Choline chloride
| Choline chloride | |
|---|---|
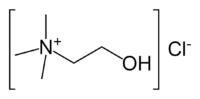 | |
| IUPAC name 2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride OR (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 67-48-1 |
| PubChem | 522265 |
| ChemSpider | 5974 |
| UNII | 45I14D8O27 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:133341 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL282468 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Cl-].OCC[N+](C)(C)C|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C5H14ClNO |
| Molar mass | 139.62 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White or deliquescent crystals |
| Melting point | 302 °C (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | very soluble (>650 g/l)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
2
0
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Choline chloride is an organic compound and a quaternary ammonium salt. It has a choline cation with chloride anion. Alternative names are hepacholine, biocolina and lipotril.
Synthesis
In the laboratory choline can be prepared by methylation of dimethylethanolamine with methyl chloride.
In the industrial Davy Process Technology route choline chloride is produced from ethylene oxide, hydrochloric acid, and trimethylamine,[2] or from the pre-formed salt:[3]
Applications
Choline chloride is mass-produced and is an important additive in feed especially for chickens where it accelerates growth. With urea it forms a deep eutectic solvent. Other commercial choline salts are choline hydroxide and choline bitartrate. In foodstuffs the compound is often present as phosphatidylcholine.
References
- ↑ "Chemical Safety Information from Intergovernmental Organizations - Choline Chloride".
- ↑ Davy Process Technology
- ↑ "Choline chloride". Screening Information Data Set (SIDS) for High Production Volume Chemicals. IPCS INCHEM.