Carbamic acid
| Carbamic acid | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| IUPAC name Carbamic acid | |
| Other names Aminomethanoic Acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 463-77-4 |
| PubChem | 277 |
| ChemSpider | 271 |
| DrugBank | DB04261 |
| KEGG | C01563 |
| MeSH | Carbamic+acid |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28616 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL125278 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | CH3NO2 |
| Molar mass | 61.040 g/mol |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Formamide Dithiocarbamate Carbonic acid Urea Ethyl carbamate |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Carbamic acid is a compound that is unstable under normal circumstances. It is technically the simplest amino acid, though its instability (and the unique nature of the carboxyl-nitrogen bond) allows glycine to assume this title. Its importance is due more to its relevance in identifying the names of larger compounds. [1] Carbamic acid itself has not been synthesized or characterized by any experimental technique.[2]
The radical is called "carbamoyl". "Carbamoyltransferases" are transferase enzymes classified under EC number 2.1.3.
-
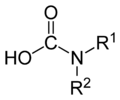
carbamic acid group
-

carbamate group
-

carbamoyl group
Carbamic acids are intermediates in the decomposition of carbamate protecting groups; the hydrolysis of an ester bond produces carbamic acid the evolution of carbon dioxide drives the deprotection reaction forward, yielding the unprotected amine.
Carbamates
Carbamate is an ester of carbamic acid. Methyl carbamate is the simplest ester of carbamic acid.
Some esters have use as muscle relaxants,[3] while others are used as insecticides, for example aldicarb.[4]
See also
- Carbamoyl phosphate
- M03BA Carbamic acid esters
References
- ↑ Thomas L. Lemke. (2003). Review of organic functional groups : introduction to medicinal organic chemistry. Philadelphia, Pa.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-7817-4381-5.
- ↑ R.K. Khanna, M.H. Moore. (1998). "A 55". Carbamic acid: molecular structure and IR spectra (pii: S1386-1425(98)00228-5). Greenbelt, MD.: Elsevier. pp. 961–967.
- ↑ ed. by John H. Block, John M. Beale. (2004). "Central Nervous System Depressant". Wilson and Gisvold's textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry. Philadelphia, Pa.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 495. ISBN 978-0-7817-3481-3.
- ↑ Risher, JF; Mink, FL; Stara, JF (1987). "The toxicologic effects of the carbamate insecticide aldicarb in mammals: a review". Environmental health perspectives 72: 267–81. doi:10.2307/3430304. JSTOR 3430304. PMC 1474664. PMID 3304999.