Cirsium flodmanii
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Cirsium flodmanii | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Tribe: | Cynareae |
| Genus: | Cirsium |
| Species: | C. flodmanii |
| Binomial name | |
| Cirsium flodmanii (Rydb.) Arthur | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
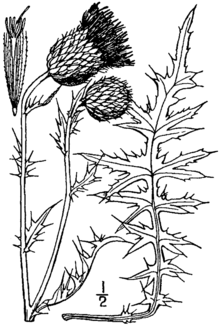
Cirsium flodmanii, common names Prairie thistle, Flodman’s thistle, or (in French) chardon de Flodman, is a plant species native to Canada and to the north-central United States. It is known from every Canadian province from Québec to Alberta, as well as from the northern Great Plains and western Great Lakes regions of the US, plus Essex County in northeastern New York State.[2][3]
Cirsium flodmanii is a perennial herb up to 140 cm (55 inches) tall. Leaves are up to 40 cm (16 inches) long, with numerous fine spines along the edges. Flowers are usually purple, occasionally white. The plant generally is found in grasslands and pastures.[2][4][5]
References
- ↑ The Plant List
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Flora of North America v 19 p 120.
- ↑ USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS)
- ↑ Arthur, Joseph Charles. Torreya 12(2): 34. 1912.
- ↑ Rydberg, Per Axel. Memoirs of The New York Botanical Garden 1: 451. 1900.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.