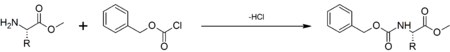Carboxybenzyl
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Carboxybenzyl (abbreviated as Cbz or Z) is a carbamate which is often used as an amine protecting group in organic synthesis.[1] It is commonly used in peptide synthesis where the carboxybenzyl protection group is introduced by reacting the amine functionality with benzyl chloroformate in the presence of a weak base:
It is used to protect amines from electrophiles. The protected amine can be deprotected by catalytic hydrogenation or treatment with HBr, yielding a terminal carbamic acid that then readily decarboxylates to yield the free amine.
The method was first used by Max Bergmann and Leonidas Zerwas in 1932 for the synthesis of peptides.[2] The abbreviation Z is in honor of Zerwas.
References
- ↑ Clayden, Jonathan; Greeves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Wothers, Peter (2001). Organic Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 248, 652–654, 1484. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
- ↑ Max Bergmann, Leonidas Zervas (1932). "Über ein allgemeines Verfahren der Peptid-Synthese". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 65 (7): 1192–1201. doi:10.1002/cber.19320650722.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.