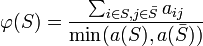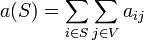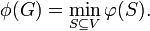Conductance (graph)
In graph theory the conductance of a graph G=(V,E) measures how "well-knit" the graph is: it controls how fast a random walk on G converges to a uniform distribution. The conductance of a graph is often called the Cheeger constant of a graph as the analog of its counterpart in spectral geometry.[citation needed] Since electrical networks are intimately related to random walks with a long history in the usage of the term "conductance", this alternative name helps avoid possible confusion.
The conductance of a cut  in a graph is defined as:
in a graph is defined as:
where the 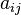 are the entries of the adjacency matrix for G, so that
are the entries of the adjacency matrix for G, so that
is the total number (or weight) of the edges incident with S.
The conductance of the whole graph is the minimum conductance over all the possible cuts:
Equivalently, conductance of a graph is defined as follows:
For a d-regular graph, the conductance is equal to the isoperimetric number divided by d.
Generalizations and applications
In practical applications, one often considers the conductance only over a cut. A common generalization of conductance is to handle the case of weights assigned to the edges: then the weights are added; if the weight is in the form of a resistance, then the reciprocal weights are added.
The notion of conductance underpins the study of percolation in physics and other applied areas; thus, for example, the permeability of petroleum through porous rock can be modeled in terms of the conductance of a graph, with weights given by pore sizes.
Markov chains
For an ergodic reversible Markov chain with an underlying graph G, the conductance is a way to measure how hard it is to leave a small set of nodes. Formally, the conductance of a graph is defined as the minimum over all sets 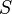 of the capacity of
of the capacity of 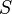 divided by the ergodic flow out of
divided by the ergodic flow out of 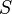 . Alistair Sinclair showed that conductance is closely tied to mixing time in ergodic reversible Markov chains. We can also view conductance in a more probabilistic way, as the minimal probability of leaving a small set of nodes given that we started in that set to begin with. Writing
. Alistair Sinclair showed that conductance is closely tied to mixing time in ergodic reversible Markov chains. We can also view conductance in a more probabilistic way, as the minimal probability of leaving a small set of nodes given that we started in that set to begin with. Writing 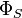 for the conditional probability of leaving a set of nodes S given that we were in that set to begin with, the conductance is the minimal
for the conditional probability of leaving a set of nodes S given that we were in that set to begin with, the conductance is the minimal 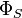 over sets
over sets 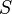 that have a total stationary probability of at most 1/2.
that have a total stationary probability of at most 1/2.
Conductance is related to Markov chain mixing time in the reversible setting.
See also
References
- Béla Bollobás (1998). Modern graph theory. GTM 184. Springer-Verlag. p. 321. ISBN 0-387-98488-7.
- Kannan, R.; Vempala, S., and Vetta, A. (May 2004). "On clusterings: Good, bad and spectral". J. ACM. 51, 3: 497–515.
- Fan Chung (1997). Spectral Graph Theory. CBMS Lecture Notes 92. AMS Publications. p. 212. ISBN 0-8218-0315-8.
- A. Sinclair. Algorithms for Random Generation and Counting: A Markov Chain Approach. Birkhauser, Boston-Basel-Berlin, 1993.
- D. Levin, Y. Peres, E. L. Wilmer: Markov Chains and Mixing Times