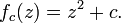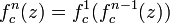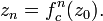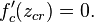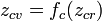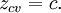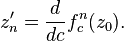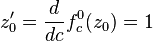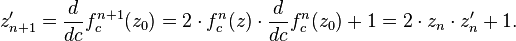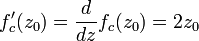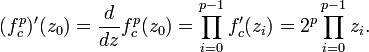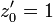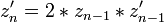Complex quadratic polynomial
A complex quadratic polynomial is a quadratic polynomial whose coefficients are complex numbers.
Forms
When the quadratic polynomial has only one variable (univariate), one can distinguish its 4 main forms:
- The general form:
 where
where 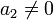
- The factored form used for logistic map

-
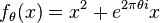 which has an indifferent fixed point with multiplier
which has an indifferent fixed point with multiplier  at the origin[1]
at the origin[1] - The monic and centered form,
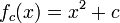
The monic and centered form has the following properties:
- It is the simplest form of a nonlinear function with one coefficient (parameter),
- It is an unicritical polynomial, i.e. it has one critical point,
- It is a centered polynomial (the sum of its critical points is zero),[2]
- It can be postcritically finite, i.e. If the orbit of the critical point is finite. It is when critical point is periodic or preperiodic.[3]
- It is a unimodal function,
- It is a rational function,
- It is an entire function.
Conjugation
Between forms
Since 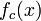 is affine conjugate to the general form of the quadratic polynomial it is often used to study complex dynamics and to create images of Mandelbrot, Julia and Fatou sets.
is affine conjugate to the general form of the quadratic polynomial it is often used to study complex dynamics and to create images of Mandelbrot, Julia and Fatou sets.
When one wants change from  to
to  :[4]
:[4]
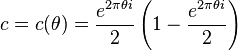 .
.
When one wants change from  to
to  :
:
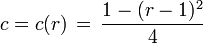 .
.
With doubling map
There is semi-conjugacy between the dyadic transformation (here named doubling map) and the quadratic polynomial.
Family
The family of quadratic polynomials 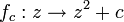 parametrised by
parametrised by 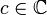 is called:
is called:
- the Douady-Hubbard family of quadratic polynomials[5]
- quadratic family
Map
The monic and centered form is typically used with variable 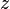 and parameter
and parameter  :
:
When it is used as an evolution function of the discrete nonlinear dynamical system:
Notation
Here 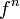 denotes the n-th iteration of the function
denotes the n-th iteration of the function 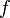 not exponentiation
not exponentiation
so
Because of the possible confusion it is customary to write 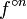 for the nth iterate of the function
for the nth iterate of the function 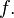
Critical items
Critical point
A critical point of 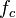 is a point
is a point  in the dynamical plane such that the derivative vanishes:
in the dynamical plane such that the derivative vanishes:
Since
implies
we see that the only (finite) critical point of 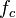 is the point
is the point 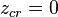 .
.
 is an initial point for Mandelbrot set iteration.[7]
is an initial point for Mandelbrot set iteration.[7]
Critical value
A critical value 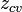 of
of 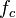 is the image of a critical point:
is the image of a critical point:
Since
we have
So the parameter  is the critical value of
is the critical value of 
Critical orbit




Forward orbit of a critical point is called a critical orbit. Critical orbits are very important because every attracting periodic orbit attracts a critical point, so studying the critical orbits helps us understand the dynamics in the Fatou set.[8][9]
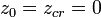
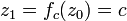
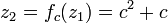
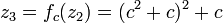
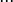
This orbit falls into an attracting periodic cycle.
Critical sector
The critical sector is a sector of the dynamical plane containing the critical point.
Critical polynomial

so
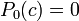
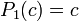
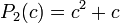
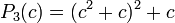
These polynomials are used for:
- finding centers of these Mandelbrot set components of period n. Centers are roots of n-th critical polynomials
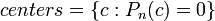
- finding roots of Mandelbrot set components of period n (local minimum of
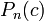 )
) - Misiurewicz points
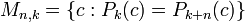
Critical curves
Diagrams of critical polynomials are called critical curves.[10]
These curves create skeleton of bifurcation diagram.[11] (the dark lines[12])
Planes

One can use the Julia-Mandelbrot 4-dimensional space for a global analysis of this dynamical system.[13]
In this space there are 2 basic types of 2-D planes:
- the dynamical (dynamic) plane,
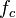 -plane or c-plane
-plane or c-plane - the parameter plane or z-plane
There is also another plane used to analyze such dynamical systems w-plane:
Parameter plane
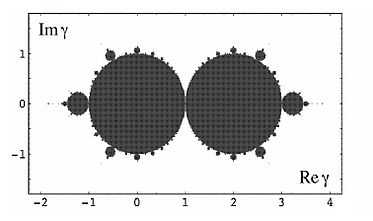
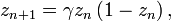
The phase space of a quadratic map is called its parameter plane. Here:
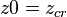 is constant and
is constant and  is variable.
is variable.
There is no dynamics here. It is only a set of parameter values. There are no orbits on the parameter plane.
The parameter plane consists of:
- The Mandelbrot set
- The bifurcation locus = boundary of Mandelbrot set
- Bounded hyperbolic components of the Mandelbrot set = interior of Mandelbrot set[16]
There are many different subtypes of the parameter plane.[17][18]
Dynamical plane
On the dynamical plane one can find:
- The Julia set
- The Filled Julia set
- The Fatou set
- Orbits
The dynamical plane consists of:
- Fatou set
- Julia set
Here,  is a constant and
is a constant and 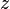 is a variable.
is a variable.
The two-dimensional dynamical plane can be treated as a Poincaré cross-section of three-dimensional space of continuous dynamical system.[19][20]
Derivatives
Derivative with respect to c
On parameter plane:
-
 is a variable
is a variable -
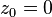 is constant
is constant
The first derivative of 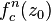 with respect to c is
with respect to c is
This derivative can be found by iteration starting with
and then replacing at every consecutive step
This can easily be verified by using the chain rule for the derivative.
This derivative is used in the distance estimation method for drawing a Mandelbrot set.
Derivative with respect to z
On dynamical plane:
-
 is a variable
is a variable -
 is a constant
is a constant
at a fixed point 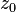
at a periodic point z0 of period p
It is used to check the stability of periodic (also fixed) points.
at nonperiodic point:
This derivative can be found by iteration starting with
and then :
This dervative is used for computing external distance to Julia set.
Schwarzian derivative
The Schwarzian derivative (SD for short) of f is:[21]
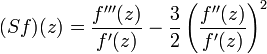 .
.
See also
- Misiurewicz point
- Periodic points of complex quadratic mappings
- Mandelbrot set
- Julia set
- Milnor–Thurston kneading theory
References
- ↑ Michael Yampolsky, Saeed Zakeri : Mating Siegel quadratic polynomials.
- ↑ B Branner: Holomorphic dynamical systems in the complex plane. Mat-Report No 1996-42. Technical University of Denmark
- ↑ Alfredo Poirier : On Post Critically Finite Polynomials Part One: Critical Portraits
- ↑ Michael Yampolsky, Saeed Zakeri : Mating Siegel quadratic polynomials.
- ↑ Yunping Jing : Local connectivity of the Mandelbrot set at certain infinitely renormalizable points Complex Dynamics and Related Topics, New Studies in Advanced Mathematics, 2004, The International Press, 236-264
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Quadratic Map." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resourc
- ↑ Java program by Dieter Röß showing result of changing initial point of Mandelbrot iterations
- ↑ M. Romera, G. Pastor, and F. Montoya : Multifurcations in nonhyperbolic fixed points of the Mandelbrot map. Fractalia 6, No. 21, 10-12 (1997)
- ↑ Burns A M : Plotting the Escape: An Animation of Parabolic Bifurcations in the Mandelbrot Set. Mathematics Magazine, Vol. 75, No. 2 (Apr., 2002), pp. 104-116
- ↑ The Road to Chaos is Filled with Polynomial Curves by Richard D. Neidinger and R. John Annen III. American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 103, No. 8, October 1996, pp. 640-653
- ↑ Hao, Bailin (1989). Elementary Symbolic Dynamics and Chaos in Dissipative Systems. World Scientific. ISBN 9971-5-0682-3.
- ↑ M. Romera, G. Pastor and F. Montoya, "Misiurewicz points in one-dimensional quadratic maps", Physica A, 232 (1996), 517-535. Preprint
- ↑ Julia-Mandelbrot Space at Mu-ency by Robert Munafo
- ↑ Carleson, Lennart, Gamelin, Theodore W.: Complex Dynamics Series: Universitext, Subseries: Universitext: Tracts in Mathematics, 1st ed. 1993. Corr. 2nd printing, 1996, IX, 192 p. 28 illus., ISBN 978-0-387-97942-7
- ↑ Holomorphic motions and puzzels by P Roesch
- ↑ Lasse Rempe, Dierk Schleicher : Bifurcation Loci of Exponential Maps and Quadratic Polynomials: Local Connectivity, Triviality of Fibers, and Density of Hyperbolicity
- ↑ Alternate Parameter Planes by David E. Joyce
- ↑ exponentialmap by Robert Munafo
- ↑ Mandelbrot set by Saratov group of theoretical nonlinear dynamics
- ↑ Moehlis, Kresimir Josic, Eric T. Shea-Brown (2006) Periodic orbit. Scholarpedia,
- ↑ The Schwarzian Derivative & the Critical Orbit by Wes McKinney 18.091 20 April 2005
External links
| Find more about Complex quadratic polynomial at Wikipedia's sister projects | |
| |
Definitions and translations from Wiktionary |
| |
Media from Commons |
| |
Quotations from Wikiquote |
| |
Source texts from Wikisource |
| |
Textbooks from Wikibooks |
| |
Learning resources from Wikiversity |
- M. Nevins and D. Rogers, "Quadratic maps as dynamical systems on the p-adic numbers"
- Wolf Jung : Homeomorphisms on Edges of the Mandelbrot Set. Ph.D. thesis of 2002