Cladinose
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Cladinose | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name (4R,5S,6S)-4-Methoxy-4,6-dimethyl-tetrahydropyran-2,5-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 470-12-2 |
| PubChem | 443504 |
| ChemSpider | 391713 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@](CC(O1)O)(C)OC)O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C8H16O4 |
| Molar mass | 176.21 g/mol |
| Density | 1.156 g/mL |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Cladinose is a hexose deoxy sugar that in several antibiotics (such as erythromycin) is attached to the macrolide ring.
In ketolides, a relatively new class of antibiotics, the cladinose is replaced with a keto group.
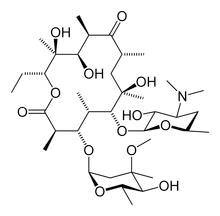
Erythromycin with cladinose visible at bottom
External links
- Cladinose at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- PubChem
- Diagrams
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.