Cationic polymerization
Cationic polymerization is a type of chain growth polymerization in which a cationic initiator transfers charge to a monomer which becomes reactive. This reactive monomer goes on to react similarly with other monomers to form a polymer.[1][2] Poly(isobutylene) used in inner tubes is the only polymer being commercially produced via cationic polymerization. The types of monomers necessary for cationic polymerization are limited to olefins with electron-donating substituents and heterocycles. Similar to anionic polymerization reactions, cationic polymerization reactions are very sensitive to the type of solvent used. Specifically, the ability of a solvent to form free ions will dictate the reactivity of the propagating cationic chain. Cationic polymerization is used in the production of polyisobutylene and poly(N-vinylcarbazole) (PVK).[3]
Monomers
Monomer scope for cationic polymerization is limited to two main types: olefins and heterocyclic monomers. Cationic polymerization of both types of monomers occurs only if the overall reaction is thermally favorable. In the case of olefins, this is due to isomerization of the monomer double bond; for heterocycles, this is due to release of monomer ring strain and, in some cases, isomerization of repeating units. Monomers for cationic polymerization are nucleophilic and form a stable cation upon polymerization.[5]
Olefins
Cationic polymerization of olefin monomers occurs with olefins that contain electron-donating substituents. These electron-donating groups make the olefin nucleophilic enough to attack electrophilic initiators or growing polymer chains. At the same time, these electron-donating groups attached to the monomer must be able to stabilize the resulting cationic charge for further polymerization. Some reactive olefin monomers are shown below in order of decreasing reactivity, with heteroatom groups being more reactive than alkyl or aryl groups. Note, however, that the reactivity of the carbenium ion formed is the opposite of the monomer reactivity.[5]
Heterocyclic monomers

Heterocyclic monomers that are cationically polymerized are lactones, lactams, and cyclic amines. Upon addition of an initiator, cyclic monomers go on to form linear polymers. The reactivity of heterocyclic monomers depends on their ring strain. Monomers with large ring strain, such as oxirane, are more reactive than 1,3-dioxepane which has considerably less ring strain. Rings that are six-membered and larger are less likely to polymerize due to lower ring strain.[6]
Synthesis
Initiation
Initiation is the first step in cationic polymerization. During initiation, a carbenium ion is generated from which the polymer chain is made. The counterion should be non-nucleophilic, otherwise the reaction is terminated instantaneously. There are a variety of initiators available for cationic polymerization, and some of them require a coinitiator to generate the needed cationic species.[7]
Classical protonic acids
Strong protic acids can be used to form a cationic initiating species. High concentrations of the acid are needed in order to produce sufficient quantities of the cationic species. The counterion (A–) produced must be weakly nucleophilic so as to prevent early termination due to combination with the protonated olefin.[5] Common acids used are phosphoric, sulfuric, fluro-, and triflic acids. Only low molecular weight polymers are formed with these initiators.[1]
Lewis acids/Friedel-Crafts catalysts
Lewis acids are the most common compounds used for initiation of cationic polymerization. The more popular Lewis acids are SnCl4, AlCl3, BF3, and TiCl4. Although these Lewis acids alone are able to induce polymerization, the reaction occurs much faster with a suitable cation source. The cation source can be water, alcohols, or even a carbocation donor such as an ester or an anhydride. In these systems the Lewis acid is referred to as a coinitiator while the cation source is the initiator. Upon reaction of the initiator with the coinitiator, an intermediate complex is formed which then goes on to react with the monomer unit. The counterion produced by the initiator-coinitiator complex is less nucleophilic than that of the Brønsted acid A– counterion. Halogens, such as chlorine and bromine, can also initiate cationic polymerization upon addition of the more active Lewis acids.[1]
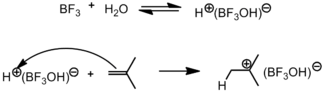
Carbenium ion salts
Stable carbenium ions are used to initiate chain growth of only the most reactive olefins and are known to give well defined structures. These initiators are most often used in kinetic studies due to the ease of being able to measure the disappearance of the carbenium ion absorbance. Common carbenium ions are trityl and tropylium cations.[5]
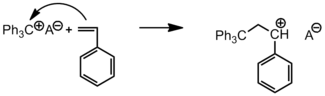
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation can form a radical-cation pair that can then react with a monomer to start cationic polymerization. Control of the radical-cation pairs are difficult and often depend on the monomer and reaction conditions. Formation of radical and anionic species are often observed.[5]
Propagation
Propagation proceeds via addition of monomer to the active species, i.e. the carbenium ion. The monomer is added to the growing chain in a head-to-tail fashion; in the process, the cationic end group is regenerated to allow for the next round of monomer addition.[6]
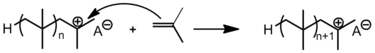
Effect of temperature
The temperature of the reaction has an effect on the rate of propagation. The overall activation energy for the polymerization (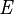 ) is based upon the activation energies for the initiation (
) is based upon the activation energies for the initiation (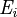 ), propagation (
), propagation (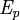 ), and termination (
), and termination ( ) steps:
) steps:
Generally, 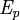 is less than
is less than 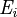 and
and  , meaning the overall activation energy is negative. When this is the case, a decrease in temperature leads to an increase in the rate of propagation. The converse is true when the overall activation energy is positive.[6]
, meaning the overall activation energy is negative. When this is the case, a decrease in temperature leads to an increase in the rate of propagation. The converse is true when the overall activation energy is positive.[6]
Chain length is also affected by temperature. Low reaction temperatures, in the range of 170–190 K, are preferred for producing longer chains.[6] This comes as a result of the activation energy for termination and other side reactions being larger than the activation energy for propagation.[5][6] As the temperature is raised, the energy barrier for the termination reaction is overcome, causing shorter chains to be produced during the polymerization process.[6]
Effect of solvent and counterion
The solvent and the counterion (the gegen ion) have a significant effect on the rate of propagation. The counterion and the carbenium ion can have different associations, ranging from a covalent bond, tight ion pair (unseparated), solvent-separated ion pair (partially separated), and free ions (completely dissociated).[1][6]

The association is strongest as a covalent bond and weakest when the pair exists as free ions.[6] In cationic polymerization, the ions tend to be in equilibrium between an ion pair (either tight or solvent-separated) and free ions.[1] The more polar the solvent used in the reaction, the better the solvation and separation of the ions. Since free ions are more reactive than ion pairs, the rate of propagation is faster in more polar solvents.[6][8]
The size of the counterion is also a factor. A smaller counterion, with a higher charge density, will have stronger electrostatic interactions with the carbenium ion than will a larger counterion which has a lower charge density.[1] Further, a smaller counterion is more easily solvated by a polar solvent than a counterion with low charge density. The result is increased propagation rate with increased solvating capability of the solvent.[6]
Termination
Termination generally occurs via unimolecular rearrangement with the counterion. In this process, an anionic fragment of the counterion combines with the propagating chain end. This not only inactivates the growing chain, but it also terminates the kinetic chain by reducing the concentration of the initiator-coinitiator complex.[1][6]

Chain transfer
Chain transfer can take place in two ways. One method of chain transfer is hydrogen abstraction from the active chain end to the counterion.[6][8][9] In this process, the growing chain is terminated, but the initiator-coinitiator complex is regenerated to initiate more chains.[5][6]

The second method involves hydrogen abstraction from the active chain end to the monomer. This terminates the growing chain and also forms a new active carbenium ion-counterion complex which can continue to propagate, thus keeping the kinetic chain intact.[6]

Cationic ring-opening polymerization
Cationic ring-opening polymerization follows the same mechanistic steps of initiation, propagation, and termination. However, in this polymerization reaction, the monomer units are cyclic in comparison to the resulting polymer chains which are linear. The linear polymers produced can have low ceiling temperatures, hence end-capping of the polymer chains is often necessary to prevent depolymerization.[6]
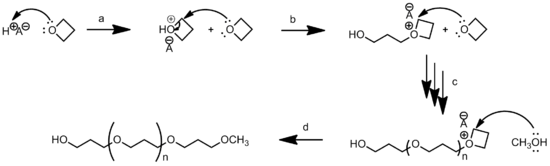
Kinetics
The rate of propagation and the degree of polymerization can be determined from an analysis of the kinetics of the polymerization. The reaction equations for initiation, propagation, termination, and chain transfer can be written in a general form:
In which I+ is the initiator, M is the monomer, M+ is the propagating center, and 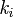 ,
,  ,
, 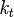 , and
, and 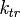 are the rate constants for initiation, propagation, termination, and chain transfer, respectively.[5][6][10] For simplicity, counterions are not shown in the above reaction equations and only chain transfer to monomer is considered. The resulting rate equations are as follows, where brackets denote concentrations:
are the rate constants for initiation, propagation, termination, and chain transfer, respectively.[5][6][10] For simplicity, counterions are not shown in the above reaction equations and only chain transfer to monomer is considered. The resulting rate equations are as follows, where brackets denote concentrations:
Assuming steady-state conditions, i.e. the rate of initiation = rate of termination:[6][10]
This equation for [M+] can then be used in the equation for the rate of propagation:[6][10]
From this equation, it is seen that propagation rate increases with increasing monomer and initiator concentration.
The degree of polymerization,  , can be determined from the rates of propagation and termination:[6][10]
, can be determined from the rates of propagation and termination:[6][10]
If chain transfer rather than termination is dominant, the equation for  becomes[6][10]
becomes[6][10]
Living polymerization
In 1984, Higashimura and Sawamoto reported the first living cationic polymerization for alkyl vinyl ethers. This type of polymerization has allowed for the control of well-defined polymers. A key characteristic of living cationic polymerization is that termination is essentially eliminated, thus the cationic chain growth continues until all monomer is consumed.[11]
Commercial applications
The largest commercial application of cationic polymerization is in the production of polyisobutylene (PIB) products which include polybutene and butyl rubber. These polymers have a variety of applications from adhesives and sealants to protective gloves and pharmaceutical stoppers. The reaction conditions for the synthesis of each type of isobutylene product vary depending on the desired molecular weight and what type(s) of monomer(s) is used. The conditions most commonly used to form low molecular weight (5–10 x 104 Da) polyisobutylene are initiation with AlCl3, BF3, or TiCl4 at a temperature range of −40 to 10 °C.[1] These low molecular weight polyisobutylene polymers are used for caulking and as sealants.[1] High molecular weight PIBs are synthesized at much lower temperatures of −100 to −90 °C and in a polar medium of methylene chloride.[5] These polymers are used to make uncrosslinked rubber products and are additives for certain thermoplasts. Another characteristic of high molecular weight PIB is its low toxicity which allows it to be used as a base for chewing gum. The main chemical companies that produce polyisobutylene are Esso, ExxonMobil, and BASF.[12]

Butyl rubber, in contrast to PIB, is a copolymer in which the monomers isobutylene (~98%) and isoprene (2%) are polymerized in a process similar to high molecular weight PIBs. Butyl rubber polymerization is carried out as a continuous process with AlCl3 as the initiator. Its low gas permeability and good resistance to chemicals and aging make it useful for a variety of applications such as protective gloves, electrical cable insulation, and even basketballs. Large scale production of butyl rubber started during World War II, and roughly 1 billion pounds/year are produced in the U.S. today.[1]
Polybutene is another copolymer, containing roughly 80% isobutylene and 20% other butenes (usually 1-butene). The production of these low molecular weight polymers (300–2500 Da) is done within a large range of temperatures (−45 to 80 °C) with AlCl3 or BF3. Depending on the molecular weight of these polymers, they can be used as adhesives, sealants, plasticizers, additives for transmission fluids, and a variety of other applications. These materials are low-cost and are made by a variety of different companies including BP Chemicals, Esso, and BASF.[5]
Other polymers formed by cationic polymerization are homopolymers and copolymers of polyterpenes, such as pinenes (plant-derived products), that are used as tackyfiers. In the field of heterocycles, 1,3,5-trioxane is copolymerized with small amounts of ethylene oxide to form the highly crystalline polyoxymethylene plastic. Also, the homopolymerization of alkyl vinyl ethers is achieved only by cationic polymerization.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 Odian, George (2004). Principles of Polymerization (4th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-27400-1.
- ↑ Mark, Herman F.; Bikales, Norbert; Overberger, Charles G.; Menges, Georg; Kroschwitz, Jacqueline I. (1990). Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Engineering (2nd ed.). Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-80950-0.
- ↑ Robello, Douglas R. (2002). "Chem 421: Introduction to Polymer Chemistry – Cationic Polymerization". Department of Chemistry, University of Rochester. Retrieved 20 March 2011.
- ↑ Jenkins, A. D.; Kratochvíl, P.; Stepto, R. F. T.; Suter, U. W. (1996). "Glossary of basic terms in polymer science (IUPAC Recommendations 1996)". Pure and Applied Chemistry 68 (12): 2287–2311. doi:10.1351/pac199668122287.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 Matyjaszewski, Krzysztof (1996). Cationic Polymerizations: Mechanisms, Synthesis, and Applications. New York, New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc. ISBN 978-0-8247-9463-7.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 6.17 6.18 6.19 Cowie, John M. G.; Arrighi, Valeria (2008). Polymers Chemistry and Physics of Modern Materials (3rd ed.). Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-8493-9813-1.
- ↑ Kennedy, J. P.; Marechal, E. (1981). "Chemistry of Initiation in Carbocationic Polymerization". Journal of Polymer Science: Macromolecular Reviews 16: 123–198. doi:10.1002/pol.1981.230160103.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Raave, A. (2000). Principles of Polymer Chemistry (2nd ed.). New York, New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers. ISBN 978-0-306-46368-6.
- ↑ Fahlman, Bradley D. (2008). Materials Chemistry. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-6119-6.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Ebewele, Robert Oboigbaotor (2000). Polymer Science and Technology. Boca Ration, FL: Chapman & Hall/CRC Press LLC. ISBN 978-0-8493-8939-9.
- ↑ Sawamoto, M. (1991). "Modern Cationic Vinyl Polymerization". Progress in Polymer Science 16: 111–172. doi:10.1016/0079-6700(91)90008-9.
- ↑ Chanda, Manas; Roy, Salil K. (2007). Plastics Technology Handbook: Plastics Engineering Series (4th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CSC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-7039-7.
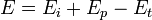
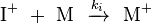
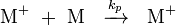
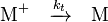
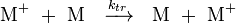
![\textstyle {\text{rate(initiation)}}=k_{i}[{\text{I}}^{+}][{\text{M}}]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/9/7/1/3/97130f04c67e3e991e98b915c224324a.png)
![\textstyle {\text{rate(propagation)}}=k_{p}[{\text{M}}^{+}][{\text{M}}]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/2/c/e/f2ced6f50d3e7d0800c645f6ac762b33.png)
![\textstyle {\text{rate(termination)}}=k_{t}[{\text{M}}^{+}]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/e/5/a/6/e5a6544d483e2d7650ea087bddc69483.png)
![\textstyle {\text{rate(chain transfer)}}=k_{{tr}}[{\text{M}}^{+}][{\text{M}}]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/8/5/f/585fb3a14ef4e059340f8307d65ae875.png)
![[{\text{M}}^{+}]={k_{i}[{\text{I}}^{+}][{\text{M}}] \over k_{t}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/e/c/3/5ec38efe394bff68013bc99e890baa36.png)
![{\text{rate(propagation)}}={k_{p}k_{i}[{\text{M}}]^{2}[{\text{I}}^{+}] \over k_{t}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/c/a/b/ccab8a4675bb0f3713e81a6bb3201ed6.png)
![Xn={{\text{rate(propagation)}} \over {\text{rate(termination)}}}={k_{p}[{\text{M}}] \over k_{t}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/4/d/d/a4ddc443fda0150a67009a12b4af1d67.png)
