Captorhinidae
| Captorhinids Temporal range: Pennsylvanian - Lopingian | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Fossil Captorhinus specimens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Eureptilia |
| Family: | †Captorhinidae Case, 1911 |
| Type species | |
| †Captorhinus aguti Cope, 1895 | |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
Captorhinidae (also known as cotylosaurs, root reptiles or stem reptiles) is one of the earliest and most basal reptile families.
Description
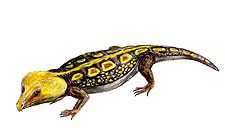
Discovery and History
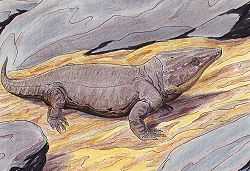
Captorhinidae contains a single subfamily, the Moradisaurinae. Moradisaurinae was named and assigned to the family Captorhinidae by A. D. Ricqlès and P. Taquet in 1982. Moradisaurinae was defined as "all captorhinids more closely related to Moradisaurus than to Captorhinus". The moradisaurines inhabited what is now China, Morocco, Niger, Russia, Texas and Oklahoma.[3] The moradisaurines were insectivores/herbivores, meaning that they only ate insects and plant life.[5]
Captorhinids were once thought to be the ancestors of turtles. The Middle Permian reptile Eunotosaurus from South Africa was seen as the "missing link" between cotylosaurs and Chelonia throughout much of the early 20th century.[6] However, more recent fossil finds have shown that Eunotosaurus is a parareptile unrelated to either turtles or captorhinids.[7]
Classification
Taxonomy
The following taxonomy follows Reisz et al., 2011 and Sumida et al., 2010 unless otherwise noted.[3][4]
- Family Captorhinidae
- Captorhinoides?
- Eocaptorhinus?
- Acrodenta[8]
- Baeotherates[9]
- Captorhinus
- Concordia
- Protocaptorhinus
- Reiszorhinus
- Rhiodenticulatus
- Romeria
- Saurorictus
- Thuringothyris
- Subfamily Moradisaurinae
- Gecatogomphius[5]
- Kahneria[5]
- Captorhinikos
- Labidosaurus
- Labidosaurikos
- Moradisaurus
- Rothianiscus
- Gansurhinus
- Dubious Captorhinids
- Puercosaurus
- Riabininus
Phylogeny
The cladogram below was recovered in a study by Sumida et al., 2010.[4]
| Captorhinidae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
The cladogram below follows the topology from a 2011 analysis by paleontologists Robert R. Reisz, Jun Liu, Jin-Ling Li and Johannes Müller.[3]
| |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
References
- ↑ Goodrich, E.S. (1916). "On the classification of the Reptilia". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London 89B: 261–276. doi:10.1098/rspb.1916.0012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Muller, J. and Reisz, R.R. (2006). "The phylogeny of early eureptiles: Comparing parsimony and Bayesian approaches in the investigation of a basal fossil clade." Systematic Biology, 55(3):503-511. doi:10.1080/10635150600755396
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Robert R. Reisz, Jun Liu, Jin-Ling Li and Johannes Müller (2011). "A new captorhinid reptile, Gansurhinus qingtoushanensis, gen. et sp. nov., from the Permian of China". Naturwissenschaften 98 (5): 435–441. doi:10.1007/s00114-011-0793-0. PMID 21484260.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Sumida, S.S.; Dodick, J,. Metcalf, A,. and Albright, G. (2010). "Reiszorhinus olsoni, a new single-tooth-rowed captorhinid reptile of the Lower Permian of Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 30 (3): 704–714. doi:10.1080/02724631003758078.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 The Paleobiology Database: Moradisaurinae
- ↑ Watson, D.M.S. (1914). "Eunotosaurus africanus Seeley and the ancestors of the Chelonia". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 11: 1011–1020.
- ↑ "Facts About Turtles: Eunotosaurus And Turtle Evolution". All-About-Reptiles.com. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ↑ Nor-Eddine Jalil and Jean-Michel Dutuit (1996). "Permian captorhinid reptiles from the Argana formation, Morocco". Palaeontology 39 (4): 907–918.
- ↑ W. J. May and Richard L. Cifelli (1998). "Baeotherates fortsillensis, A New Captorhinid Reptile from the Fort Sill Fissures, Lower Permian of Oklahoma". Oklahoma Geology Notes 58: 128–137.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||