Chloroplatinic acid
| Chloroplatinic acid | |
|---|---|
_hexahydrate.svg.png) | |
 | |
| IUPAC name Dihydrogen hexachloroplatinate(2–) | |
| Other names Hexachloroplatinic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 16941-12-1 |
| PubChem | 61859 |
| ChemSpider | 55731 |
| UNII | Q65224GJ7F |
| EC number | 241-010-7 |
| RTECS number | TP1510000 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[H+].[H+].Cl[Pt-2](Cl)(Cl)(Cl)(Cl)Cl|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | H2PtCl6 |
| Molar mass | 409.81 g/mol |
| Appearance | Reddish brown solid |
| Density | 2.431 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 60 °C (333 K) |
| Boiling point | decomp |
| Solubility in water | highly soluble |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Anti-fluorite. |
| Coordination geometry |
octahedral |
| Dipole moment | 0 D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| EU Index | 078-009-00-4 |
| EU classification | Toxic (T) Corrosive (C) |
| R-phrases | R25, R34, R42/43 |
| S-phrases | (S1/2), S22, S26, S36/37/39, S45 |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
2
1
|
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Hexachloropalladic acid |
| Other cations | Potassium hexachloroplatinate, Ammonium hexachloroplatinate, Rubidium hexachloroplatinate, Caesium hexachloroplatinate |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Chloroplatinic acid or hexachloroplatinic acid is the chemical compound usually found as the hexahydrate with the formula H2PtCl6·(H2O)6. This is one of the most readily available soluble compounds of platinum. It is rarely obtained in the pure state. The commercial product is the hydronium salt of the hexachloroplatinate(IV) anion. Therefore, the correct formula is [H3O]2[PtCl6]·4H2O.[1][2] The related palladium compound, [H3O]2[PdCl6], is extremely unstable and has not been isolated in pure form.[3]
Production

Chloroplatinic acid is produced by dissolving platinum metal sponge in aqua regia. This reaction is rumored to produce nitrogen-containing platinum compounds, but the product is H2PtCl6.[citation needed] Chloroplatinic acid is brownish-red, and can be isolated by evaporating this solution to a syrup.[4]
- Pt + 4 HNO3 + 6 HCl → H2PtCl6 + 4 NO2 + 4 H2O
Alternative methods have been heavily investigated, but the older literature can be unreliable.[5]
Reactions
When hexachloroplatinic acid is heated, it decomposes through platinum(IV) chloride and platinum(II) chloride to elemental platinum, although the reactions do not occur stepwise, cleanly:[1]
- (H3O)2PtCl6·n H2O
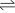 PtCl4 + 2 HCl + (n + 2) H2O
PtCl4 + 2 HCl + (n + 2) H2O
- PtCl4
 PtCl2 + Cl2
PtCl2 + Cl2
- PtCl2
 Pt + Cl2
Pt + Cl2
All three reactions are reversible.
Applications
Potassium determination
Chloroplatinic acid was popularized for the determination of potassium. The potassium is selectively precipitated as potassium chloroplatinate. Determinations were done in 85% (v/v) alcohol solutions with excess platinate ions, and the precipitated product was weighed. Potassium could be detected for solutions as dilute as 0.02 to 0.2% (m/v).[6]
This method for determination of potassium was advantageous vs. the cobaltinitrite method used previously, since it required a single precipitation reaction.[citation needed] Today, the concentration of potassium is determined with an ion-selective electrode. These modern methods remain subject to interference.
Purification of platinum
Treatment with an ammonium salt, such as ammonium chloride, gives ammonium hexachloroplatinate,[7] which is very insoluble in ammonium solutions. Heating the ammonium salt in hydrogen reduces it to elemental platinum. Platinum is often isolated from ores or recycled from residues thus.[8]
Catalysis
Like many platinum compounds, chloroplatinic acid is used in catalysis. This compound was first reported by John Speier and colleagues from Dow Corning Corporation to catalyze the reaction of silyl hydrides with olefins, hydrosilylation. Typical of his reactions, Speier used isopropanol solutions containing trichlorosilane (SiHCl3), and methyldichlorosilane (CH3HSiCl2), with pentenes. Prior work on the addition of silanes to alkenes required radical reactions that were inefficient. [9][10] It is generally agreed that chloroplatinic acid is a catalyst precursor. A possible role for colloidal platinum or zero-valent complexes has also been considered. [11]
Related compounds
Chloroplatinic acid prepared from aqua regia is occasionally contaminated with nitrosonium hexachloroplatinate, (NO)2PtCl6. This species is obtained by the reaction of nitrosyl chloride, NOCl, and Pt metal.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 A. E. Schweizer, G. T. Kerr (1978). "Thermal Decomposition of Hexachloroplatinic Acid". Inorg. Chem. 17 (8): 2326–2327. doi:10.1021/ic50186a067.
- ↑ Holleman, Wiberg (2001). Inorganic Chemistry (First ed.). New York: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ Greenwood, N.N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (Second ed.). New York: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-3365-9.
- ↑ George B. Kauffman; Thurner, Joseph J.; Zatko, David A. (1967). "Ammonium Hexachloroplatinate(IV)". Inorganic Syntheses 9: 182–185. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch51.
- ↑ Paul Rudnick and R. D. Cooke (1917). "The Preparation of Hydrochloroplatinic Acid by means of Hydrogen Peroxide". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 39 (4): 633–635. doi:10.1021/ja02249a011.
- ↑ G. F. Smith, J. L. Gring (1933). "The Separation and Determination of the Alkali Metals Using Perchloric Acid. V. Perchloric Acid and Chloroplatinic Acid in the Determination of Small Amounts of Potassium in the Presence of Large Amounts of Sodium". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55 (10): 3957–3961. doi:10.1021/ja01337a007.
- ↑ George B. Kauffman; Thurner, Joseph J.; Zatko, David A. (1967). "Ammonium Hexachloroplatinate(IV)". Inorganic Syntheses 9: 182–185. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch51.
- ↑ Cotton, S. A. Chemistry of Precious Metals, Chapman and Hall (London): 1997. ISBN 0-7514-0413-6.
- ↑ J. L. Speier, J. A. Webster, G. H. Barnes (1957). "The Addition of Silicon Hydrides to Olefinic Double Bonds. Part II. The Use of Group VIII Metal Catalysts". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (4): 974–979. doi:10.1021/ja01561a054.
- ↑ John C. Saam, John L. Speier (1958). "The Addition of Silicon Hydrides to Olefinic Double Bonds. Part III. The Addition to Non-terminal Olefins in the Presence of Chloroplatinic Acid". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80 (15): 4104–4106. doi:10.1021/ja01548a073.
- ↑ L. N. Lewis, K. G. Sy, G. L. Bryant and P. E. Donahue (1991). "Platinum-catalyzed hydrosilylation of alkynes". Organometallics 10 (10): 3750–3759. doi:10.1021/om00056a055.
- ↑ R. T. Moravek, G. B. Kauffman and T. Mahmood (1967). "Nitrosyl Hexachloroplatinate(IV)". Inorganic Syntheses 9: 217–220. doi:10.1002/9780470132555.ch63.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||