Clubbed thumb
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Clubbed thumb | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources |

Top view of a child with asymmetric clubbed thumb.
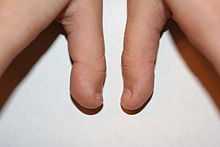
Side view of a child with asymmetric clubbed thumb
A clubbed thumb or stub thumb, known clinically as brachydactyly type D (BDD),[1] is a genetic trait characterized by the last bone of one or both thumbs being short and round with an accompanying short and wide nail bed.[2]
The condition is sometimes known as murderer's thumb, a name originally coined by fortune-tellers,[3] potter's thumb[1] or Dutch thumb.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) Brachydactyly, Type D; BDD. -113200
- ↑ Alessandro Castriota-Scanderbeg, Bruno Dallapiccola (2005). Abnormal Skeletal Phenotypes: From Simple Signs to Complex Diagnoses. Springer. p. 962. ISBN 3540679979.
- ↑ "The Curious Case of the Stubby Thumb". Science in Society Blog. 2011-11-03. Retrieved 2013-03-15.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.