Causal model
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A causal model is an abstract model that describes the causal mechanisms of a system. The model must express more than correlation because correlation does not imply causation.
Judea Pearl defines a causal model as an ordered triple 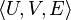 , where U is a set of exogenous variables whose values are determined by factors outside the model; V is a set of endogenous variables whose values are determined by factors within the model; and E is a set of structural equations that express the value of each endogenous variable as a function of the values of the other variables in U and V.[1]
, where U is a set of exogenous variables whose values are determined by factors outside the model; V is a set of endogenous variables whose values are determined by factors within the model; and E is a set of structural equations that express the value of each endogenous variable as a function of the values of the other variables in U and V.[1]
Further reading
- Greenland, S.; Brumback, B. (2002). "An overview of relations among causal modelling methods". International Journal of Epidemiology 31 (5): 1030–1037. doi:10.1093/ije/31.5.1030. PMID 12435780.
See also
- Causal diagram – representing causal relations with diagrams
- Causal network – a Bayesian network with an explicit requirement that the relationships be causal
- Structural equation modeling – a statistical technique for testing and estimating causal relations
External links
References
- ↑ Pearl, Judea (2000). Causality: Models, Reasoning, and Inference, Cambridge University Press.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.