Carpacin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Carpacin | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
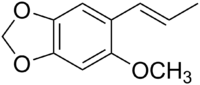
| IUPAC name (E)-2-Methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxypropenylbenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 194605-01-1 |
| PubChem | 5281763 |
| ChemSpider | 4445077 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 Image 2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C11H12O3 |
| Molar mass | 192.21 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Carpacin is a naturally occurring organic compound first isolated from the Carpano tree (Cinnamomum sp.), from which it derives its name. It is related to the lignan carpanone.[1] Carpacin is classified as a phenylpropanoid.
Carpacin has been prepared synthetically from sesamol[2] and has been studied for potential use as an insecticide,[3] an antidepressant, and an inhibitor of carcinogenesis.[2]
References
- ↑ J. Mohandas, M. Slaytor, T.R. Watson (1969). "Trans-2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxypropenylbenzene (carpacin) from a Cinnamomum sp. from Bougainville". Aust. J. Chem. 22 (8): 1803–1804. doi:10.1071/CH9691803.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Tsui-Hwa Tseng, Yen-Min Tsheng, Yean-Jang Lee, Hsing-Ling Hsu (2000). "Total Synthesis of Carpacin and Its Geometric Isomer as a Cancer Chemopreventer". Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 47: 1165–1169.
- ↑ BH Alexander, SI Gertler, RT Brown, TA Oda, M Beroza (1959). "Synthesis of Methylenedioxyphenyl Compounds from Isosafrole and Sesamol". J. Org. Chem. 24 (10): 1504. doi:10.1021/jo01092a029.
| |||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.