Compsognathus
| Compsognathus Temporal range: Late Jurassic, 150.8Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Reconstruction of a skeleton, Museum of Ancient Life – Thanksgiving Point, model sculpted by Bruce J. Mohn | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Compsognathidae |
| Subfamily: | †Compsognathinae Cope, 1875 |
| Genus: | †Compsognathus Wagner, 1861 |
| Type species | |
| †Compsognathus longipes Wagner, 1861 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Compsognathus corallestris | |
Compsognathus (/kɒmpˈsɒɡnəθəs/;[1] Greek kompsos/κομψός; "elegant", "refined" or "dainty", and gnathos/γνάθος; "jaw")[2] is a genus of small, bipedal, carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Members of its single species Compsognathus longipes could grow to the size of a turkey. They lived around 150 million years ago, the latest Kimmeridgian age of the late Jurassic period, in what is now Europe. Paleontologists have found two well-preserved fossils, one in Germany in the 1850s and the second in France more than a century later. Today, C. longipes is the only recognized species, although the larger specimen discovered in France in the 1970s was once thought to belong to a separate species and named C. corallestris.
Many presentations still describe Compsognathus as "chicken-sized" dinosaurs because of the small size of the German specimen, which is now believed to be a juvenile. Compsognathus longipes is one of the few dinosaur species for which diet is known with certainty: the remains of small, agile lizards are preserved in the bellies of both specimens. Teeth discovered in Portugal may be further fossil remains of the genus.
Although not recognized as such at the time of its discovery, Compsognathus is the first theropod dinosaur known from a reasonably complete fossil skeleton. Until the 1990s, it was the smallest known non-avialan dinosaur; earlier it was the closest supposed relative of the early bird Archaeopteryx.
Description

For decades, Compsognathus were famed as the smallest dinosaurs known; the first specimen collected was around 1 m (3.3 ft) in length. However, dinosaurs discovered later, such as Caenagnathasia, Microraptor and Parvicursor, were even smaller. The largest Compsognathus specimen is estimated to have weighed somewhere between 0.83 and 3.5 kg (between 1.8 and 7.7 lb).[3][4]
Compsognathus were small, bipedal animals with long hind legs and longer tails, which they used for balance during locomotion. The forelimbs were smaller than the hindlimbs and featured three digits equipped with solid claws suited for grasping prey. Their delicate skulls were narrow and long, with tapered snouts. The skull had five pairs of fenestrae (skull openings), the largest of which was for the orbit (eye socket).[5] The eyes were large in proportion to the rest of the skull.
The lower jaw was slender and had no mandibular fenestra, a hole in the side of the lower jawbone commonly seen in archosaurs. The teeth were small but sharp, suited for its diet of small vertebrates and possibly other small animals, such as insects. Its frontmost teeth (those on the premaxilla) were unserrated, unlike those further back in the jaw which were flattened and more strongly recurved.[6] Scientists have used these dental characteristics to identify Compsognathus and its closest relatives.[7] Reisdorf and Wuttke (2012) described the taphonomical phenomena of the German specimen of Compsognathus.[8]
Integument
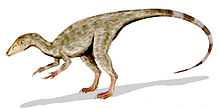
Some relatives of Compsognathus, namely Sinosauropteryx and Sinocalliopteryx, have been preserved with the remains of simple feathers covering the body like fur,[9] promoting some scientists to suggest that Compsognathus might have been feathered in a similar way.[10] Consequently, many depictions of Compsognathus show them with coverings of downy proto-feathers. However, no feathers or feather-like covering have been preserved with Compsognathus fossils, in contrast to Archaeopteryx, which are found in the same sediments. Karin Peyer, in 2006, reported skin impressions preserved on the side of the tail starting at the 13th tail vertebra. The impressions showed small bumpy tubercles, similar to the scales found on the tail and hind legs of Juravenator.[11] Additional scales had in 1901 been reported by Von Huene, in the abdominal region of the German Compsognathus, but Ostrom subsequently disproved this interpretation;[12][13] in 2012 they were by Achim Reisdorf seen as plaques of adipocere, corpse wax.[8]
Like Compsognathus, and unlike Sinosauropteryx, a patch of fossilized skin from the tail and hindlimb of the possible relative Juravenator starki shows mainly scales, though there is some indication that simple feathers were also present in the preserved areas.[14] This may mean that a feather covering was not ubiquitous in this group of dinosaurs.[15]
Discovery and species

Compsognathus is known from two almost complete skeletons, one from Germany that is 89 cm long (35 in) and another from France that is 125 cm (49 in).[16] The physician and fossil collector Joseph Oberndorfer acquired the German specimen (BSP AS I 563) in 1859, discovered about the same year in the Solnhofen lithographic limestone deposits in the Riedenburg-Kelheim region of Bavaria.[17] The limestone of the Solnhofen area has also yielded such well-preserved fossils as Archaeopteryx with feather impressions and some pterosaurs with imprints of their wing membranes. The German Compsognathus fossil itself most likely came from the Painten Formation of the Kapfelberg locality, specifically dated to the uppermost Kimmeridgian stage (150.8 million years ago);[8] however, alternative possibilities include quarries near Jachenhausen[18] or Goldberg, both from the Tithonian, to which stage Compsognathus has traditionally been dated.[8] Johann A. Wagner discussed the specimen briefly in 1859, when he coined the name Compsognathus longipes,[19] and described it in detail in 1861.[20] In early 1868, Thomas Huxley compared the two species and, following earlier suggestions by Karl Gegenbaur[21] and Edward Drinker Cope,[22] concluded that, apart from its arms and feathers, the Archaeopteryx skeleton was closely similar to Compsognathus, and that the proto-bird was related to the dinosaurs.[23][24] In 1896, Othniel Marsh recognized the fossil as a true member of the Dinosauria.[25] John Ostrom thoroughly redescribed the species in 1978, making it one of the best-known small theropods at that time.[12] The German specimen is on display at the Bayerische Staatsammlung für Paläontologie und historische Geologie (Bavarian State Institute for Paleontology and Historical Geology) in Munich, Germany, which bought the fossil from Oberndorfer in 1865.[17]

The larger French specimen (MNHN CNJ 79) was discovered by quarry owner Louis Ghirardi around 1971 in the Portlandian lithographic limestone of Canjuers near Nice in southeastern France.[26] It dates to the lower Tithonian. Although Alain Bidar originally described the specimen as a separate species called Compsognathus corallestris,[27] Ostrom, Jean-Guy Michard and others have since relabeled it as another example of Compsognathus longipes.[26][28] Quimby identified the smaller German specimen as a juvenile of the same species.[29] In 1983, the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle in Paris acquired the French Compsognathus fossil; Michard thoroughly studied it there.[28]
Collector Heinrich Fischer had originally labelled a partial foot, also from Solnhofen, as belonging to Compsognathus longipes. Though this identification was rejected by Wilhelm Barnim Dames in 1884,[30] Friedrich von Huene nevertheless in 1925 provisionally referred the specimen to Compsognathus.[31] However, Ostrom's study of 1978 has disproven this. Jens Zinke has in 1998 assigned forty-nine teeth from the Kimmeridgian Guimarota formation of Portugal to the genus. These were not identical to those of C. longipes, having serrations on the front edge, but were because of general similarities in form referred to a Compsognathus sp.[32]
In 1997 Virginia Morell renamed a related Chinese form, Sinosauropteryx prima, into a Compsognathus prima;[33] this has found no general acceptance.
Classification
The genus Compsognathus gives its name to the family Compsognathidae, a group composed mostly of small dinosaurs from the late Jurassic and early Cretaceous periods of China, Europe and South America.[26] For many years it was the only member known; however in recent decades paleontologists have discovered several related genera. The clade includes Aristosuchus,[34] Huaxiagnathus,[35] Mirischia,[36] Sinosauropteryx,[9][37] and perhaps Juravenator[38] and Scipionyx.[39] At one time, Mononykus was proposed as a member of the family, but this was rejected by Chen and coauthors in a 1998 paper; they considered the similarities between Mononykus and the compsognathids to be an example of convergent evolution.[7] The position of Compsognathus and its relatives within the coelurosaur group is uncertain. Some, such as theropod expert Thomas Holtz Jr. and co-authors Ralph Molnar and Phil Currie in the landmark 2004 text Dinosauria, hold the family as the most basal of the coelurosaurs,[40] while others as part of the Maniraptora.[41][42]
For almost a century, Compsognathus longipes was the only well-known small theropod species. This led to comparisons with Archaeopteryx and to suggestions of an especially close relationship with birds. In fact, Compsognathus, rather than Archaeopteryx, piqued Huxley's interest in the origin of birds.[43] The two animals share similarities in shape and proportions, so many in fact that two specimens of Archaeopteryx, the "Eichstätt" and the "Solnhofen", were for a time misidentified as those of Compsognathus.[5] Many other types of dinosaur, including Deinonychus, Oviraptor and Segnosaurus, are now known to have been more closely related to birds.[44]


Below is a cladogram placing Compsognathus in Coelurosauria by Senter et al. in 2012.[45]
| Coelurosauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Paleoecology

During the late Jurassic, Europe was a dry, tropical archipelago at the edge of the Tethys Sea. The fine limestone in which the skeletons of Compsognathus have been found originated in calcite from the shells of marine organisms. Both the Solnhofen and Canjuers areas where Compsognathus specimens have been preserved were lagoons situated between the beaches and coral reefs of the Jurassic European islands in the Tethys Sea.[46] Contemporaries of Compsognathus longipes include the early bird Archaeopteryx lithographica and the pterosaurs Rhamphorhynchus muensteri and Pterodactylus antiquus. The same sediments in which Compsognathus have been preserved also contain fossils of a number of marine animals such as fish, crustaceans, echinoderms and marine mollusks, confirming the coastal habitat of this theropod. No other dinosaur has been found in association with Compsognathus, indicating that these little dinosaurs might in fact have been the top land predator in these islands.[44]
Paleobiology
In a 2001 study conducted by Bruce Rothschild and other paleontologists, nine foot bones referred to Compsognathus were examined for signs of stress fracture, but none were found.[47]
Hand
The Compsognathus specimen discovered in Germany in the 19th century featured only two digits on each forelimb, leading scientists to conclude that this was how the creature appeared in life.[12] However, the fossil discovered later in France revealed the manus (hands) to have had three digits,[48] similar to other members of compsognathid genera. The fossilization of the German Compsognathus had simply failed to preserve the specimen's forefeet completely. Bidar supposed that the French specimen had webbed forefeet, which would look like flippers in life.[27] In the 1975 book The Evolution and Ecology of the Dinosaurs, L. B. Halstead depicts the animal as an amphibious dinosaur capable of feeding on aquatic prey and swimming out of reach of larger predators.[49] Ostrom debunked this hypothesis[12] by showing conclusively that the French specimen was nearly identical to the German specimen in every aspect but its size. Peyer confirmed these conclusions.[26]
Diet

The remains of a lizard in the German specimen's thoracic cavity show that Compsognathus preyed on small vertebrates.[7] Marsh, who examined the specimen in 1881, thought that this small skeleton inside Compsognathus belly was an embryo, but in 1903, Franz Nopcsa concluded that it was a lizard.[50] Ostrom identified the remains as belonging to a lizard of the genus Bavarisaurus,[51] which he concluded was a fast and agile runner owing to its long tail and limb proportions. This in turn led to the conclusion that its predators, Compsognathus, must have had sharp vision and the ability to rapidly accelerate and outrun the lizard.[12] The Bavarisaurus is in a single piece, indicating that the Compsognathus must have swallowed its prey whole. The French specimen's gastric contents consist of unidentified lizards or sphenodontids.[26]
Possible eggs
The plate of the German Compsognathus shows several circular irregularities 10 mm in diameter near the skeletal remains. Peter Griffiths interpreted them as immature eggs in 1993.[52] However, later researchers have doubted their connection to the genus because they were found outside the body cavity of the animal. A well-preserved fossil of a Sinosauropteryx, a genus related to Compsognathus, shows two oviducts bearing two unlaid eggs. These proportionally larger and less numerous eggs of Sinosauropteryx cast further doubt on the original identification of the purported Compsognathus eggs.[7] In 1964 German geologist Karl Werner Barthel had explained the discs as gas bubbles formed in the sediment because of the putrefaction of the carcass.[53]
In popular culture
Children's dinosaur books commonly feature Compsognathus. For a long time they were unique in their small size, as most other small dinosaurs were discovered and described a century or more later.[54][55] These animals have appeared in the movies The Lost World: Jurassic Park and Jurassic Park III. In The Lost World: Jurassic Park, one of the characters incorrectly identifies the species as "Compsognathus triassicus", combining the genus name of Compsognathus longipes with the specific name of Procompsognathus triassicus, a distantly related small carnivore featured in the Jurassic Park novels.[56]
References
- ↑ "Compsognathus", Oxford English Dictionary, Second Edition
- ↑ Liddell & Scott (1980). Greek-English Lexicon, Abridged Edition. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK. ISBN 0-19-910207-4.
- ↑ Therrien, F.; Henderson, D.M. (2007). "My theropod is bigger than yours...or not: estimating body size from skull length in theropods". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 27 (1): 108–115. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[108:MTIBTY]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Seebacher, F. (2001). "A new method to calculate allometric length-mass relationships of dinosaurs". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 21 (1): 51–60. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2001)021[0051:ANMTCA]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Lambert, David (1993). The Ultimate Dinosaur Book. New York: Dorling Kindersley. pp. 38–81. ISBN 1-56458-304-X.
- ↑ Stromer, E., 1934, "Die Zähne des Compsognathus und Bemerkungen über das Gebiss der Theropoda", Zentralblatt für Mineralalogie, Geologie und Paläontologie, Abteilung B, Jahrgang 1934: 74–85
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Chen, P.; Dong, Z. and Zhen, S. (1998). "An exceptionally well-preserved theropod dinosaur from the Yixian Formation of China". Nature 391 (6663): 147–152. Bibcode:1998Natur.391..147C. doi:10.1038/34356.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Reisdorf, A.G., and Wuttke, M. (2012). "Re-evaluating Moodie's Opisthotonic-Posture Hypothesis in fossil vertebrates. Part I: Reptiles - The taphonomy of the bipedal dinosaurs Compsognathus longipes and Juravenator starki from the Solnhofen Archipelago (Jurassic, Germany)." Palaeobiodiversity and Palaeoenvironments, 92(1): 119-168 doi:10.1007/s12549-011-0068-y
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Currie, P.J.; P. Chen (2001). "Anatomy of Sinosauropteryx prima from Liaoning, northeastern China". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 38 (12): 1705–1727. Bibcode:2001CaJES..38.1705C. doi:10.1139/cjes-38-12-1705.
- ↑ Ji, S.; Ji, Q.; Lu, J.; Yuan, C. (2007). "A new giant compsognathid dinosaur with long filamentous integuments from Lower Cretaceous of Northeastern China". Acta Geologica Sinica 81 (1): 8–15.
- ↑ Peyer, K. (2006). "A reconsideration of Compsognathus from the Upper Tithonian of Canjuers, southeastern France". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26 (4): 879–896. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[879:AROCFT]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 Ostrom, J.H. (1978). "The osteology of Compsognathus longipes". Zitteliana 4: 73–118.
- ↑ von Huene, F. (1901). "Der vermuthliche Hautpanzer des "Compsognathus longipes" Wagner". Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie, Geologie and Palaeontologie 1: 157–160.
- ↑ Goehlich, U.B.; Tischlinger, H.; Chiappe, L.M. (2006). "Juraventaor starki (Reptilia, Theropoda) ein nuer Raubdinosaurier aus dem Oberjura der Suedlichen Frankenalb (Sueddeutschland): Skelettanatomie und Wiechteilbefunde". Archaeopteryx 24: 1–26.
- ↑ Xu, Xing (2006). "Palaeontology: Scales, feathers and dinosaurs". Nature 440 (7082): 287–8. Bibcode:2006Natur.440..287X. doi:10.1038/440287a. PMID 16541058.
- ↑ Paul, G.S. (1988). "Early Avetheropods". Predatory Dinosaurs of the World. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 297–300. ISBN 0-671-61946-2.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Wellnhofer, P. (2008). "Dinosaurier". Archaeopteryx — der Urvogel von Solnhofen. Munich: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. p. 256. ISBN 978-3-89937-076-8.
- ↑ Mäuser M. 1983, "Neue Gedanken über Compsognathus longipes WAGNER und dessen Fundort", In: Erwin Rutte-Festschrift, Weitenburger Akademie, pp 157–162
- ↑ Wagner, J. A. (1859). "Über einige im lithographischen Schiefer neu aufgefundene Schildkröten und Saurier". Gelehrte Anzeigen der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften 49: 553.
- ↑ Wagner, A. (1861). "Neue Beiträge zur Kenntnis der urweltlichen Fauna des lithographischen Schiefers; V. Compsognathus longipes Wagner". Abhandlungen der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften 9: 30–38.
- ↑ Gegenbaur, C. (1863). "Vergleichend-anatomische Bemerkungen über das Fußskelet der Vögel". Archiv für Anatomie, Physiologie und Wissenschaftliche Medicin 1863: 450–472.
- ↑ Cope, E.D. (1867). "An account of the extinct reptiles which approached the birds". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 19: 234–235.
- ↑ Huxley, T.H. (1868). "On the animals which are most nearly intermediate between birds and reptiles". Annals and Magazine of Natural History 2: 66–75.
- ↑ Foster, Michael; Lankester, E. Ray 1898–1903. The scientific memoirs of Thomas Henry Huxley. 4 vols and supplement, London: Macmillan.
- ↑ Marsh, O.C. (1896). "Classification of dinosaurs". Geological Magazine 3 (9): 388–400. doi:10.1017/S0016756800131826.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 26.4 Peyer, K. (2006). "A Reconsideration Of Compsognathus From The Upper Tithonian Of Canjuers, Southeastern France". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26 (4): 879–896. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[879:AROCFT]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Bidar, A.; Demay L., Thomel G. (1972). "Compsognathus corallestris, une nouvelle espèce de dinosaurien théropode du Portlandien de Canjuers (Sud-Est de la France)". Annales du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Nice 1: 9–40.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Michard, J. G. (1991). "Description du Compsognathus (Saurischia, Theropoda) de Canjuers (Jurassique supérieur du Sud-est de la France), position phylogénétique, relation avec Archaeopteryx et implications sur l'origine théropodienne des oiseaux,". Ph.D. dissertation, Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris.
- ↑ Callison, G.; H. M. Quimby (1984). "Tiny dinosaurs: Are they fully grown?". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 3 (4): 200–209. doi:10.1080/02724634.1984.10011975.
- ↑ Dames, W.B., 1884, "Vorlegung der Metatarsen eines Compsognathus-ähnlichen Reptils von Solenhofen", Sitzungsberichte der Gesellschaft Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin, Jahrgang 1884, pp. 179-180
- ↑ Huene, F.R., von, 1925, "Eine neue Rekonstruktion von Compsognathus longipes", Zentralblatt für Mineralogie, Geologie und Palaeontologie Jahrgang 1925, Abteilung B(5): 157-160
- ↑ Zinke, J. (1998). "Small theropod teeth from the Upper Jurassic coal mine of Guimarota (Portugal)". Palaontologische Zeitschrift 72: 179–189.
- ↑ Morell, V. (1997). "The origin of birds: the dinosaur debate". Audubon Magazine 99 (2): 36–45.
- ↑ Seeley, H.G. (1887). "On Aristosuchus pusillus (Owen), being further notes on the fossils described by Sir. R. Owen as Poikilopleuron pusillus, Owen". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London 43: 221–228. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1887.043.01-04.22.
- ↑ Hwang, S.H.; M. A. Norell, J. Qiang and G. Keqin (2004). "A large compsognathid from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation of China". Journal of Systematic Paleontology 2: 13–39. doi:10.1017/S1477201903001081.
- ↑ Naish, D.; Martill, D. M. and Frey, E. (2004). "Ecology, systematics and biogeographical relationships of dinosaurs, including a new theropod, from the Santana Formation (?Albian, Early Cretaceous) of Brazil". Historical Biology: 1–14.
- ↑ Ji, Q.; Ji S.A. (1996). "On discovery of the earliest bird fossil in China and the origin of birds (in Chinese)". Chinese Geology 233: 30–33.
- ↑ Göhlich, U.; L. M Chiappe (2006). "A new carnivorous dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Solnhofen archipelago". Nature 440 (7082): 329–332. Bibcode:2006Natur.440..329G. doi:10.1038/nature04579. PMID 16541071.
- ↑ Dal Sasso, C.; M. Signore (1998). "Exceptional soft-tissue preservation in a theropod dinosaur from Italy". Nature 392 (6674): 383–387. Bibcode:1998Natur.392..383D. doi:10.1038/32884.
- ↑ Holtz TR, Molnar RE, Currie PJ (2004). "Basal Tetanurae". In Weishampel DB, Osmólska H, Dodson P. The Dinosauria (2nd Edition). University of California Press. p. 105. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
- ↑ Gauthier, J.A. (1986). "Saurischian monophyly and the origin of birds". In Padian, K. (ed.) the Origin of Birds and the Evolution of Flight, Memoirs of the California Academy of Sciences 8: 1–55.
- ↑ Forster, C.A.; Sampson, S.D., Chiappe, L.M. & Krause, D.W. (1998). "The theropod ancestry of birds: new evidence from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar". Science 279 (5358): 1915–1919. Bibcode:1998Sci...279.1915F. doi:10.1126/science.279.5358.1915. PMID 9506938.
- ↑ Fastovsky DE, Weishampel DB (2005). "Theropoda I:Nature red in tooth and claw". In Fastovsky DE, Weishampel DB. The Evolution and Extinction of the Dinosaurs (2nd Edition). Cambridge University Press. pp. 265–299. ISBN 0-521-81172-4.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Weishampel, D.B., Dodson, P., Oslmolska, H. (2004). The Dinosauria (Second ed.). University of California Press.
- ↑ Senter, P.; Kirkland, J. I.; Deblieux, D. D.; Madsen, S.; Toth, N. (2012). "New Dromaeosaurids (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah, and the Evolution of the Dromaeosaurid Tail". In Dodson, Peter. PLoS ONE 7 (5): e36790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036790. PMC 3352940. PMID 22615813.
- ↑ Viohl, G. (1985). "Geology of the Solnhofen lithographic limestone and the habitat of Archaeopteryx". In Hecht MK, Ostrom JH, Viohl G, Wellnhofer P, (eds.). The Beginnings of Birds: Proceedings of the International Archaeopteryx Conference. Eichstätt: Freunde des Jura-Museums. pp. 31–44. OCLC 13213820.
- ↑ Rothschild, B., Tanke, D. H., and Ford, T. L., 2001, Theropod stress fractures and tendon avulsions as a clue to activity: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 331-336.
- ↑ Gauthier, J.; Gishlick A.D. (2000). "Re-examination of the manus of Compsognathus and its relevance to the original morphology of the Coelurosaur manus". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 20 (3, Supplement): 43A.
- ↑ Halstead L.B. (1975). The evolution and ecology of the dinosaurs. Eurobook. ISBN 0-85654-018-8.
- ↑ Nopcsa, Baron F. (1903). "Neues ueber Compsognathus". Neues Jahrbuch fur Mineralogie, Geologie und Palaeontologie (Stuttgart) 16: 476–494.
- ↑ Evans, S.E. (1994). "The Solnhofen (Jurassic: Tithonian) lizard genus Bavarisaurus: new skull material and a reinterpretation". Neues Jahrbuch für Paläontologie und Geologie, Abhandlungen 192: 37–52.
- ↑ Griffiths, P. (1993). "The question of Compsognathus eggs". Revue de Paleobiologie Spec. 7: 85–94.
- ↑ Barthel, K.W. (1964). "Zur Entstehung der Solnhofener Plattenkalke (unteres Untertithon)". Mitteilungen der Bayerischen Staatssammlung für Paläontologie und historische Geologie 4: 7–69.
- ↑ Wilson, Ron (1986). 100 Dinosaurs from A to Z. New York: Grosset & Dunlap. p. 18. ISBN 0-448-18992-5.
- ↑ Attmore, Stephen (1988). Dinosaurs. Newmarket, England: Brimax Books. p. 18. ISBN 0-86112-460-X.
- ↑ Berry, Mark F. (2002). The dinosaur filmography. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland. p. 273. ISBN 0-7864-1028-0.
| Wikispecies has information related to: Compsognathidae |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Compsognathus. |