Comedo
| Blackhead | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
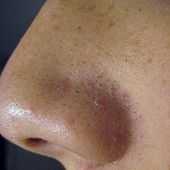 A male with blackheads on his nose | |
| ICD-9 | 706.1 |
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin.[1] Keratin (skin debris) combines with oil to block the follicle.[2] A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead), and occur with or without acne.[2] The word comedo comes from Latin to suggest the worm-like look of a blackhead that has been secreted.[3] The plural of comedo is comedones.[3]
The chronic inflammatory condition that usually includes both comedones and inflamed papules and pustules (pimples) is called acne.[2][4] Infection causes inflammation and the development of pus.[1] Whether or not a skin condition classifies as acne depends on the amount of comedones and infection.[4] Comedones should not be confused with sebaceous filaments.
Comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is not related to the skin conditions discussed here. DCIS is a non-invasive form of breast cancer, but comedo-type DCIS may be more aggressive and so may be more likely to become invasive.[5]
Causes
Oil production in the sebaceous glands increases during puberty, causing comedones and acne to be common in teenagers.[2][4] Acne is also found pre-menstrually and in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome.[2] Smoking may worsen acne.[2]
Oxidation rather than poor hygiene or dirt causes blackheads to be black.[1] Washing or scrubbing the skin too much could make it worse, by irritating the skin.[1] Touching and picking at comedones might cause irritation and spread infection.[1] It is not clear what effect shaving has on the development of comedones or acne.[1]
Some, but not all, skin products might increase comedones by blocking pores,[1] and greasy hair products (like pomades) can worsen acne.[2] Skin products that claim to not clog pores may be labeled noncomedogenic or non-acnegenic.[6] Make-up and skin products that are oil-free and water-based may be less likely to cause acne.[6] It is not known whether dietary factors or sun exposure make comedones better, worse or have no effect.[2]
A hair that does not emerge normally can also block the pore and cause a bulge or lead to infection (causing inflammation and pus).[4]
Genes may play a role in the chances of developing acne.[2] Comedones may be more common in some ethnic groups.[2][7] Africans and African-Americans may experience more inflammation in comedones, more comedonal acne, and earlier onset of inflammation.[2][7]
Pathophysiology

Comedones are associated with the pilosebaceous unit, which includes a hair follicle and sebaceous gland. These units are mostly on the face, neck, upper chest, shoulders and back.[2] Excess keratin combined with sebum can plug the opening of the follicle.[2][8] This small plug is called a microcomedo.[8] Androgens increase sebum (oil) production.[2] If sebum continues to build up behind plug, it can enlarge and form a visible comedo.[8]
A comedo may be open to the air ("blackhead") or closed by skin ("whitehead").[1] Being open to the air causes oxidization, which turns it black.[1] Propionibacterium acne is the infectious agent in acne.[2] It can proliferate in sebum and cause inflamed pustules (pimples) characteristic of acne.[2] Nodules are inflamed, painful deep bumps under the skin.[2]
Comedones that are 1mm or larger are called macrocomedones.[9] They are closed comedones and are more frequent on the face than neck.[10]
Solar comedones (sometimes called senile comedones) are related to many years of exposure to the sun, usually on the cheeks, not to acne-related pathophysiology.[11]
Management
Using non-oily cleansers or mild soap may not cause as much irritation to the skin as regular soap.[12][13] Blackheads can be removed across an area with commercially available pore-cleansing strips or the more aggressive cyanoacrylate method used by dermatologists.[14]
Squeezing blackheads and whiteheads can remove them, but it can also damage the skin.[1] Doing so increases the risk of causing or transmitting infection and scarring, as well as potentially pushing any infection deeper into the skin.[1] Comedone extractors are used with careful hygiene in beauty salons and by dermatologists, usually after using steam or warm water to open up the pores.[1]
Complementary medicine options for acne in general have not been shown to be effective in trials.[2] These include aloe vera, pyroxidine (vitamin B6), fruit-derived acids, kampo (Japanese herbal medicine), ayurvedic herbal treatments and acupuncture.[2]
Some acne treatments target infection specifically, but there are treatments that are aimed at the formation of comedones as well.[15] Others remove the dead layers of the skin and may help clear blocked pores.[1][2][4]
Dermatologists can often extract open comedones with minimal skin trauma, but closed comedones are more difficult.[2] Laser treatment for acne might reduce comedones,[16] but dermabrasion and laser therapy have also been known to cause scarring.[9]
Macrocomedones (1 mm or larger) can be removed by a dermatologist using surgical instruments or cauterized with a device that uses light.[9][10] The acne drug isotretinoin can cause severe flare-ups of macrocomedones, so dermatologists recommend removal before starting the drug and during treatment.[9][10]
Some research suggests that the common acne medications, retinoids and azelaic acid, are beneficial and do not cause hyper-pigmentation in skin of color.[17]
Rare conditions
Favre–Racouchot syndrome occurs in sun-damaged skin and includes open and closed comedones.[18]
Nevus comedonicus or comedo nevus is a benign hamartoma (birthmark) of the pilosebaceous unit around the oil-producing gland in the skin.[19] It has widened open hair follicles with dark keratin plugs that resemble comedones - but they are not actually comedones.[19][20]
Dowling-Degos disease is a genetic pigment disorder that includes comedo-like lesions and scars.[21][22]
Familial dyskeratotic comedones is a rare autosomal dominant genetic condition, with keratotic (tough) papules and comedo-like lesions.[23][24]
References
| Wikisource has the text of the 1920 Encyclopedia Americana article Comedones. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 Informed Health Online. "Acne". Fact sheet. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). Retrieved 9 June 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 2.20 Williams, HC; Dellavalle, RP; Garner, S (Jan 28, 2012). "Acne vulgaris.". Lancet 379 (9813): 361–72. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60321-8. PMID 21880356.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Comedo". Oxford dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Purdy, S; de Berker, D (January 2011). Acne vulgaris. pp. pii: 1714. PMC 3275168.
- ↑ National Cancer Institute. "Breast cancer treatment". Physician Desk Query. National Cancer Institute. Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 British Association of Dermatologists. "Acne". Patient information leaflet. British Association of Dermatologists. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Davis, EC; Callender, VD (April 2010). "A review of acne in ethnic skin: pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and management strategies.". The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology 3 (4): 24–38. PMID 20725545.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Burkhart, CG; Burkhart, CN (October 2007). "Expanding the microcomedone theory and acne therapeutics: Propionibacterium acnes biofilm produces biological glue that holds corneocytes together to form plug.". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 57 (4): 722–4. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.05.013. PMID 17870436.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Wise, EM; Graber, EM (November 2011). "Clinical pearl: comedone extraction for persistent macrocomedones while on isotretinoin therapy.". The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology 4 (11): 20–1. PMID 22132254.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Primary Care Dermatology Society. "Acne: macrocomedones". Clinical Guidance. Primary Care Dermatology Society. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- ↑ DermNetNZ. "Solar comedones". New Zealand Dermatological Society. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ↑ Poli, F (Apr 15, 2002). "[Cosmetic treatments and acne].". La Revue du praticien 52 (8): 859–62. PMID 12053795.
- ↑ Korting, HC; Ponce-Pöschl, E; Klövekorn, W; Schmötzer, G; Arens-Corell, M; Braun-Falco, O (1995 Mar-Apr). "The influence of the regular use of a soap or an acidic syndet bar on pre-acne.". Infection 23 (2): 89–93. PMID 7622270.
- ↑ Pagnoni, A; Kligman, AM; Stoudemayer, T (1999). "Extraction of follicular horny impactions the face by polymers. Efficacy and safety of a cosmetic pore-cleansing strip (Bioré)". Journal of Dermatological Treatment 10 (1): 47–52. doi:10.3109/09546639909055910.
- ↑ Gollnick, HP; Krautheim, A (2003). "Topical treatment in acne: current status and future aspects.". Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland) 206 (1): 29–36. PMID 12566803.
- ↑ Orringer, JS; Kang, S; Hamilton, T; Schumacher, W; Cho, S; Hammerberg, C; Fisher, GJ; Karimipour, DJ; Johnson, TM; Voorhees, JJ (Jun 16, 2004). "Treatment of acne vulgaris with a pulsed dye laser: a randomized controlled trial.". JAMA: the Journal of the American Medical Association 291 (23): 2834–9. doi:10.1001/jama.291.23.2834. PMID 15199033.
- ↑ Woolery-Lloyd, HC; Keri, J; Doig, S (Apr 1, 2013). "Retinoids and azelaic Acid to treat acne and hyperpigmentation in skin of color.". Journal of drugs in dermatology : JDD 12 (4): 434–7. PMID 23652891.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1847. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Zarkik, S; Bouhllab, J; Methqal, A; Afifi, Y; Senouci, K; Hassam, B (Jul 15, 2012). "Keratoacanthoma arising in nevus comedonicus.". Dermatology online journal 18 (7): 4. PMID 22863626.
- ↑ DermNetNZ. "Comedo Naevus". New Zealand Dermatological Society. Retrieved 16 June 2013.
- ↑ Bhagwat, PV; Tophakhane, RS; Shashikumar, BM; Noronha, TM; Naidu, V (2009 Jul-Aug). "Three cases of Dowling Degos disease in two families.". Indian journal of dermatology, venereology and leprology 75 (4): 398–400. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.53139. PMID 19584468.
- ↑ Khaddar, RK; Mahjoub, WK; Zaraa, I; Sassi, MB; Osman, AB; Debbiche, AC; Mokni, M (January 2012). "[Extensive Dowling-Degos disease following long term PUVA therapy].". Annales de dermatologie et de venereologie 139 (1): 54–7. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2011.10.403. PMID 22225744.
- ↑ Hallermann, C; Bertsch, HP (2004 Jul-Aug). "Two sisters with familial dyskeratotic comedones.". European journal of dermatology : EJD 14 (4): 214–5. PMID 15319152.
- ↑ OMIM. "Comedones, familial dyskeratotic". OMIM database. OMIM. Retrieved 13 June 2013.