, the trochlea and capitulum of the humerus act as condyles in the elbow.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ↑ OED 2nd edition, 1989.
- ↑ Entry "condyle" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.