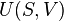Carnot cycle
| Thermodynamics | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||
|
Branches |
||||||||||||||
|
History / Culture
|
||||||||||||||
The Carnot cycle is a theoretical thermodynamic cycle proposed by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot in 1823 and expanded by in the 1830s and 1840s. It can be shown that it is the most efficient cycle for converting a given amount of thermal energy into work, or conversely, creating a temperature difference (e.g. refrigeration) by doing a given amount of work.
Every single thermodynamic system exists in a particular state. When a system is taken through a series of different states and finally returned to its initial state, a thermodynamic cycle is said to have occurred. In the process of going through this cycle, the system may perform work on its surroundings, thereby acting as a heat engine. A system undergoing a Carnot cycle is called a Carnot heat engine, although such a "perfect" engine is only a theoretical limit and cannot be built in practice.[citation needed]
Stages of the Carnot Cycle
The Carnot cycle when acting as a heat engine consists of the following steps:
- Reversible isothermal expansion of the gas at the "hot" temperature, T1 (isothermal heat addition or absorption). During this step (1 to 2 on Figure 1, A to B in Figure 2) the gas is allowed to expand and it does work on the surroundings. The temperature of the gas does not change during the process, and thus the expansion is isothermal. The gas expansion is propelled by absorption of heat energy Q1 and of entropy
 from the high temperature reservoir.
from the high temperature reservoir. - Isentropic (reversible adiabatic) expansion of the gas (isentropic work output). For this step (2 to 3 on Figure 1, B to C in Figure 2) the mechanisms of the engine are assumed to be thermally insulated, thus they neither gain nor lose heat. The gas continues to expand, doing work on the surroundings, and losing an equivalent amount of internal energy. The gas expansion causes it to cool to the "cold" temperature, T2. The entropy remains unchanged.
- Reversible isothermal compression of the gas at the "cold" temperature, T2. (isothermal heat rejection) (3 to 4 on Figure 1, C to D on Figure 2) Now the surroundings do work on the gas, causing an amount of heat energy Q2 and of entropy
 to flow out of the gas to the low temperature reservoir. (This is the same amount of entropy absorbed in step 1, as can be seen from the Clausius inequality.)
to flow out of the gas to the low temperature reservoir. (This is the same amount of entropy absorbed in step 1, as can be seen from the Clausius inequality.) - Isentropic compression of the gas (isentropic work input). (4 to 1 on Figure 1, D to A on Figure 2) Once again the mechanisms of the engine are assumed to be thermally insulated. During this step, the surroundings do work on the gas, increasing its internal energy and compressing it, causing the temperature to rise to T1. The entropy remains unchanged. At this point the gas is in the same state as at the start of step 1.
The pressure-volume graph

When the Carnot cycle is plotted on a pressure volume diagram, the isothermal stages follow the isotherm lines for the working fluid, adiabatic stages move between isotherms and the area bounded by the complete cycle path represents the total work that can be done during one cycle.
Properties and significance
The temperature-entropy diagram


The behaviour of a Carnot engine or refrigerator is best understood by using a temperature-entropy diagram (TS diagram), in which the thermodynamic state is specified by a point on a graph with entropy (S) as the horizontal axis and temperature (T) as the vertical axis. For a simple system with a fixed number of particles, any point on the graph will represent a particular state of the system. A thermodynamic process will consist of a curve connecting an initial state (A) and a final state (B). The area under the curve will be:
which is the amount of thermal energy transferred in the process. If the process moves to greater entropy, the area under the curve will be the amount of heat absorbed by the system in that process. If the process moves towards lesser entropy, it will be the amount of heat removed. For any cyclic process, there will be an upper portion of the cycle and a lower portion. For a clockwise cycle, the area under the upper portion will be the thermal energy absorbed during the cycle, while the area under the lower portion will be the thermal energy removed during the cycle. The area inside the cycle will then be the difference between the two, but since the internal energy of the system must have returned to its initial value, this difference must be the amount of work done by the system over the cycle. Referring to figure 1, mathematically, for a reversible process we may write the amount of work done over a cyclic process as:
Since dU is an exact differential, its integral over any closed loop is zero and it follows that the area inside the loop on a T-S diagram is equal to the total work performed if the loop is traversed in a clockwise direction, and is equal to the total work done on the system as the loop is traversed in a counterclockwise direction.

The Carnot cycle
Evaluation of the above integral is particularly simple for the Carnot cycle. The amount of energy transferred as work is
The total amount of thermal energy transferred between the hot reservoir and the system will be
and the total amount of thermal energy transferred between the system and the cold reservoir will be
The efficiency  is defined to be:
is defined to be:
where
-
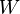 is the work done by the system (energy exiting the system as work),
is the work done by the system (energy exiting the system as work), -
 is the heat put into the system (heat energy entering the system),
is the heat put into the system (heat energy entering the system), -
 is the absolute temperature of the cold reservoir, and
is the absolute temperature of the cold reservoir, and -
 is the absolute temperature of the hot reservoir.
is the absolute temperature of the hot reservoir. -
 is the maximum system entropy
is the maximum system entropy -
 is the minimum system entropy
is the minimum system entropy
This efficiency makes sense for a heat engine, since it is the fraction of the heat energy extracted from the hot reservoir and converted to mechanical work. A Rankine cycle is usually the practical approximation.
The Reversed Carnot cycle
The Carnot heat-engine cycle described is a totally reversible cycle. Therefore, all the processes that comprised it can be reversed, in which case it becomes the Carnot refrigeration cycle. This time, the cycle remains exactly the same, except that the directions of any heat and work interactions are reversed: Heat is absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir, heat in is rejected to a high-temperature reservoir, and a work input is required to accomplish all this. The P-V diagram of the reversed Carnot cycle is the same as for the Carnot cycle, except that the directions of the processes are reversed.[1]
Carnot's theorem
It can be seen from the above diagram, that for any cycle operating between temperatures  and
and  , none can exceed the efficiency of a Carnot cycle.
, none can exceed the efficiency of a Carnot cycle.

Carnot's theorem is a formal statement of this fact: No engine operating between two heat reservoirs can be more efficient than a Carnot engine operating between those same reservoirs. Thus, Equation 3 gives the maximum efficiency possible for any engine using the corresponding temperatures. A corollary to Carnot's theorem states that: All reversible engines operating between the same heat reservoirs are equally efficient. Rearranging the right side of the equation gives what may be a more easily understood form of the equation. Namely that the theoretical maximum efficiency of a heat engine equals the difference in temperature between the hot and cold reservoir divided by the absolute temperature of the hot reservoir. To find the absolute temperature in kelvin, add 273.15 degrees to the Celsius temperature. Looking at this formula an interesting fact becomes apparent. Lowering the temperature of the cold reservoir will have more effect on the ceiling efficiency of a heat engine than raising the temperature of the hot reservoir by the same amount. In the real world, this may be difficult to achieve since the cold reservoir is often an existing ambient temperature.
In other words, maximum efficiency is achieved if and only if no new entropy is created in the cycle. Otherwise, since entropy is a state function, the required dumping of heat into the environment to dispose of excess entropy leads to a reduction in efficiency. So Equation 3 gives the efficiency of any reversible heat engine.
In mesoscopic heat engines, work per cycle of operation fluctuates due to thermal noise. For the case when work and heat fluctuations are counted, there is exact equality that relates average of exponents of work performed by any heat engine and the heat transfer from the hotter heat bath.[2] This relation transforms the Carnot's inequality into exact equality that is applied to an arbitrary heat engine coupled to two heat reservoirs and operating at arbitrary rate.
Efficiency of real heat engines
- See also: Heat engine efficiency and other performance criteria
Carnot realized that in reality it is not possible to build a thermodynamically reversible engine, so real heat engines are less efficient than indicated by Equation 3. In addition, real engines that operate along this cycle are rare. Nevertheless, Equation 3 is extremely useful for determining the maximum efficiency that could ever be expected for a given set of thermal reservoirs.
Although Carnot's cycle is an idealisation, the expression of Carnot efficiency is still useful. Consider the average temperatures,
at which heat is input and output, respectively. Replace TH and TC in Equation (3) by ⟨TH⟩ and ⟨TC⟩ respectively.
For the Carnot cycle, or its equivalent, ⟨TH⟩ is the highest temperature available and ⟨TC⟩ the lowest. For other less efficient cycles, ⟨TH⟩ will be lower than TH, and ⟨TC⟩ will be higher than TC. This can help illustrate, for example, why a reheater or a regenerator can improve the thermal efficiency of steam power plants—and why the thermal efficiency of combined-cycle power plants (which incorporate gas turbines operating at even higher temperatures) exceeds that of conventional steam plants.
See also
- Carnot heat engine
- Reversible process (thermodynamics)
- Carnot cycle graphs (above) should not be confused with Karnaugh maps in boolean logic and digital electronics.
References
- Carnot, Sadi, Reflections on the Motive Power of Fire
- Feynman, Richard P.; Leighton, Robert B.; Sands, Matthew (1963). The Feynman Lectures on Physics. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company. pp. 44–4f. ISBN 0-201-02116-1.
- Halliday, David; Resnick, Robert (1978). Physics (3rd ed. ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 541–548. ISBN 0-471-02456-2.
- Kittel, Charles; Kroemer, Herbert (1980). Thermal Physics (2nd ed. ed.). W. H. Freeman Company. ISBN 0-7167-1088-9.
- Kostic, M., Revisiting The Second Law of Energy Degradation and Entropy Generation: From Sadi Carnot's Ingenious Reasoning to Holistic Generalization.
AIP Conf. Proc. 1411, pp. 327–350; doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3665247. American Institute of Physics, 2011. ISBN 978-0-7354-0985-9. Abstract at: . Full article (24 pages ), also at .
External links
- Hyperphysics article on the Carnot cycle.
- Interactive Java applet showing behavior of a Carnot engine.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||