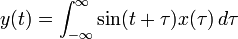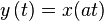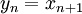Causal system
A causal system (also known as a physical or nonanticipative system) is a system where the output depends on past and
current inputs but not future inputs i.e. the output 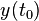 only depends on the input
only depends on the input  for values of
for values of 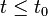 .
.
The idea that the output of a function at any time depends only on past and present values of input is defined by the property commonly referred to as causality. A system that has some dependence on input values from the future (in addition to possible dependence on past or current input values) is termed a non-causal or acausal system, and a system that depends solely on future input values is an anticausal system. Note that some authors have defined an anticausal system as one that depends solely on future and present input values or, more simply, as a system that does not depend on past input values.
Classically, nature or physical reality has been considered to be a causal system. Physics involving special relativity or general relativity require more careful definitions of causality, as described elaborately in causality (physics).
The causality of systems also plays an important role in digital signal processing, where filters are constructed so that they are causal, sometimes by altering a non-causal formulation to remove the lack of causality so that it is realizable. For more information, see causal filter. For a causal system, the impulse response of the system must be 0 for all  . That is the sole necessary as well as sufficient condition for causality of a system, linear or non-linear. Note that similar rules apply to either discrete or continuous cases.
. That is the sole necessary as well as sufficient condition for causality of a system, linear or non-linear. Note that similar rules apply to either discrete or continuous cases.
Mathematical definitions
Definition 1: A system mapping  to
to  is causal if and only if, for any pair of input signals
is causal if and only if, for any pair of input signals  and
and  such that
such that
the corresponding outputs satisfy
Definition 2: Suppose  is the impulse response of the system
is the impulse response of the system 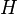 . (only fully accurate for a system described by linear constant coefficient differential equation). The system
. (only fully accurate for a system described by linear constant coefficient differential equation). The system 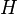 is causal if and only if
is causal if and only if
otherwise it is non-causal.
Examples
The following examples are for systems with an input  and output
and output  .
.
Examples of causal systems
- Memoryless system
- Autoregressive filter
Examples of non-causal (acausal) systems
- Central moving average
- For coefficients of t
Examples of anti-causal systems
- Look-ahead
References
- Oppenheim, Alan V.; Willsky, Alan S.; Nawab, Hamid; with S. Hamid (1998). Signals and Systems. Pearson Education. ISBN 0-13-814757-4.