Flavan-3-ol



Flavan-3-ols (sometimes referred to as flavanols) are derivatives of flavans that use the 2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-ol skeleton. These compounds include the catechin, epicatechin gallate, epigallocatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, proanthocyanidins, theaflavins, thearubigins.
Flavanols (with an "a") are not to be confused with flavonols (with an "o"), a class of flavonoids containing a ketone group.
The single-molecule (monomer) catechin, or isomer epicatechin (see diagram), adds four hydroxyls to flavan-3-ol, making building blocks for concatenated polymers (proanthocyanidins) and higher order polymers (anthocyanidins).[1]
Flavanols possess two chiral carbons, meaning four diastereoisomers occur for each of them.
Catechins are distinguished from the yellow, ketone-containing flavonoids such as quercitin and rutin, which are called flavonols. Early use of the term bioflavonoid was imprecisely applied to include the flavanols, which are distinguished by absence of ketone(s). Catechin monomers, dimers, and trimers (oligomers) are colorless. Higher order polymers, anthocyanidins, exhibit deepening reds and become tannins.[1]
Sources of catechins
The catechins are abundant in teas derived from the tea plant Camellia sinensis, as well as in some cocoas and chocolates[2] (made from the seeds of Theobroma cacao).
Catechins are also present in the human diet in fruits, vegetables and wine,[3] and are found in many other plant species, as well as cocoa.[4][5]
Catechin and the gallates
Catechin and epicatechin are epimers, with (-)-epicatechin and (+)-catechin being the most common optical isomers found in nature. Catechin was first isolated from the plant extract catechu, from which it derives its name. Heating catechin past its point of decomposition releases pyrocatechol (also called catechol), which explains the common origin of the names of these compounds.
Epigallocatechin and gallocatechin contain an additional phenolic hydroxyl group when compared to epicatechin and catechin, respectively, similar to the difference in pyrogallol compared to pyrocatechol.
Catechin gallates are gallic acid esters of the catechins; an example is epigallocatechin gallate, which is commonly the most abundant catechin in tea.
Biosynthesis of (-)-epicatechin
The flavonoids are products from a cinnamoyl-CoA starter unit, with chain extension using three molecules of malonyl-CoA. Reactions are catalyzed by a type III PKS enzyme. These enzyme do not use ACPSs, but instead employ coenzyme A esters and have a single active site to perform the necessary series of reactions, e.g. chain extension, condensation, and cyclization. Chain extension of 4-hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA with three molecules of malonyl-CoA gives initially a polyketide (Figure 1), which can be folded. These allow Claisen-like reactions to occur, generating aromatic rings.[6][7]

Figure 1:Schematic overview of the flavan-3-ol (-)-epicatechin biosynthesis in plants: Enzymes are indicated in blue, abbreviated as follows: E1, phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), E2, tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL), E3, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase, E4, 4-coumaroyl: CoA-ligase, E5, chalcone synthase (naringenin-chalcone synthase), E6, chalcone isomerase, E7, Flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase, E8, flavonone 3-hydroxylase, E9, dihydroflavanol 4-reductase, E10, anthocyanidin synthase (leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase), E11, anthocyanidin reductase. HSCoA, Coenzyme A. L-Tyr, L-tyrosine, L-Phe, L-phenylalanine.
Potential health effects of catechins
The health benefits of catechins have been studied extensively in humans and animal models. Reduction in atherosclerotic plaques was seen in animal models.[8] Reduction in carcinogenesis was seen in vitro.[9]
Many studies on health benefits have been linked to the catechin content. According to Norman Hollenberg, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, epicatechin can reduce the risk of four of the major health problems: stroke, heart failure, cancer and diabetes. He studied the Kuna people in Panama, who drink up to 40 cups of cocoa a week, and found the prevalence of the “big four” is less than 10%. He believes epicatechin should be considered essential to the diet and thus classed as a vitamin.[10][11][12]
According to one researcher[13] epigallocatechin-3-gallate as an antioxidant helps protect the skin from UV radiation-induced damage and tumor formation.
DNA protection
Catechins, when combined with habitual exercise, have been shown to delay some forms of aging. Mice fed catechins showed decreased levels of aging, lowering of oxidative stress in mitochondria, and an increase in mRNA transcription of mitochondrial-related proteins.[14]
Possible reduced benefits in treated chocolate
An editorial in The Lancet warned against increasing one’s intake of dark chocolate to improve health because the beneficial compounds are sometimes removed due to their bitter taste without an indication on the label.[15] Additionally, such product may be high in fat, sugar, and calories, which can increase the risk for heart disease.
Anticarcinogenic effects
In 2008, UCLA cancer researchers found the study participants who ate foods containing certain flavonoids seemed to be protected from developing lung cancer. Dr. Zhang, (professor of public health and epidemiology at the UCLA School of Public Health) said the flavonoids that appeared to be the most protective included catechin, found in strawberries and green and black teas; kaempferol, found in Brussels sprouts and apples; and quercetin, found in beans, onions (particularly red) and apples.[16] More than 38 different clinical trials conducted on mice, hamsters, monkeys and rats have shown catechins to reduce cancerous biomarkers.[17]
Liver damage effects
In a study of 85 patients with liver injuries linked to herbal pills and powders, green tea extract can have very high doses of catechins (which can be toxic to the liver), and "a small percentage of people appear to be particularly susceptible". Dec 26, 2013 NY Times article.
Other possible health effects
Flavanols, usually from cocoa beans or tea, are believed to keep arteries flexible,[18] increase small vessel circulation,[19] reduce blood pressure[20] and protect against sunburns.[21][22] None of these effects, however, has been adequately proven by rigorous science and clinical trials.
Aglycones
| Image | Name | Formula | Oligomers |
|---|---|---|---|
/-/(%2B)-Catechin.png) | Catechin, C, (+)-Catechin | C15H14O6 | Proanthocyanidins |
 | Epicatechin, EC, (-)-Epicatechin (cis) | C15H14O6 | Proanthocyanidins |
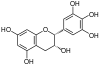 | Epigallocatechin, EGC | C15H14O7 | Prodelphinidins |
 | Epicatechin gallate, ECG | C22H18O10 | |
 | Epigallocatechin gallate, EGCG, (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate | C22H18O11 | |
 | Epiafzelechin | C15H14O5 | |
| | Fisetinidol | C15H14O5 | |
 | Guibourtinidol | C15H14O4 | Proguibourtinidins |
| | Mesquitol | C15H14O6 | |
 | Robinetinidol | C15H14O6 | Prorobinetinidins |
Analysis
Fluorescence-lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) can be used to detect flavanols in plant cells[23]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 OPC in Practice, 1995 3rd Edition, by Bert Schwitters in collaboration with Prof. Jack Masquelier.
- ↑ Hammerstone JF, Lazarus SA, Schmitz HH (August 2000). "Procyanidin content and variation in some commonly consumed foods". J. Nutr. 130 (8S Suppl): 2086S–92S. PMID 10917927.
- ↑ Ruidavets J, Teissedre P, Ferrières J, Carando S, Bougard G, Cabanis J (November 2000). "Catechin in the Mediterranean diet: vegetable, fruit or wine?". Atherosclerosis 153 (1): 107–17. doi:10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00377-4. PMID 11058705.
- ↑ BBC News | Health | Chocolate 'has health benefits'
- ↑ Mabry, Helga; Harborne, J. B.; Mabry, T. J. (1975). The Flavonoids. London: Chapman and Hall. ISBN 0-412-11960-9.
- ↑ Dewick, Paul M.Medicinal Natural Products: a biosynthetic approach. 3rd ed. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2009, p. 168.
- ↑ Winkel-Shirley, Brenda.Flavonoid Biosynthesis. A Colorful Model for Genetics, Biochemistry, Cell Biology, and Biotechnology. Plant Physiol. Vol. 126, 2001, p. 485-493.
- ↑ Chyu KY; Babbidge, SM; Zhao, X; Dandillaya, R; Rietveld, AG; Yano, J; Dimayuga, P; Cercek, B; Shah, PK (May 2004). "Differential effects of green tea-derived catechin on developing versus established atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice". Circulation 109 (20): 2448–53. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000128034.70732.C2. PMID 15136500.
- ↑ Mittal A, Pate MS, Wylie RC, Tollefsbol TO, Katiyar SK (March 2004). "EGCG down-regulates telomerase in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells, leading to suppression of cell viability and induction of apoptosis". Int. J. Oncol. 24 (3): 703–10. PMID 14767556.
- ↑ BBC news: Cocoa nutrient for lethal ills
- ↑ Science Daily March 12, 2007.
- ↑ Int J Med Sci 2007; 4:53-58
- ↑ Katiyar S, Elmets CA, Katiyar SK (May 2007). "Green tea and skin cancer: photo-immunology, angiogenesis and DNA repair". J. Nutr. Biochem. 18 (5): 287–96. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2006.08.004. PMID 17049833.
- ↑ Murase T, Haramizu S, Ota N, Hase T (July 2008). "Tea catechin ingestion combined with habitual exercise suppresses the aging-associated decline in physical performance in senescence-accelerated mice". Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 295 (1): R281–9. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00880.2007. PMID 18480242.
- ↑ The Lancet (22 December 2007). "The devil in the dark chocolate". The Lancet 370 (9605): 2070. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61873-X. PMID 18156011. Retrieved August 16, 2009.
- ↑ UCLA news 2008 - Fruits, vegetables, teas may protect smokers from lung cancer
- ↑ Bechtel, Jonathan. "Green Tea: Health Benefits, Catechins, and Cancer Prevention". Health Kismet. Retrieved 19 January 2012.
- ↑ Harvard Health newsletter on CocoaVia
- ↑ doi:10.1007/s00394-006-0627-6 PMID 17164979
- ↑ Taubert D, Roesen R, Lehmann C, Jung N, Schömig E (July 2007). "Effects of low habitual cocoa intake on blood pressure and bioactive nitric oxide: a randomized controlled trial". JAMA 298 (1): 49–60. doi:10.1001/jama.298.1.49. PMID 17609490.
- ↑ Williams S, Tamburic S, Lally C (September 2009). "Eating chocolate can significantly protect the skin from UV light". J Cosmet Dermatol 8 (3): 169–73. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2009.00448.x. PMID 19735513.
- ↑ Heinrich U, Neukam K, Tronnier H, Sies H, Stahl W (June 2006). "Long-term ingestion of high flavanol cocoa provides photoprotection against UV-induced erythema and improves skin condition in women". J. Nutr. 136 (6): 1565–9. PMID 16702322.
- ↑ Mueller-Harvey I., Feucht W., Polster J., Trnková L., Burgos P., Parker A.W., Botchway S.W. Two-photon excitation with pico-second fluorescence lifetime imaging to detect nuclear association of flavanols. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 719, 68-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.068
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||