Comanche Campaign
The Comanche Campaign is a general term for efforts by the United States government to control the violence of the Comanche tribe in the newly settled west. Between 1867 and 1875, military units fought against the Comanche people in a series of battles until the Comanche surrendered and moved onto their reservation.
Background

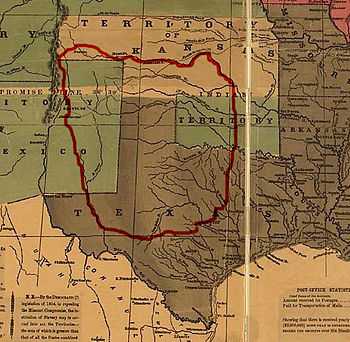
"Comanche Campaign"

A faction of the Comanche tribe, the Quahadi, was arguably the most resistant towards the Anglo settlers. Skeptical of what they would bring, the Quahadi avoided contact with these men. Their avoidance was so absolute that no records of them exist before 1872. Goods were never exchanged between the groups, and because of this seclusion, they were largely unaffected by the cholera plagues in 1816 and 1849. Led by chief Quanah Parker, the Quahadi were noted for their fierce nature; so much so that other Comanche feared them. They were the wealthiest of the Comanche in terms of horses and cattle, and they had never signed a peace treaty. It was this faction of the Comanche that gave the American troops the most trouble during the Comanche Campaign.[3] Sherman sent four cavalry companies from the United States Army to capture the Indians responsible for the Warren Wagon raid, but this assignment eventually developed into eliminating the threat of the Comanche tribe, namely the Quanah Parker and his Quahadi. Following on the heels of the Civil War, the Army had a low number of recruits, and very little money to pay the soldiers they did have, so few men were sent west to fight the Indian threat. Approximately 5,000 enlisted men, divided into ten regiments made up the American forces that would face the powerful Comanche.[4] General Sherman picked Ranald S. Mackenzie, described by President Grant as “the most promising young officer in the army,” commanding the 4th Cavalry, to lead the attack against the Comanche tribe.[5] Mackenzie and his men developed a style of fighting designed to slowly defeat the Comanche rather than face them in open battle. Colonel Mackenzie embarked on several expeditions into the Comancheria in an effort to destroy the Comanche winter camps and crops, as well as their horses and cattle. Reminiscent of General Sherman’s “March to the Sea,” the 4th Cavalry fought the Comanche by destroying their means of survival.[6]
Llano Estacado
In the fall of 1871, Mackenzie and his 4th Cavalry, as well as two companies in the 11th Infantry, arrived in Texas, began to seek out their target.[7] The campaign began in the Llano Estacado region where Comanche were rumored to have been camping. In his first expedition, Mackenzie and his men attacked these camps twice. The campaign began with the Battle of Blanco Canyon. Through the use of Tonkawa scouts, Mackenzie was able to track Quanah Parker’s faction, and save another group of American soldiers from slaughter.[8] They succeeded in pushing Quanah Parker and the Quahadi far into the region before they were forced to abandon the hunt for the winter.[9] The second expedition lasted longer than the first, from September to November, and succeeded in making it clear to the Comanche that the peace policy was no longer in effect. Mackenzie established a strong border patrol at several forts in the area, such as Fort Richardson, Fort Griffin, and Fort Concho. While there was little direct combat between the two forces, the American tactics were successful. By following the Comanche tribe throughout the region and destroying each of their camps, Mackenzie and his cavalry were able to hinder the Comanche’s ability to prepare properly for winter.[5] Mackenzie’s third expedition, in September of 1872, was, by far, the largest. Capturing 130 Indian women and children, stealing horses, and ransacking Indian camps, Mackenzie and the Fourth Cavalry spanned the region several times with the assistance of the Twenty-fourth Infantry and his Tonkawa scouts.[5] These captives were later used in a deal made between the soldiers at Fort Sill and the Comanche tribe: peace in exchange for hostages. The Comanche agreed to the terms, and there was a period of peace in the region.[9] During this period of peace, Mackenzie continued to take control of the Llano Estacado region through the south and central areas, while also creating a second front in the west in order to separate the Comanche from their source of weapons and food.[10] In the winter of 1873, record numbers of Comanche people resided at Fort Sill, and after the exchange of hostages, there was a noticeable drop in violence between the Anglos and the Native Indians. However, in an attempt to finalize the submission of the Comanche people, there was a movement towards bison hunting. The species became threatened as a result, and those Comanche people who were not at Fort Sill were on the brink of starvation.[11] The remaining Native American Tribes began to gather at the North Fork of the Red River, the center of the slowly diminishing Comancheria region. Due to tensions between them and the Indian Office, the Indians saw the withholding of rations as a declaration of war, and acted accordingly.[11]
Red River War

One of the deciding battle of the Red River War was fought at Palo Duro Canyon on September 28, 1874. Colonel Mackenzie and his Tonkawa scouts surprised the Comanche, as well as a number of other tribes, and destroyed their camps. The battle ended with only three Comanche casualties, but resulted in the destruction of both the camp and the Comanche pony herd. This defeat spelled the end of the war between the Comanche and the Americans.[14]
Aftermath
Following the Red River War, a campaign that lasted from August-November in 1874, the Comanche surrendered and moved to their new lands on the reservation. However even after that loss, it was not until June of 1875 that the last of the Comanche, those under the command of Quanah Parker, finally surrendered at Fort Sill.[15] Though the U.S. troops themselves were directly responsible for just a few hundred deaths, their tactics in the Comanche Campaign were the most devastating to the tribe. The tactics they used eventually led to the economic, rather than military, downfall of the tribe. The Comanche tribe, starting with nearly 5,000 people in 1870, finally surrendered and moved onto the reservation with barely 1,500 remaining in 1875.
Notes
- ↑ Thomas W. Kavanagh. Comanche political history : an ethnohistorical perspective, 1706-1875. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press in cooperation with the American Indian Studies Research Institute, Indiana University, Bloomington, 1996. P.399
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.313
- ↑ S. C. Gwynne (Samuel C. ). Empire of the summer moon : Quanah Parker and the rise and fall of the Comanches, the most powerful Indian tribe in American history. 1st Scribner hardcover ed.. New York: Scribner, 2010. P.6
- ↑ Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.332
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Paul Howard Carlson. The Buffalo Soldier Tragedy of 1877. 1st ed.. College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 2003. P.63
- ↑ Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.332
- ↑ S. C. Gwynne (Samuel C. ). Empire of the summer moon : Quanah Parker and the rise and fall of the Comanches, the most powerful Indian tribe in American history. 1st Scribner hardcover ed.. New York: Scribner, 2010. P.2
- ↑ S. C. Gwynne (Samuel C. ). Empire of the summer moon : Quanah Parker and the rise and fall of the Comanches, the most powerful Indian tribe in American history. 1st Scribner hardcover ed.. New York: Scribner, 2010. P.10-11
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.334
- ↑ Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.335
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.337
- ↑ Paul Howard Carlson. The Buffalo Soldier Tragedy of 1877. 1st ed.. College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 2003. P.64
- ↑ Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.338
- ↑ Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008. P.341
- ↑ Paul Howard Carlson. The Buffalo Soldier Tragedy of 1877. 1st ed.. College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 2003. P.65
Bibliography
Paul Howard Carlson. The Buffalo Soldier Tragedy of 1877. 1st ed.. College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 2003.
Pekka Hamalainen. The Comanche Empire. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2008.
S. C. Gwynne (Samuel C. ). Empire of the summer moon : Quanah Parker and the rise and fall of the Comanches, the most powerful Indian tribe in American history. 1st Scribner hardcover ed.. New York: Scribner, 2010.
Thomas W. Kavanagh. Comanche political history : an ethnohistorical perspective, 1706-1875. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press in cooperation with the American Indian Studies Research Institute, Indiana University, Bloomington, 1996.
See also
- Texas-Indian Wars