Charles Sylvester
| Charles Sylvester | |
|---|---|
 Bust in Derby Museum by Francis Chantrey | |
| Born | 1774 |
| Died | 1828 |
| Occupation | Chemist, Inventor |
Charles Sylvester (1774–1828) was a chemist and inventor born in Sheffield, United Kingdom. He worked on galvanization, public building heating and sanitation, and railroad friction amongst other things.
Biography
Sylvester was christened July 10, 1774 in Sheffield, in the West Riding of Yorkshire. He was the son of Joseph Sylvester and Sarah Mills who had been married in nearby Rotherham on March 5, 1767. It was thought for a time that Charles Sylvester was part of the Sylvester family from Norton, Derbyshre. His links to the Sylvesters in Sheffield and Rotherham have been well documented (genealogy). He married Sarah Dixon August 13, 1798, in Sheffield, three months before the birth of their son John. Sarah had two more boys and three girls, but John was the only boy to survive to adulthood. Sylvester experimented with coating iron and steel with zinc. The method patented by Sylvester and two others involved building a battery (galvanic cell) from the items that one wanted to plate with zinc, and then leaving the construction in seawater.[1]

In 1807 Sylvester moved to Derby where he worked with William Strutt who was building Derby's Royal Infirmary. Sylvester was instrumental in documenting a novel heating system for the new hospital. He published his ideas in The Philosophy of Domestic Economy; as exemplified in the mode of Warming, Ventilating, Washing, Drying, & Cooking, . . . in the Derbyshire General Infirmary in 1819. However the book is dedicated to Strutt, and Sylvester is careful to assign many of the inventions to Strutt, and to note that the heating designs installed in the new Infirmary had already been tried on Strutt and his friends' houses. Sylvester documented the new ways of heating hospitals that were included in the design, and the healthier features such as self-cleaning and air-refreshing toilets.[2] The toilets had a carefully designed door that would exchange the air for fresh as each user exited. The same door action also washed the basin.[2]
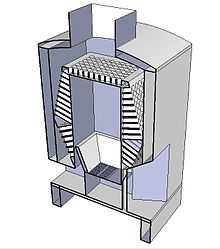
Sylvester described the infirmary's features including its fireproof construction, laundry and novel heating that allowed the patients to breathe fresh heated air whilst old air was channeled up to a glass and iron dome at the centre.[3] Sylvester described the advances that Strutt had made and this was successful in three ways. Sylvester was able to take the new ideas for heating and apply them in numerous other building projects.[2] The Derby Infirmary was seen as a leader in European architecture and architects and visiting royalty were brought to see its features. Finally Strutt was proposed to become a member of the Royal Society by five distinguished proposers which included Marc Isambard Brunel and James Watt.[3]
Sylvester with Strutt was a member of Erasmus Darwin's Derby Philosophical Society.[4]
Sylvester was commissioned by the Chairman of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway to advise them on the subject of the railroad and he wrote a Report on rail-roads and locomotive engines. Sylvester included a comparison between canals and railways. He observed that greater power will deliver more speed on a railroad, but on the canal the power required to increase speed varies by the square of the velocity.[5]
Sylvester's bust was modelled by Chantry and one copy of it is in Derby Museum and Art Gallery.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sylvester, Charles. |
- ↑ Zamenzadeh, Dr. Some Failure Analysis Case Histories in Galvanized Steel Products. Retrieved 19 August 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Sylvester, Charles (1819). The philosophy of domestic economy: as exemplified in the mode of warming ... p.48 et al.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Elliott, Paul (2000). "The Derbyshire General Infirmary and the Derby Philosophers: The Application of Industrial Architecture and Technology to Medical Institutions in Early-Nineteenth-Century England". Medical History 46: 65–92. PMC 1044459. PMID 11877984.
- ↑ R.P. Sturges. "The membership of Derby Philosophical Society" (PDF). Midland history. Birminghan University. pp. 215–223. Retrieved 2009-01-01.
- ↑ Sylvester, Charles (1825). Report on rail-roads and locomotive engines. p. 39.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||