Compound matrix
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, the kth compound matrix 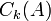 ,[1] of an
,[1] of an 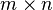 matrix A is the
matrix A is the 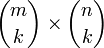 matrix formed from the determinants of all
matrix formed from the determinants of all  submatrices of A, i.e., all
submatrices of A, i.e., all  minors, arranged with the submatrix index sets in lexicographic order.
minors, arranged with the submatrix index sets in lexicographic order.
References
- ↑ R.A. Horn and C.R. Johnson, Matrix Analysis, Cambridge University Press, 1990, pp. 19–20
External links
- Gantmacher, F. R. and Krein, M. G., Oscillation Matrices and Kernels and Small Vibrations of Mechanical Systems, Revised Edition, http://www.ams.org/bookstore?fn=20&arg1=diffequ&ikey=CHEL-345-H
- To efficiently calculate compound matrices see: "Compound matrices: properties, numerical issues and analytical computations" - Christos Kravvaritis · Marilena Mitrouli - DOI 10.1007/s11075-008-9222-7
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.
![{\begin{aligned}C_{1}(A)&=A\\[6pt]C_{n}(A)&=\det(A){\text{ if }}A{\text{ is }}n\times n\\[6pt]C_{k}(AB)&=C_{k}(A)C_{k}(B)\\[6pt]C_{k}(aX)&=a^{k}C_{k}(X)\\[6pt]{\text{For }}n\times n{\text{ identity }}I,C_{k}(I)&=I\,,{\text{ the }}\textstyle {{\binom nk}\times {\binom nk}}{\text{ identity }}\\[6pt]C_{k}(A^{T})&=C_{k}(A)^{T}\,,{\text{ over any field}}\\[6pt]C_{k}(A^{*})&=C_{k}(A)^{*}\,,{\text{ over }}{\mathbb {C}}\\[6pt]C_{k}(A^{{-1}})&=C_{k}(A)^{{-1}}\,,{\text{ for }}n\times n,{\text{ invertible }}A\end{aligned}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/4/6/0/e/460e861c14537131507cf01af6c9615a.png)