Charge-exchange ionization
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Charge-exchange ionization (also known as charge-transfer ionization) is a gas phase reaction between an ion and an atom or molecule in which the charge of the ion is transferred to the neutral species.[1]
For example
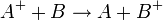 .
.
See also
References
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "charge-exchange ionization".
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.