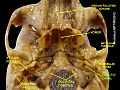
Carotid canal
| Carotid canal | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Left temporal bone. Inferior surface. ("Opening of carotid canal" labeled at center left.) | |
| Latin | canalis caroticus |
| Gray's | p.143 |
The carotid canal is the passage way in the temporal bone through which the internal carotid artery enters the middle cranial fossa from the neck. The canal starts on the inferior surface of the temporal bone at the external opening of the carotid canal (also referred to as the carotid foramen). The canal ascends at first vertically, and then, making a bend, runs horizontally forward and medialward. The canal's internal opening is near the foramen lacerum above which the internal carotid artery passes on its way to the cavernous sinus.
Contents
It transmits into the cranium, the internal carotid artery, and the carotid plexus of nerves.
Sympathetics to the head from the superior cervical ganglion also pass through the carotid canal. They have several motor functions: raise the eyelid (superior tarsal muscle), dilate pupil, innervate sweat glands of face and scalp and constricts blood vessels in head.
Additional images
-
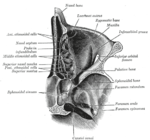
Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities.
-

Coronal section of right temporal bone.
-
Carotid canal.
External links
- n3a8p1 at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 34257.000-1
- Photo at Winona.edu
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||