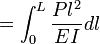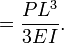Castigliano's method
Castigliano's method, named for Carlo Alberto Castigliano, is a method for determining the displacements of a linear-elastic system based on the partial derivatives of the Energy principle structures, he is known for his two theorems. The basic concept may be easy to understand by recalling that a change in energy is equal to the causing force times the resulting displacement. Therefore, the causing force is equal to the change in energy divided by the resulting displacement. Alternatively, the resulting displacement is equal to the change in energy divided by the causing force. Partial derivatives are needed to relate causing forces and resulting displacements to the change in energy.
- Castigliano's first theorem – for forces in an elastic structure
Castigliano's method for calculating forces is an application of his first theorem, which states:
- If the strain energy of an elastic structure can be expressed as a function of generalised displacement qi; then the partial derivative of the strain energy with respect to generalised displacement gives the generalised force Qi.
In equation form,
where U is the strain energy.
- Castigliano's second theorem – for displacements in a linearly elastic structure.
Castigliano's method for calculating displacements is an application of his second theorem, which states:
- If the strain energy of a linearly elastic structure can be expressed as a function of generalised force Qi; then the partial derivative of the strain energy with respect to generalised force gives the generalised displacement qi in the direction of Qi.
As above this can also be expressed as:
Examples
For a thin, straight cantilever beam with a load P at the end, the displacement  at the end can be found by Castigliano's second theorem :
at the end can be found by Castigliano's second theorem :
where E is Young's Modulus and I is the second moment of area of the cross-section, and M(l)=P x l is the expression for the internal moment at a point at distance l from the end, therefore:
The result is the standard formula given for cantilever beams under end loads.
External links
- Carlo Alberto Castigliano
- Castigliano's theorems module of Wikibooks
- Castigliano's method: some examples – German language page
- Castigliano's method: some examples – Google's translation of the above German language page
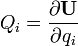
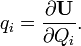
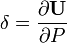
![\delta ={\frac {\partial }{\partial P}}\int _{0}^{L}{{\frac {[M(l)]^{2}}{2EI}}dl}={\frac {\partial }{\partial P}}\int _{0}^{L}{{\frac {[Pl]^{2}}{2EI}}dl}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/a/5/c/5a5cede5ea42f0a1890247294064fc4a.png)