Carnosic acid
| Carnosic acid | |
|---|---|
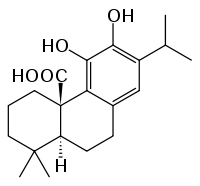 | |
| IUPAC name (4aR,10aS)-5,6-dihydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-7-propan-2-yl-2,3,4,9,10,10a-hexahydrophenanthrene-4a-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names Salvin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 3650-09-7 |
| PubChem | 65126 |
| ChemSpider | 58635 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:65585 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL484853 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C20H28O4 |
| Molar mass | 332.42 g/mol |
| Melting point | 185–190 °C |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Carnosic acid is a natural benzenediol abietane diterpene found in rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) and common sage (Salvia officinalis).[1] Dried leaves of rosemary or sage contain 1.5 to 2.5% carnosic acid.
Carnosic acid has medicinal properties, is a potent antioxidant and protects skin cells against UV-A radiation (photoprotection). Studies in animals have also found a protection against carcinogens.
Carnosic acid is used as a preservative or antioxidant in food and nonfood products (e.g. toothpaste, mouthwash and chewing gum -in which it has an antimicrobial effect on the microbes responsible for bad breath- or skin care products).[citation needed]
References
- ↑ Schwarz, Karin; Ternes, Waldemar (1992). "Antioxidative constituents of Rosmarinus officinalis and Salvia officinalis". Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung 195: 99–103. doi:10.1007/BF01201766.