Cauxin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Cauxin is a peptidase that is excreted in large amounts in cat urine. Cauxine has been shown to hydrolyze 3-methylbutanol-cysteinylglycine (3-MBCG) in the urine into felinine which then slowly degrades into the putative cat pheromone 3-mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol (MMB).[1]
Cauxin protein from feline urine was reported in 2008 to act as a nucleator for struvite crystals, in an in vivo system containing magnesium, ammonium, and phosphate ions. [2] Thus, this protein may act as one cause for feline urinary stones.
Chemistry
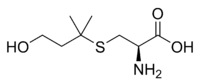 | → |
| Felinine | MMB |
See also
References
- ↑ M. Miyazaki, T. Yamashita, Y. Suzuki, Y. Saito, S. Soeta, H. Taira, and A. Suzuki (October 2006). "A major urinary protein of the domestic cat regulates the production of felinine, a putative pheromone precursor" (pdf). Chem. Biol. 13 (10): 1071–1079. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.08.013. PMID 17052611.
- ↑ Cauxin from feline urine as nucleator for struvite
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.