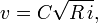Chézy formula
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics, the Chézy formula describes the mean flow velocity of steady, turbulent open channel flow:
where
 is the mean velocity [m/s],
is the mean velocity [m/s], is the Chézy coefficient [m½/s],
is the Chézy coefficient [m½/s], is the hydraulic radius (~ water depth) [m], and
is the hydraulic radius (~ water depth) [m], and is the bottom slope [m/m].
is the bottom slope [m/m].
The formula is named after Antoine de Chézy, the French hydraulics engineer who devised it in 1775.
Usage with Manning coefficient
This formula can also be used with Manning's Roughness Coefficient, instead of Chézy's coefficient. Manning derived[1] the following relation to C based upon experiments:
where
 is the Chézy coefficient [m½/s],
is the Chézy coefficient [m½/s], is the hydraulic radius (~ water depth) [m], and
is the hydraulic radius (~ water depth) [m], and is Manning's roughness coefficient.
is Manning's roughness coefficient.
Unlike the Manning equation, which is empirical, the Chézy equation is derived from hydrodynamics theory.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Manning, R., "On the flow of Water in Open Channels and Pipes." Transactions Institute of Civil Engineers of Ireland, vol. 20, pp 161-209, Dublin, 1891, Supplement, vol 24, pp. 179-207, 1895
- ↑ Martin & McCutcheon, 1999, Hydrodynamics and Transport, Lewis
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.