Canberra
| Canberra Australian Capital Territory | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Clockwise: Parliament House, Australian War Memorial, view of the city along the parliamentary axis, Black Mountain Tower, National Library of Australia, and Australian National University | |||||||
 Canberra | |||||||
| Coordinates | 35°18′27″S 149°07′27.9″E / 35.30750°S 149.124417°ECoordinates: 35°18′27″S 149°07′27.9″E / 35.30750°S 149.124417°E | ||||||
| Population | 374,245 (30 June 2013)[3] (8th) | ||||||
| • Density | 428.6/km2 (1,110/sq mi) | ||||||
| Established | 12 March 1913 | ||||||
| Area | 814.2 km2 (314.4 sq mi)[4] | ||||||
| Time zone | AEST (UTC+10) | ||||||
| • Summer (DST) | AEDT (UTC+11) | ||||||
| Location | |||||||
| Territory electorate(s) | |||||||
| Federal Division(s) | |||||||
| |||||||
Canberra (/ˈkænb(ə)rə/ or /ˈkænbɛrə/)[5] is the capital city of Australia. With a population of 374,245, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The city is located at the northern end of the Australian Capital Territory (ACT), 280 km (170 mi) south-west of Sydney, and 660 km (410 mi) north-east of Melbourne. A resident of Canberra is known as a "Canberran".
The site of Canberra was selected for the location of the nation's capital in 1908 as a compromise between rivals Sydney and Melbourne, Australia's two largest cities. It is unusual among Australian cities, being an entirely planned city outside of any state, similar to the American Federal District of Columbia. Following an international contest for the city's design, a blueprint by the Chicago architects Walter Burley Griffin and Marion Mahony Griffin was selected and construction commenced in 1913.[6] The Griffins' plan featured geometric motifs such as circles, hexagons and triangles, and was centred on axes aligned with significant topographical landmarks in the Australian Capital Territory.
The city's design was influenced by the garden city movement and incorporates significant areas of natural vegetation that have earned Canberra the title of the "bush capital". The growth and development of Canberra were hindered by the World Wars and the Great Depression, which exacerbated a series of planning disputes and the ineffectiveness of a procession of bodies that were created in turn to oversee the development of the city. The national capital emerged as a thriving city after World War II, as Prime Minister Robert Menzies championed its development and the National Capital Development Commission was formed with executive powers. Although the Australian Capital Territory is now self-governing, the federal government retains some influence through the National Capital Authority.
As the seat of the government of Australia, Canberra is the site of Parliament House, the High Court and numerous government departments and agencies. It is also the location of many social and cultural institutions of national significance, such as the Australian War Memorial, Australian National University, Australian Institute of Sport, National Gallery, National Museum and the National Library. The Australian Army's officer corps are trained at the Royal Military College, Duntroon and the Australian Defence Force Academy is also located in the capital.
The ACT, like Washington, D.C. in the United States, is independent of any state, to prevent any one state from gaining an advantage by hosting the seat of Federal power. Unlike Washington, however, the ACT has voting representation in the Federal Parliament, and has its own independent Legislative Assembly and government, similar to the states.
As the city has a high proportion of public servants, the federal government contributes the largest percentage of Gross State Product and is the largest single employer in Canberra. As the seat of government, the unemployment rate is lower and the average income higher than the national average, while property prices are relatively high, in part due to comparatively restricted development regulations. Tertiary education levels are higher, while the population is younger.
Etymology
The word "Canberra" is popularly thought to derive from the word Kambera or Canberry which is claimed to mean "meeting place" in the old Ngunnawal language, one of several Indigenous languages spoken in the district by Aboriginal people before European settlers arrived.[7] According to Ngunnawal Elder, Don Bell, the correct translation is "woman's breasts" and is the Indigenous name for the two mountains, Black Mountain and Mount Ainslie which lie almost opposite each other.[8] In the 1860s, the name was reported by Queanbeyan newspaper owner John Gale to be an anglicisation of the indigenous name 'nganbra' or 'nganbira', meaning "hollow between a woman's breasts", and referring to the Sullivans Creek floodplain between Mount Ainslie and Black Mountain.[9]
Alternatively, R.H. Cambage in his 1919 book Notes on the Native Flora of New South Wales, Part X, the Federal Capital Territory noted that Joshua John Moore, the first settler in the region, named the area Canberry in 1823 stating that "there seems no doubt that the original was a native name, but its meaning is unknown."[10] Survey plans of the district dated 1837 refer to the area as the Canberry Plain. In 1920, some of the older residents of the district claimed that the name was derived from the Australian Cranberry which grew abundantly in the area, noting that the local name for the plant was canberry. Although popularly pronounced /ˈkænb(ə)rə/ or /ˈkænbɛrə/, the original pronunciation at its official naming in 1913 was /ˈkæn.brə/.[8]
History
Before European settlement, the area in which Canberra would eventually be constructed was seasonally inhabited by Indigenous Australians. Anthropologist Norman Tindale suggested the principal group occupying the region were the Ngunnawal people, while the Ngarigo lived immediately to the south of the ACT, The Wandandian to the east, the Walgulu also to the south, Gandangara people to the north, and Wiradjuri to the north west. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the region includes inhabited rock shelters, rock paintings and engravings, burial places, camps and quarry sites, and stone tools and arrangements.[11] The evidence suggests human habitation in the area for at least 21,000 years.[12]

The European population in the Canberra area continued to grow slowly throughout the 19th century.[17] Among them was the Campbell family of "Duntroon";[18] their imposing stone house is now the officers' mess of the Royal Military College, Duntroon.[19] The Campbells sponsored settlement by other farmer families to work their land, such as the Southwells of "Weetangera".[20] Other notable early settlers included the inter-related Murray and Gibbes families, who owned the Yarralumla estate—now the site of the official residence of the Governor-General of Australia—from the 1830s through to 1881.[21]
The oldest surviving public building in the inner-city is the Anglican Church of St John the Baptist, in the suburb of Reid,[22] which was consecrated in 1845.[23][24] St John's churchyard contains the earliest graves in the district.[25] As the European presence increased, the indigenous population dwindled, mainly from disease such as smallpox and measles.[26]
Decisions to start and locate a capital
The district's change from a rural area in New South Wales to the national capital started during debates over Federation in the late 19th century.[27][28] Following a long dispute over whether Sydney or Melbourne should be the national capital,[29] a compromise was reached: the new capital would be built in New South Wales, so long as it was at least 100 miles (160 km) from Sydney,[27] with Melbourne to be the temporary seat of government (but not referred to as the "capital") while the new capital was built.[30] Newspaper proprietor John Gale circulated a pamphlet titled 'Dalgety or Canberra: Which?' advocating Canberra to every member of the Commonwealth's seven state and federal parliaments. By many accounts, it was decisive in the selection of Canberra as the site in 1908, as was a result of survey work done by the government surveyor Charles Scrivener.[31] The NSW government ceded the Federal Capital Territory (as it was then known) to the federal government.[27] In an international design competition conducted by the Department of Home Affairs, on 24 May 1911,[32] the design by Walter Burley Griffin and Marion Mahony Griffin was chosen for the city,[33][34] and in 1913 Griffin was appointed Federal Capital Director of Design and Construction and construction began.[35]

History of Canberra as a capital city
On 12 March 1913,[36] the city was officially given its name by Lady Denman, the wife of Governor-General Lord Denman, at a ceremony at Kurrajong Hill,[37][38][39] which has since become Capital Hill and the site of the present Parliament House.[40] Canberra Day is a public holiday observed in the ACT on the second Monday in March to celebrate the founding of Canberra.[26] After the ceremony, bureaucratic disputes hindered Griffin's work;[41] a Royal Commission in 1916 ruled his authority had been usurped by certain officials.[42] Griffin's relationship with the Australian authorities was strained and a lack of funding meant that by the time he was fired in 1920, little work had been done.[43][44] By this time, Griffin had revised his plan, overseen the earthworks of major avenues,[45] and established the Glenloch Cork Plantation.[46]
The federal legislature moved to Canberra on 9 May 1927, with the opening of the Provisional Parliament House.[47][48] Prime Minister, Stanley Bruce,[49] had officially taken up residence in The Lodge a few days earlier.[50] Planned development of the city slowed significantly during the depression of the 1930s and during World War II.[51] Some projects planned for that time, including Roman Catholic and Anglican cathedrals, were never completed.[52]

From 1920 to 1957, three bodies, successively the Federal Capital Advisory Committee,[53] the Federal Capital Commission,[54] and the National Capital Planning and Development Committee continued to plan the further expansion of Canberra in the absence of Griffin; however, they were only advisory,[55] and development decisions were made without consulting them, increasing inefficiency.[45]
Immediately after the end of the war, Canberra was criticised for resembling a village,[56][57] and its disorganised collection of buildings was deemed ugly.[58] Canberra was often derisively described as "several suburbs in search of a city".[59] Prime Minister Robert Menzies[60] regarded the state of the national capital as an embarrassment. Over time his attitude changed from one of contempt to that of championing its development. He fired two ministers charged with the development of the city for poor performance. He ruled for over a decade and in that time the development of the capital sped up rapidly.[61][62] The population grew by more than 50 per cent in every five-year period from 1955 to 1975.[62] Several Government departments, together with public servants, were moved to Canberra from Melbourne following the war.[63] Government housing projects were undertaken to accommodate the city's growing population.[64]
Most of rapid expansion was achieved after the National Capital Development Commission (NCDC) was formed in 1957 with executive powers, replacing its ineffective advisory predecessors.[65] The NCDC ended four decades of disputes over the shape and design of Lake Burley Griffin—the centrepiece of Griffin's design—and construction was completed in 1964 after four years of work.[66] The completion of the lake finally the laid the platform for the development of Griffin's Parliamentary Triangle.[67] Since the initial construction of the lake, various buildings of national importance have been constructed on its shores.[68]
The newly built Australian National University was expanded,[68] and sculptures and monuments were built.[69] A new National Library was constructed within the Parliamentary Triangle, followed by the High Court and the National Gallery.[22][70] Suburbs in Canberra Central (often referred to as North Canberra and South Canberra) were further developed in the 1950s,[71] and urban development in the districts of Woden Valley and Belconnen commenced in the mid and late 1960s respectively.[72] Many of the new suburbs were named after Australian politicians, such as Barton, Deakin, Reid, Braddon, Curtin, Chifley and Parkes.[73]

On 27 January 1972 the Aboriginal Tent Embassy was first established by indigenous people on the grounds of Parliament House; it was created to draw attention to Indigenous rights and land issues and has been continuously occupied since 1992.
On 9 May 1988,[74] a larger and permanent Parliament House was opened on Capital Hill as part of Australia's bicentenary celebrations,[22][70] and the Federal Parliament moved there from the Provisional Parliament House, now known as Old Parliament House.[74]
In December 1988, the ACT was granted full self-government through an Act of the Commonwealth Parliament. Following the first election on 4 March 1989,[75] a 17-member Legislative Assembly sat at temporary offices at 1 Constitution Avenue, Civic,[76] on 11 May 1989.[77] Permanent premises were opened on London Circuit in 1994.[77] The Australian Labor Party formed the ACT's first government,[78] led by the Chief Minister Rosemary Follett, who made history as Australia's first female head of government.[79]
Parts of Canberra were engulfed by bushfires on 18 January 2003 that killed four people, injured 435, and destroyed more than 500 homes and the major research telescopes of Australian National University's Mount Stromlo Observatory.[80] Throughout 2013, several events will be held to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the naming of Canberra.[81]
Geography

Canberra covers an area of 814.2 square kilometres (314.4 sq mi)[4] (314.3 sq. mi) and is located near the Brindabella Ranges, approximately 150 kilometres (93 mi) inland from Australia's east coast. It has an elevation of approximately 580 metres (1,900 ft) AHD;[82] the highest point is Mount Majura at 888 metres (2,913 ft).[83][84] Other large hills include Mount Taylor 855 metres (2,805 ft),[85] Mount Ainslie 843 metres (2,766 ft),[86] Mount Mugga Mugga 812 metres (2,664 ft)[87] and Black Mountain 812 metres (2,664 ft).[88][89]
The native forest in the Canberra region was almost wholly eucalypt species and provided a resource for fuel and domestic purposes. By the early 1960s, logging had depleted the eucalypt, and concern about water quality led to the forests being closed. Interest in forestry began in 1915 with trials of a number of species including Pinus radiata on the slopes of Mount Stromlo. Since then, plantations have been expanded, with the benefit of reducing erosion in the Cotter catchment, and the forests are also popular recreation areas.[90]
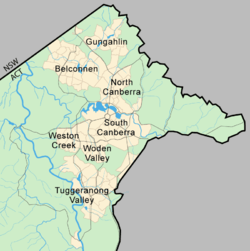
The urban environs of the city of Canberra straddle the Ginninderra plain, Molonglo plain, the Limestone plain, and the Tuggeranong plain (Isabella's Plain).[91] The Molonglo River which flows across the Molonglo plain has been dammed to form the national capital's iconic feature Lake Burley Griffin.[92] The Molonglo then flows into the Murrumbidgee north-west of Canberra, which in turn flows north-west toward the New South Wales town of Yass. The Queanbeyan River joins the Molonglo River at Oaks Estate just within the ACT.[91]
A number of creeks, including Jerrabomberra and Yarralumla Creeks, flow into the Molonglo and Murrumbidgee.[91] Two of these creeks, the Ginninderra and Tuggeranong, have similarly been dammed to form Lakes Ginninderra and Tuggeranong.[93][94][95] Until recently the Molonglo River had a history of sometimes calamitous floods; the area was a flood plain prior to the filling of Lake Burley Griffin.[96][97]
Climate
Canberra has a relatively dry continental climate with warm to hot summers and cool to cold winters,[82] under Köppen-Geiger classification it has an oceanic climate (Cfb).[98] Canberra experiences warm, generally dry summers, and chilly winters with heavy fog and frequent frosts. Snow is rare in the CBD (central business district), but the surrounding areas get annual snowfall through winter and often the snow capped mountains can be seen from the CBD—the last significant snowfall in the city centre was in 1968.[82] The highest recorded maximum temperature is variously reported as 42.2 °C (108.0 °F) on 1 February 1968,[82] or as 42.8 °C (109.0 °F) at Acton on 11 January 1939.[99]
The lowest recorded minimum temperature was −10.0 °C (14.0 °F) on 11 July 1971.[82] Light snow falls only once or twice per year, and it is usually not widespread and quickly dissipates.[82] Canberra is protected from the west by the Brindabellas which create a slight rain shadow in Canberra's valleys.[82]
Annual rainfall is the third lowest of the capital cities (after Adelaide and Hobart)[100] but is spread fairly evenly over the seasons, with late spring bringing the highest rainfall.[101] Thunderstorms occur mostly between October and April,[82] owing to the effect of summer and the mountains. The area is not very windy and the breeze is at its strongest from August to November. Canberra is less humid than the nearby coastal areas.[82]
| Climate data for Canberra Airport | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 42.0 (107.6) |
42.2 (108) |
37.5 (99.5) |
32.6 (90.7) |
24.5 (76.1) |
20.1 (68.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
24.0 (75.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
32.7 (90.9) |
38.9 (102) |
39.2 (102.6) |
42.2 (108) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28.0 (82.4) |
27.1 (80.8) |
24.5 (76.1) |
20.0 (68) |
15.6 (60.1) |
12.3 (54.1) |
11.4 (52.5) |
13.0 (55.4) |
16.2 (61.2) |
19.4 (66.9) |
22.7 (72.9) |
26.1 (79) |
19.7 (67.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 13.2 (55.8) |
13.1 (55.6) |
10.7 (51.3) |
6.7 (44.1) |
3.2 (37.8) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
1.0 (33.8) |
3.3 (37.9) |
6.1 (43) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
6.5 (43.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
3.0 (37.4) |
−1.1 (30) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−10.0 (14) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
1.1 (34) |
−10.0 (14) |
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 58.5 (2.303) |
56.4 (2.22) |
50.7 (1.996) |
46.0 (1.811) |
44.4 (1.748) |
40.4 (1.591) |
41.4 (1.63) |
46.2 (1.819) |
52.0 (2.047) |
62.4 (2.457) |
64.4 (2.535) |
53.8 (2.118) |
616.4 (24.268) |
| Avg. precipitation days | 7.3 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 8.4 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 11.1 | 10.2 | 10.4 | 9.8 | 7.8 | 106.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 294.5 | 254.3 | 251.1 | 219 | 186 | 156 | 179.8 | 217 | 231 | 266.6 | 267 | 291.4 | 2,813.7 |
| Source #1: [102] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: [103] | |||||||||||||
Urban structure


Canberra is a planned city and the inner-city area was originally designed by Walter Burley Griffin, a major 20th-century American architect.[104] Within the central area of the city near Lake Burley Griffin, major roads follow a wheel-and-spoke pattern rather than a grid.[105] Griffin's proposal had an abundance of geometric patterns, including concentric hexagonal and octagonal streets emanating from several radii.[105] However, the outer areas of the city, built later, are not laid out geometrically.[106]
Lake Burley Griffin was deliberately designed so that the orientation of the components was related to various topographical landmarks in Canberra.[107][108] The lakes stretch from east to west and divided the city in two; a land axis perpendicular to the central basin stretches from Capital Hill—the eventual location of the new Parliament House on a mound on the southern side—north northeast across the central basin to the northern banks along Anzac Parade to the Australian War Memorial.[57] This was designed so that looking from Capital Hill, the War Memorial stood directly at the foot of Mount Ainslie. At the southwestern end of the land axis was Bimberi Peak,[108] the highest mountain in the ACT, approximately 52 km (32 mi) south west of Canberra.[89]
The straight edge of the circular segment that formed the central basin of Lake Burley Griffin was perpendicular to the land axis and designated the water axis, and it extended northwest towards Black Mountain.[108] A line parallel to the water axis, on the northern side of the city, was designated the municipal axis.[109] The municipal axis became the location of Constitution Avenue, which links City Hill in Civic Centre and both Market Centre and the Defence precinct on Russell Hill. Commonwealth Avenue and Kings Avenue were to run from the southern side from Capital Hill to City Hill and Market Centre on the north respectively, and they formed the western and eastern edges of the central basin. The area enclosed by the three avenues was known as the Parliamentary Triangle, and formed the centrepiece of Griffin's work.[108][109]
The Griffins assigned spiritual values to Mount Ainslie, Black Mountain, and Red Hill and originally planned to cover each of these in flowers. That way each hill would be covered with a single, primary color which represented its spiritual value.[110] This part of their plan never came to fruition, as World War I slowed construction and planning disputes led to Walter's dismissal by Prime Minister Billy Hughes after the war ended.[43][44][111]
The urban areas of Canberra are organised into a hierarchy of districts, town centres, group centres, local suburbs as well as other industrial areas and villages. There are seven residential districts, each of which is divided into smaller suburbs, and most of which have a town centre which is the focus of commercial and social activities.[112] The districts were settled in the following chronological order:
- Canberra Central, mostly settled in the 1920s and 1930s, with expansion up to the 1960s,[113] 25 suburbs
- Woden Valley, first settled in 1964,[72] 12 suburbs
- Belconnen, first settled in 1966,[72] 25 suburbs (1 not yet developed)
- Weston Creek, settled in 1969, 8 suburbs[114]
- Tuggeranong, settled in 1974,[115] 18 suburbs
- Gungahlin, settled in the early 1990s, 18 suburbs (6 not yet developed)
- Molonglo Valley, development began in 2010, 13 suburbs planned.
The Canberra Central district is substantially based on Walter Burley Griffin's designs.[108][109][116] In 1967 the then National Capital Development Commission adopted the "Y Plan" which laid out future urban development in Canberra around a series of central shopping and commercial area known as the 'town centres' linked by freeways, the layout of which roughly resembled the shape of the letter Y,[117] with Tuggeranong at the base of the Y and Belconnen and Gungahlin located at the ends of the arms of the Y.[117]
Development in Canberra has been closely regulated by government,[118][119] both through planning processes and the use of crown lease terms that have tightly limited the use of parcels of land. Land in the ACT is held on 99-year crown leases from the national government, although most leases are now administered by the Territory government.[120] There have been persistent calls for constraints on development to be liberalised.[119]
Many of Canberra's suburbs are named after former Prime Ministers, famous Australians, early settlers, or use Aboriginal words for their title.[121] Street names typically follow a particular theme; for example, the streets of Duffy are named after Australian dams and reservoirs, the streets of Dunlop are named after Australian inventions, inventors and artists and the streets of Page are named after biologists and naturalists.[121] Most diplomatic missions are located in the suburbs of Yarralumla, Deakin and O'Malley.[122] There are three light industrial areas: the suburbs of Fyshwick, Mitchell and Hume.[123]
Governance

and the statue Ethos (Tom Bass, 1961)
Outside Canberra, the Australian Capital Territory has no settlements larger than a village. The Australian Capital Territory Legislative Assembly performs the roles of both a city council and territory government.[124] The assembly consists of 17 members, elected from three districts using proportional representation.[78] The three districts are Molonglo, Ginninderra and Brindabella, which elect seven, five and five members, respectively.[125]
The Chief Minister is elected by the Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) and selects colleagues to serve as ministers alongside him or her in the Executive, known informally as the cabinet.[124] Whereas the ACT has federally been dominated by Labor,[26][126] the Liberals have been able to gain some footing in the ACT Legislative Assembly, and were in government for just over eight of the Assembly's 21-year history, mostly during a period of six and half years from 1995 and 2001, when Labor won power.[78] At the 2004 election the Australian Labor Party, headed by then Chief Minister Jon Stanhope, won nine of the 17 seats and formed the ACT's first majority government,[78] but after the 2008 election was forced into minority government with the Greens.[78][127]
As almost all of the ACT's population lives in Canberra, political trends for both areas are closely aligned. The ACT was given its first federal parliamentary representation in 1949, when it gained a seat in the House of Representatives, the Division of Australian Capital Territory.[128][129] The ACT member could only vote on matters directly affecting the territory.[129] In 1974, the ACT was allocated two Senate seats. In 1974, the House of Representatives seat was divided into two.[128] A third was created in 1996, but was abolished in 1998 because of changes to the regional demographic distribution.[26]
Both House of Representatives seats have mostly been held by Labor, usually by comfortable margins.[26][126] The Labor Party has polled at least seven percentage points more than the Liberal Party at every federal election since 1990, and their average lead since then has been 15 percentage points.[78] The ALP and the Liberal Party have always held one Senate seat each.[130]
The Australian federal government retains some influence over the ACT government. In the administrative sphere, most frequently this is through the actions of the National Capital Authority which is responsible for planning and development in areas of Canberra which are considered to be of national importance or which are central to Griffin's plan for the city,[131] such as the Parliamentary Triangle, Lake Burley Griffin, major approach and processional roads, areas where the Commonwealth retains ownership of the land or undeveloped hills and ridge-lines (which form part of the Canberra Nature Park).[131][132][133] The national government also retains a level of control over the Territory Assembly through the provisions of the Australian Capital Territory (Self-Government) Act 1988.[134] This federal act defines the legislative power of the ACT assembly.[135]
The Australian Federal Police (AFP) provides all of the constabulary services in the territory in a manner similar to state police forces, under a contractual agreement with the ACT Government.[136] The AFP does so through its community policing arm, ACT Policing (Australian Capital Territory Police).[137]
People who have been charged with offences are tried either in the ACT Magistrates Court or for more severe offences, the ACT Supreme Court.[138][139] Prisoners were held in remand at the Belconnen Remand Centre in the ACT but usually jailed in New South Wales.[140] The new prison, Alexander Maconochie Centre, was officially opened on 11 September 2008 by Jon Stanhope, the Chief Minister. The total cost for construction was $130 million.[141] Courts such as a Small Claims Tribunal and a Family Court exist for civil law actions and other non-criminal legal matters.[142][143]
Economy

In May 2012, the unemployment rate in Canberra was 3.4% which was lower than the national unemployment rate of 5.1%.[144] As a result of low unemployment and substantial levels of public sector and commercial employment, Canberra has the highest average level of disposable income of any Australian capital city.[145] The gross average weekly wage in Canberra is $1702 compared with the national average of $1485.80 (May 2013).[146]
The median house price in Canberra as of September 2009 was $511,820, lower than only Sydney among capital cities of more than 100,000 people, having surpassed Melbourne and Perth since 2005.[147][148] The median weekly rent paid by Canberra residents is higher than rents in all other states and territories.[149] As at the March quarter of 2009 the median rent in Canberra was $420 per week,[150] the third highest in the country.[151] Factors contributing to this higher weekly rental market include; higher average weekly incomes, restricted land supply,[152] and inflationary clauses in the ACT Residential Tenancies Act.[153]
The city's main industry is public administration and safety, which accounted for 29.8% of Gross Territory Product in 2011–12 and employed 33.9% of Canberra's workforce.[154][155] The headquarters of many Australian public service agencies are located in Canberra, and Canberra is also host to several Australian Defence Force establishments, most notably the Australian Defence Force headquarters and HMAS Harman, which is a naval communications centre that is being converted into a tri-service, multi-user depot.[156]
The former RAAF Fairbairn, adjacent to the Canberra International Airport was sold to the operators of the Airport,[157] but the base continues to be used for RAAF VIP flights.[158][159] A growing number of software vendors have based themselves in Canberra, to capitalise on the concentration of government customers; these include Tower Software and RuleBurst.[160][161] A consortium of private and government investors is currently making plans for a billion-dollar data hub, with the aim of making Canberra a leading centre of such activity in the Asia-Pacific region.[162]
Sustainability and environment
In 2012 the ACT Government legislated greenhouse gas targets to reduce its emissions by 40 per cent from 1990 levels by 2020, 80 per cent by 2050, with no net emissions by 2060.[163]
In 1996 Canberra was the first city in the world to set a vision of no waste by 2010.[164] The strategy aimed to achieve a waste-free society by 2010, through the combined efforts of industry, government and community.[165] By early 2010, it was apparent that the ACT Government initiative had failed.[166][167]
Plastic bags made of polyethylene polymer with a thickness of less than 35 µm were banned from retail distribution in the ACT from November 2011.[168][169][170] The ban was introduced by the ACT Government in an effort to make Canberra more sustainable.[169]
Of all waste produced in the ACT, 75 per cent is recycled.[171] Average household food waste in the ACT is above the Australian average, costing an average $641 per household per annum.[172] The average Canberran was responsible for 13.7 tonnes of greenhouse gases in 2005.[173]
Demographics

As at census night in August 2011, the population of Canberra was 355,596,[174] up from 323,056 people in 2006.[175] The 2011 census showed Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people made up 1.4% of ACT's population, while 28.6% of the population were born overseas.[174] The largest group of people born overseas came from the United Kingdom (3.7%) and then China (1.8%).[174]
Significant numbers of immigrants have also come from New Zealand, India and Vietnam.[174] Recent immigrants have arrived from countries in East and South Asia.[176] Most locals only speak English at home (77.8%); other languages spoken at home include Mandarin, Italian, Vietnamese, Cantonese and Spanish.[174]
Canberrans are relatively young, highly mobile, and well educated. The median age is 34 years, and only 10.7% of the population is aged over 65 years.[174] Between 1996 and 2001, 61.9% of the population either moved to or from Canberra, which was the second highest mobility rate of any Australian capital city.[177] According to statistics collected by the National Australia Bank and reported in The Canberra Times, Canberrans on average give significantly more money to charity than Australians in other states and territories, for both dollar giving and as a proportion of income.[178]
As at May 2013, 45% of ACT residents (25–64) had a level of educational attainment equal to at least a bachelor's degree, significantly higher that the national average of 29%.[179] On census night in 2011, approximately 44% of ACT residents described themselves as Christian, the most common denominations being Catholic and Anglican; 29% described themselves as having no religion.[174]
As of 2002 the most common crimes in Canberra are property related crimes, unlawful entry with intent and motor vehicle theft. They affect 1,961 and 630 of every 100,000 persons respectively. Homicide and related offences—including murder, attempted murder, manslaughter and driving causing death—affect 1.5/100,000 persons, which is below the national average of 4.9/100,000. Rates of assault and sexual assault are also below the national average.[180]
Education

The two main tertiary institutions are the Australian National University (ANU) in Acton and the University of Canberra (UC) in Bruce, with over 10,500 and 8,000 full-time-equivalent students respectively.[181][182] Established in 1946,[183] the ANU has always had a strong research focus and is ranked among the leading universities in the world and the best in Australia by The Times Higher Education Supplement and the Shanghai Jiao Tong World University Rankings.[182][184] There are two religious university campuses in Canberra: Signadou in the northern suburb of Watson is a campus of the Australian Catholic University;[185] St Mark's Theological College in Barton is part of the secular Charles Sturt University.[186]
The Australian Defence Force Academy (ADFA) and the Royal Military College, Duntroon are located in the inner-northern suburb of Campbell.[187][188] ADFA teaches military undergraduates and postgraduates and includes UNSW@ADFA, a campus of the University of New South Wales;[189][190] Duntroon provides Australian Army officer training.[191] Tertiary level vocational education is also available through the multi-campus Canberra Institute of Technology.[192]
In February 2004 there were 140 schools in Canberra; 96 were operated by the government and 44 were private. During 2006, the ACT Government announced closures of up to 39 schools, to take effect from the end of the school year, and after a series of consultations unveiled its Towards 2020: Renewing Our Schools policy.[193] As a result, some schools closed during the 2006–08 period, while others were merged; the creation of combined primary and secondary government schools will proceed over the next decade. The new policy has provoked significant opposition.[194][195][196] Most suburbs are planned to include a primary and a nearby preschool; these are usually located near open areas where recreational and sporting activities are easily available.[197]
Arts and entertainment


Canberra is home to many national monuments and institutions such as the Australian War Memorial, the National Gallery of Australia, the National Portrait Gallery, the National Library,[116] the National Archives,[198] the Australian Academy of Science,[199] the National Film and Sound Archive and the National Museum.[116] Many Commonwealth government buildings in Canberra are open to the public, including Parliament House, the High Court and the Royal Australian Mint.[200][201][202]
Lake Burley Griffin is the site of the Captain James Cook Memorial and the National Carillon.[116] Other sites of interest include the Black Mountain Tower, the Australian National Botanic Gardens, the National Zoo and Aquarium, the National Dinosaur Museum and Questacon – the National Science and Technology Centre.[116][203]

The Canberra Museum and Gallery in the city is a repository of local history and art, housing a permanent collection and visiting exhibitions.[204] Several historic homes are open to the public: Lanyon and Tuggeranong Homesteads in the Tuggeranong Valley,[205][206] Mugga-Mugga in Symonston,[207] and Blundells' Cottage in Parkes all display the lifestyle of the early European settlers.[1] Calthorpes' House in Red Hill is a well preserved example of a 1920s house from Canberra's very early days.[208] Canberra has many venues for live music and theatre: the Canberra Theatre and Playhouse which hosts many major concerts and productions;[209] and Llewellyn Hall (within the ANU School of Music), a world-class concert hall are two of the most notable.[210] The Street Theatre is a venue with less mainstream offerings.[210] The Albert Hall was the city's first performing arts venue, opened in 1928. It was the original performance venue for theatre groups such as the Canberra Repertory Society.[211]
Stonefest at the University of Canberra was a large two-day music festival.[212] There are numerous bars and nightclubs which also offer live entertainment, particularly concentrated in the areas of Dickson, Kingston and the city.[213] Most town centres have facilities for a community theatre and a cinema, and they all have a library.[214] Popular cultural events include the National Folk Festival, the Royal Canberra Show, the Summernats car festival, the Canberra Multicultural Festival in February and the Celebrate Canberra festival held over 10 days in March in conjunction with Canberra Day.[212]

Canberra maintains sister-city relationships with both Nara, Japan and Beijing, China. Canberra has friendship-city relationships with both Dili, East Timor and Hangzhou, China.[215] City-to-city relationships encourage communities and special interest groups both locally and abroad to engage in a wide range of exchange activities. The Canberra Nara Candle Festival held annually in spring, is a community celebration of the Canberra Nara Sister City relationship.[216] The festival is held in Canberra Nara Park on the shores of Lake Burley Griffin.[217][218]
Media
As Australia's capital, Canberra is the most important centre for much of Australia's political reportage and thus all the major media, including the Australian Broadcasting Corporation, the commercial television networks, and the metropolitan newspapers maintain local bureaus. News organisations are represented in the "press gallery", a group of journalists who report on the national parliament. The National Press Club of Australia in Barton has regular television broadcasts of its lunches at which a prominent guest, typically a politician or other public figure, delivers a speech followed by a question-and-answer session.[219]
Television
Five free-to-air television stations service Canberra:
- ABC Canberra (ABC)
- SBS New South Wales (SBS)
- Prime7 Southern NSW & ACT (CBN) - Seven Network affiliate
- Win Television Southern NSW & ACT (WIN) - Nine Network affiliate
- Southern Cross Ten Southern NSW & ACT (CTC) - Network Ten affiliate
Each station broadcasts a primary channel and several multichannels.
Prior to 1989, Canberra was serviced by just the ABC, SBS and Capital Television (CTC), which later became Southern Cross Ten, with Prime7 and WIN Television arriving as part of the Government's regional aggregation programme in that year.[220]
Pay television services are available from Foxtel (via satellite) and telecommunications company TransACT (via cable).[221]
Radio
There are a number of AM and FM stations broadcasting in Canberra (AM/FM Listing). The main commercial operators are the Capital Radio Network (2CA and 2CC), and Austereo/ARN (104.7 and Mix 106.3). There are also several community operated stations.
A DAB+ digital radio trial is also currently in operation, it simulcasts some of the AM/FM stations, and also provides several digital only stations (DAB+ Trial Listing).
Canberra has a daily newspaper, The Canberra Times, which was established in 1926.[222][223] There are also several free weekly publications, including news magazines CityNews and Canberra Weekly as well as entertainment guide BMA Magazine. BMA Magazine first went to print in 1992; the inaugural edition featured coverage of the Nirvana Nevermind tour.[224]
Sport

In addition to local sporting leagues, Canberra has a number of sporting teams that compete in national and international competitions. The best known teams are the Canberra Raiders and the Brumbies who play rugby league and rugby union respectively; both have been champions of their leagues.[225][226] Both teams play their home games at Canberra Stadium,[227] which is the city's largest stadium and was used to hold group matches in soccer for the 2000 Summer Olympics and in rugby union for the 2003 Rugby World Cup.[228][229] The city also has a successful basketball team, the Canberra Capitals, which has won seven out of the last eleven national women's basketball titles.[230] Canberra United FC represents the city in the W-League, the national women's association football league, and were champions in the 2011-12 season.[231]
There are also teams that participate in national competitions in netball, field hockey, ice hockey, cricket and baseball. Manuka Oval is another large outdoor sporting facility where cricket and Australian Rules football are played.
Expansion AFL club Greater Western Sydney Giants commenced a partnership with Canberra in 2012 will play three home games at Manuka Oval each season until at least 2021. Prior to this the Melbourne based AFL team the Kangaroos played some home games at Manuka Oval until July 2006.[232] Following the move of the Kangaroos' alternative home ground to Carrara in Queensland, Melbourne and the Western Bulldogs played some home games at Manuka Oval from 2007 against the Sydney Swans.[233] Canberra is also home to the Barassi International Australian Football Youth Tournament.[234] The historic Prime Minister's XI cricket match is played at Manuka Oval annually.[235] Other significant annual sporting events include the Canberra Marathon[236] and the City of Canberra Half Ironman Triathlon. The Canberra Women's Tennis Classic was held as a lead up to the Australian Open until 2006.[237]
The Australian Institute of Sport (AIS) is located in the Canberra suburb of Bruce.[238] The AIS is a specialised educational and training institution providing coaching for elite junior and senior athletes in a number of sports. The AIS has been operating since 1981 and has achieved significant success in producing elite athletes, both local and international.[238] The majority of Australia's team members and medallists at the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney were AIS graduates.[239]
Canberra has numerous sporting ovals, golf courses, skate parks, tennis courts and swimming pools that are open to the public. A Canberra-wide series of bicycle paths are available to cyclists for recreational and sporting purposes. Canberra Nature Parks have a large range of walking paths, horse and mountain bike trails. Water sports like sailing, rowing, dragon boating and water skiing are held on Canberra's lakes.[240][241] The Rally of Canberra is an annual motor sport event and a facility for drag racing is currently being planned for construction.[242][243]
Infrastructure
Health

Canberra has two large public hospitals, the approximately 600-bed Canberra Hospital—formerly the Woden Valley Hospital—in Garran and the 174-bed Calvary Public Hospital in Bruce. Both are teaching institutions.[244][245][246][247] The largest private hospital is the Calvary John James Hospital in Deakin.[248][249] Calvary Private Hospital in Bruce and Healthscope's National Capital Private Hospital in Garran are also major healthcare providers.[244][246]
The Royal Canberra Hospital was located on Acton Peninsula on Lake Burley Griffin; it was closed in 1991 and was demolished in 1997 in a controversial and fatal implosion to facilitate construction of the National Museum of Australia.[68][109][116][250][251] The city has 10 aged care facilities. Canberra's hospitals receive emergency cases from throughout southern New South Wales,[252] and ACT Ambulance Service is one of four operational agencies of the ACT Emergency Services Authority.[253] NETS provides a dedicated ambulance service for inter-hospital transport of sick newborns within the ACT and into surrounding New South Wales.[254]
Transport


The automobile is by far the dominant form of transport in Canberra.[255] The city is laid out so that arterial roads connecting inhabited clusters run through undeveloped areas of open land or forest, which results in a low population density;[256] this also means that idle land is available for the development of future transport corridors if necessary without the need to build tunnels or acquire developed residential land. In contrast, other capital cities in Australia have substantially less green space.[257]
Canberra's districts are generally connected by parkways—limited access dual carriageway roads[255][258] with speed limits generally set at a maximum of 100 km/h (62 mph).[259][260] An example is the Tuggeranong Parkway which links Canberra's CBD and Tuggeranong, and bypasses Weston Creek.[261] In most districts, discrete residential suburbs are bounded by main arterial roads with only a few residential linking in, to deter non-local traffic from cutting through areas of housing.[262]
ACTION, the government-operated bus service, provides public transport throughout the city.[263] Deane's Transit Group provides bus services between Canberra and nearby areas of New South Wales through their Transborder Express (Murrumbateman and Yass)[264] and Deane's Buslines (Queanbeyan) brands.[265] In the 2006 census, 7.7% of the journeys to work involved a bus; with 7.4% walking or cycling to work.[175] There are two local taxi companies. Aerial Capital Group enjoyed monopoly status until the arrival of Cabxpress in 2007.[266]
An interstate NSW TrainLink railway service connects Canberra to Sydney.[267] Canberra's railway station is in the inner south suburb of Kingston.[268] Between 1920 and 1922 the train line crossed the Molonglo River and ran as far north as the city centre, although the line was closed following major flooding and was never rebuilt, while plans for a line to Yass were abandoned. A 1067 mm gauge construction railway was built in 1923 between the Yarralumla brickworks and the provisional Parliament House; it was later extended to Civic, but the whole line was closed in May 1927.[269] Train services to Melbourne are provided by way of a NSW TrainLink bus service which connects with a rail service between Sydney and Melbourne in Yass, about a one hour drive from Canberra.[270][271]
Plans to establish a High speed rail service between Melbourne, Canberra and Sydney,[272] have not been implemented, as the various proposals have been deemed economically unviable.[273][274] The original plans for Canberra included proposals for railed transport within the city,[45] however none eventuated.[45] A railway connecting Canberra to Jervis Bay was also planned but never constructed.[275]
Canberra is about three hours by road from Sydney on the Federal Highway (National Highway 23),[276] which connects with the Hume Highway (National Highway 31) near Goulburn, and seven hours by road from Melbourne on the Barton Highway (National Highway 25), which joins the Hume Highway at Yass.[276] It is a two-hour drive on the Monaro Highway (National Highway 23) to the ski fields of the Snowy Mountains and the Kosciuszko National Park.[271] Batemans Bay, a popular holiday spot on the New South Wales coast, is also two hours away via the Kings Highway.[271]
Canberra International Airport provides direct domestic services to Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Adelaide, Gold Coast and Perth, with connections to other domestic centres.[277] There are direct daily flights to Albury and Newcastle in New South Wales. No regular commercial international flights operate from the airport. Canberra Airport is, as of September 2013, designated by the Australian Government Department of Infrastructure and Regional Development as a restricted use designated international airport.[278] Until 2003 the civilian airport shared runways with RAAF Base Fairbairn. In June of that year, the Air Force base was decommissioned and from that time the airport was fully under civilian control.[279]
Utilities

The government-owned ACTEW Corporation manages Canberra's water and sewerage infrastructure.[280][281] ActewAGL is a joint venture between ACTEW and AGL, and is the retail provider of Canberra's utility services including water, natural gas, electricity, and also some telecommunications services via a subsidiary TransACT.[282]
Canberra's water is stored in four reservoirs, the Corin, Bendora and Cotter dams on the Cotter River and the Googong Dam on the Queanbeyan River. Although the Googong Dam is located in New South Wales, it is managed by the ACT government.[283] ACTEW Corporation owns Canberra's two wastewater treatment plants, located at Fyshwick and on the lower reaches of the Molonglo River.[284][285]
Electricity for Canberra comes from the national power grid through substations at Holt and Fyshwick (via Queanbeyan).[286] Some limited local renewable power is produced via a hydro generator on the main water supply pipeline for Canberra at Mount Stromlo and methane plants at waste landfill sites at Belconnen and Mugga Lane.[287][288] Power was first supplied from a plant built in 1913, near the Molonglo River.[289] The ACT has the highest rate of home computer access (88 per cent of households) and broadband internet connection (74 per cent of households) in Australia.[290]
International relations
Sister cities
Canberra is twinned with:
See also
- 1971 Canberra flood
- 2003 Canberra bushfires
- Lists of capitals
- List of planned cities
- List of tallest buildings in Canberra
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Blundells Cottage". National Capital Authority. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Section 201". Copyright Act 1968. Australasian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 9 October 2007.
- ↑ "3218.0 - Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2012". Bureau of Statistics. 20 August 2013. Retrieved 24 January 2014.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Planning Data Statistics". ACT Planning & Land Authority. 21 July 2009. Archived from the original on 2 August 2008. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ Macquarie ABC Dictionary. The Macquarie Library. 2003. p. 144. ISBN 1-876429-37-2.
- ↑ Lewis, Wendy; Balderstone, Simon; Bowan, John (2006). Events That Shaped Australia. New Holland. p. 106. ISBN 978-1-74110-492-9.
- ↑ "Place Names". The Australian Women's Weekly (1932–1982) (1932–1982: National Library of Australia). 13 May 1964. p. 61. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Frei, Patricia. "Discussion on the Meaning of 'Canberra'". Canberra History Web. Patricia Frei. Retrieved 11 August 2013.
- ↑ Hull, Crispin. "European settlement and the naming of Canberra". Canberra – Australia’s National Capital. Crispin Hull. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ Cambage, R. H. (Richard Hind); Linnean Society of New South Wales (1919). Notes on the native flora of New South Wales. Part X, The Federal Capital Territory. Linnean Society of New South Wales. Retrieved 14 October 2013
- ↑ Gillespie, Lyall (1984). Aborigines of the Canberra Region. Canberra: Wizard (Lyall Gillespie). pp. 1–25. ISBN 0-9590255-0-2.
- ↑ Flood, J. M.; David, B.; Magee, J.; English, B. (1987). "Birrigai: a Pleistocene site in the south eastern highlands", Archaeology in Oceania 22:9–22
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Fitzgerald 1987, p. 5.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Gillespie 1991, pp. 3-8.
- ↑ Gillespie 1991, p. 9.
- ↑ "LETTERS.". The Sydney Morning Herald (NSW : 1842 - 1954) (NSW: National Library of Australia). 31 January 1934. p. 6. Retrieved 8 October 2012.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, p. 48.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 9.
- ↑ "The Royal Military College, Duntroon". Defence Housing Australia. p. 81. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, pp. 87-95.
- ↑ "Government House". Governor General of Australia. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Sparke 1988, p. 116.
- ↑ Gillespie 1991, p. 78.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 17.
- ↑ Weatherill, David (2007). "Church of St John the Baptist Cemetery". The Heraldry & Genealogy Society of Canberra. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 26.4 "Canberra – Australia's capital city". Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. 4 February 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 Fitzgerald 1987, p. 92.
- ↑ Gillespie 1991, pp. 220-230.
- ↑ Davison, Graeme; Hirst, John; Macintyre, Stuart, eds. (1998). The Oxford Companion to Australian History. Oxford University Press. pp. 464–465, 662–663. ISBN 9780195535976
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, p. 24.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 93.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 100.
- ↑ Gillespie 1991, p. 178.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, pp. 160-166.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, p. 63.
- ↑ Gillespie 1991, p. 303.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 103.
- ↑ Australian Bureau of Statistics 1963.
- ↑ "View Naming the Federal Capital of Australia". 12 March 1913.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 105.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, pp. 70-71.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 101.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 National Capital Development Commission 1988, p. 4.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Wigmore 1971, pp. 69-79.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 45.3 "History of the NCA". National Capital Authority. 11 June 2009. Retrieved 26 February 2010.
- ↑ "Glenloch Cork Oak Plantation". Territory and Municipal Services. Archived from the original on 21 July 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2010.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 130.
- ↑ Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House (12 April 2010). Witness to history: the opening of the Provisional Parliament House in 1927. Museum of Australian Democracy at Old Parliament House. Archived from the original on 13 May 2013
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, p. 101.
- ↑ "Ethel Bruce – Stanley Melbourne Bruce – Australia's PMs – Australia's Prime Ministers". National Archives of Australia. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, pp. 125-128.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, pp. 116-126.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 115.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 128.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, p. 113.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, p. 6.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 Sparke 1988, pp. 1-3.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 7-9.
- ↑ Minty, A. E. (1973). "Lake Burley Griffin, Australia". In Ackermann, William C.; White, Gilbert F.; Worthington, E. B. Man-Made Lakes: Their Problems and Environmental Effects. American Geophysical Union. p. 804. ISBN 87590-017-8
- ↑ Sparke 1988, p. 30.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 31-32.
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 Sparke 1988, pp. 103-104, 145, 188, 323.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, pp. 111-120.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, pp. 230-242.
- ↑ Andrews, p. 90.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 130-140.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 170-180.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 68.2 National Capital Development Commission 1988, p. 18.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 173-174.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Fitzgerald 1987, p. 138.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, p. 250.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 Sparke 1988, p. 180.
- ↑ Universal Publishers 2007, p. 6.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 "Australian Parliament House – 10 Years On". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 5 May 1998. Archived from the original on 18 April 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Election timetable – 1989 Election". Elections ACT. Archived from the original on 28 March 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Fact sheets". Legislative Assembly for the ACT. Archived from the original on 29 March 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 "Role of the Assembly". Legislative Assembly for the ACT. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 78.2 78.3 78.4 78.5 "Past Election Results". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 13 January 2010.
- ↑ Jerga, Josh (3 December 2009). "NSW boasts first female leadership team". The Sydney Morning Herald (Fairfax Media). Archived from the original on 15 May 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2010.
- ↑ Doogan, Maria (December 2006). The Canberra Firestorm: Inquests and inquiry into four deaths and four fires between 8 and 18 January 2003 1. Canberra: ACT Coroners Court. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ "About the Centenary of Canberra". Centenary of Canberra unit - ACT Government. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 82.3 82.4 82.5 82.6 82.7 82.8 "Climate of Canberra Area". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Lady luck or lucky lady?". The Queanbeyan Age. 19 July 2002. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Nature Park: Mt Majura Nature Reserve". ACT Government Territory and Municipal Services. 2004. Archived from the original on 26 March 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Nature Park: Mt Taylor Nature Reserve". ACT Government Territory and Municipal Services. 2004. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 24 Feb 2013.
- ↑ "Canberra Nature Park: Mt Ainslie Nature Reserve". ACT Government Territory and Municipal Services. 2004. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 24 Feb 2013.
- ↑ "Canberra Nature Park: Mt Mugga Mugga Nature Reserve". ACT Government Territory and Municipal Services. 2004. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 24 Feb 2013.
- ↑ "Canberra Nature Park: Black Mountain Nature Reserve". ACT Government Territory and Municipal Services. 2004. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 24 Feb 2013.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 Penguin Books Australia 2000, p. 28.
- ↑ McLeod, R. (2003). Inquiry into the Operational Response to the January 2003 Bushfires in the ACT. Canberra, ACT. ISBN 0-642-60216-6
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 91.2 Gibbney 1988, inside cover.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 131-132.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 181-182.
- ↑ "Lake Ginninderra". ACT Government Territory and Municipal Services. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ↑ Williams 2006, p. 260.
- ↑ Sparke 1988, pp. 4-7, 13-14.
- ↑ Scrivener Dam (PDF). National Capital Authority. pp. 1–2. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 2 June 2009.
- ↑ "Climate: Canberra - Climate graph, Temperature graph, Climate table". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 5 September 2013.
- ↑ 1301.0 - Year Book Australia, 2002. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 25 January 2002. Archived from the original on 12 October 2012
- ↑ "Australia – Climate of Our Continent". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Climate information for Canberra Aero". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Climate statistics for Australian locations". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ↑ "Special Climate Statement 43 – extreme heat in January 2013". Bureau of Meteorology. 1 February 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2013.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, pp. 60-63.
- ↑ 105.0 105.1 Wigmore 1971, p. 67.
- ↑ Universal Publishers 2007, pp. 10-120.
- ↑ National Capital Development Commission 1988, p. 3.
- ↑ 108.0 108.1 108.2 108.3 108.4 Wigmore 1971, p. 64.
- ↑ 109.0 109.1 109.2 109.3 National Capital Development Commission 1988, p. 17.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, pp. 64-67.
- ↑ "Timeline Entries for William Morris Hughes". National Archives of Australia. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ Universal Publishers 2007, pp. 10-60.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, pp. 110-200.
- ↑ "About Weston Creek, Canberra". Weston Creek Community Council. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Fitzgerald 1987, p. 167.
- ↑ 116.0 116.1 116.2 116.3 116.4 116.5 "Lake Burley Griffin Interactive Map". National Capital Authority. Retrieved 1 June 2009.
- ↑ 117.0 117.1 Sparke 1988, pp. 154-155.
- ↑ "How to cut through the ACT's planning thicket". The Canberra Times. 2 March 2005. Archived from the original on 13 November 2011. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ 119.0 119.1 Trail, Jim (9 April 2010). "It's time to review the grand plan for Canberra, says the NCA". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Grants of leases". ACT Planning & Land Authority. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ 121.0 121.1 "Place name processes". ACT Planning & Land Authority. 11 May 2009. Archived from the original on 19 April 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2010.
- ↑ "Diplomatic and Consular Premises – Protocol Guidelines". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Johnston, Dorothy (September 2000). "Cyberspace and Canberra Crime Fiction". Australian Humanities Review. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ 124.0 124.1 "Role of the Assembly". Legislative Assembly for the ACT. 2010. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Election Summary". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 13 January 2010.
- ↑ 126.0 126.1 "Fraser". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 29 December 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- ↑ "Turbulent 20yrs of self-government". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 11 May 2009. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- ↑ 128.0 128.1 Sparke 1988, p. 289.
- ↑ 129.0 129.1 "ACT Representation (House of Representatives) Act 1974 (Cth)". National Archives of Australia. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- ↑ "Senate – A.C.T.". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 6 November 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- ↑ 131.0 131.1 "Administration of National Land". National Capital Authority. 2008, 18 December. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Capital Works Overview". National Capital Authority. 2008, 23 October. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Maintenance and Operation of Assets". National Capital Authority. 2008, 23 October. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Australian Capital Territory (Self-Government) Act 1988". Australasian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- ↑ "Australian Capital Territory (Self-Government) Act 1988. Schedule 4". Australasian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Frequently Asked Questions". Australian Federal Police. 19 November 2009. Archived from the original on 3 January 2010. Retrieved 21 January 2010.
- ↑ "ACT Policing". Australian Federal Police. 16 March 2010. Archived from the original on 27 January 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "History". The Supreme Court of the ACT. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "General Information". The Supreme Court of the ACT. 16 October 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Laverty, Jo (21 May 2009). "The Belconnen Remand Centre". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Kittel, Nicholas (26 November 2008). "ACT prison built to meet human rights obligations". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Court List". Family Court of Australia. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Court Listing". ACT Law Courts and Tribunals. Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "1367.0 State and Territory Statistical Indicators - Unemplyment rate: ABS". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 12 June 2012. Retrieved 6 July 2012.
- ↑ "ACT Stats, 2005". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 12 September 2005. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "6302.0 - Average Weekly Earnings, Australia, May 2013". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 15 August 2013. Retrieved 4 November 2013.
- ↑ Janda, Michael (29 October 2009). "House prices surge as rate hike looms". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "It’s official: the property market has cooled". Real Estate Institute of Australia. 9 September 2010. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ January 2004&Latest "Census of Population and Housing Australia in Profile A Regional Analysis". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2004. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra homes cheaper to buy than rent: REIA". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 17 June 2009. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ "Australian house prices surge!". Global Property Guide. 22 November 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ All of the land in the ACT land is held by the government.
- ↑ s68 allows for an annual increase linked to a Rental Housing CPI index, which is usually significantly higher than CPI. For 2008 this deems an increase up to 10.12% as not excessive on the face of it.
- ↑ "Gross State Product 2011–12". ACT Government Chief Minister and Treasury Directorate, Economics Branch. 21 November 2012. Archived from the original on 30 July 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ↑ "Industry of employment by place of work". ACT Government Chief Minister and Treasury Directorate. 28 June 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ↑ "HMAS Harman". Royal Australian Navy. 2008. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ↑ "Fairbairn: Australian War Memorial". Australian War Memorial. 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "RAAF Museum Fairbairn". RAAF Museum. 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "No 34 Squadron". RAAF Museum. 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ Sutherland, Tracy (15 January 2007). "USFTA begins to reap results". Australian Financial Review. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Sharma, Mahesh (2 April 2008). "HP bids for Tower Software". The Australian. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Colley, Andrew (2 October 2007). "HP bids for Tower Software". The Australian. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Corbell, Simon (28 August 2013). "Minister showcases Canberra's sustainability success" (Press release).
- ↑ Zero waste. Residua. September 2001. Archived from the original on 18 November 2011
- ↑ Lauer, Sandra (23 May 2007). Reducing commercial waste going to landfill in Canberra by improving the waste management practices of micro businesses. ACT Government. Archived from the original on 19 May 2013
- ↑ Canberra's waste dilemma. CityNews Canberra. 2 March 2011. Archived from the original on 5 May 2013
- ↑ Allen, Craig (1 March 2010). No waste. ABC News
- ↑ Plastic Bag Ban. ACT Government. 1 November 2011
- ↑ 169.0 169.1 Dyett, Kathleen (1 November 2011). "ACT bag ban begins". ABC News. Archived from the original on 12 January 2012.
- ↑ "Bin bag sales booming". ABC News. 9 January 2012. Archived from the original on 12 January 2012.
- ↑ Nash, Lucy (18 January 2010). No waste 2010=some waste 2010. 666 ABC Canberra
- ↑ Pryor, Penny (30 October 2011). "Saving money can help save others". The Canberra Times (Fairfax Media). Archived from the original on 4 June 2012.
- ↑ Sustainability issues in Canberra – background. ACT Government. 13 June 2012. Archived from the original on 26 April 2013
- ↑ 174.0 174.1 174.2 174.3 174.4 174.5 174.6 Australian Bureau of Statistics (31 October 2012). "Canberra - Queanbeyan (Canberra Part)". 2011 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 24 January 2014.
- ↑ 175.0 175.1 Australian Bureau of Statistics (25 October 2007). "Community Profile Series : Canberra (Statistical Division)". 2006 Census of Population and Housing. Retrieved 24 January 2009.
- ↑ "2006 Census QuickStats : Canberra (Statistical Division)". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 25 October 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Australian Demographic Statistics, Dec 2002". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 5 June 2003. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ "Sweet charity: territory leads in giving". The Canberra Times (Fairfax Media). 4 November 2013. Archived from the original on 4 November 2013.
- ↑ "6227.0.55.003 - Education and Work, Australia - Additional data cubes, May 2013". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 29 November 2013. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ↑ "Recorded Crime, Australia 2002". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 29 May 2003. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ "University of Canberra". Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations. Archived from the original on 11 December 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 182.0 182.1 "Australian National University". Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, pp. 258-262.
- ↑ "Academic Ranking of World Universities 2004". Institute of Higher Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. 2004. Archived from the original on 27 November 2007. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Campus". Australian Catholic University. 5 May 2010. Archived from the original on 14 October 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra School of Theology". Charles Sturt University. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Australian Defence College". Australian Defence College. Archived from the original on 8 August 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Campbell". North Canberra Community Council. Archived from the original on 23 April 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "The Program". Australian Defence Force Academy. Archived from the original on 27 August 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Introduction". Australian Defence Force Academy. 2 April 2009. Archived from the original on 12 November 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Officer Training". Defence Jobs. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Campus Maps". Canberra Institute of Technology. 25 February 2010. Archived from the original on 23 August 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Barr, Andrew (2007). "Towards 2020: Renewing Our Schools – Message from the Minister". ACT Department of Education and Training. Archived from the original on 2 March 2011. Retrieved 13 May 2005.
- ↑ "Closing date for primary school". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 29 October 2009. Retrieved 10 May 2010.
- ↑ "Tharwa, Hall schools should be reopened: committee". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 17 September 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "School closures report 'doesn't go far enough'". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 18 September 2009. Archived from the original on 31 January 2010. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ Universal Publishers 2007, pp. 1-90.
- ↑ "Locations and opening hours". National Archives of Australia. Archived from the original on 6 October 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "The Shine Dome". Australian Academy of Science. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Visiting the High Court". High Court of Australia. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Visitors". Parliament of Australia. Archived from the original on 17 February 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Opening hours". Royal Australian Mint. Archived from the original on 18 May 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ↑ "Outdoor and Nature". Visit Canberra. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Canberra Museum and Gallery. ACT Government. Archived from the original on 11 May 2013
- ↑ "Lanyon". ACT Museums and Galleries. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Minders of Tuggeranong Homestead". Chief Minister's Department. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Mugga-Mugga". ACT Museums and Galleries. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Calthorpes' House". ACT Museums and Galleries. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ Atkinson, Ann; Knight, Linsay; McPhee, Margaret (1996). The Dictionary of Performing Arts in Australia: Opera, Dance, Music. Allen & Unwin. pp. 46–47. ISBN 1-86448-005-X.
- ↑ 210.0 210.1 Daly, Margo (2003). Rough Guide to Australia. Rough Guides. p. 67. ISBN 1-84353-090-2.
- ↑ "Fact sheets". National Archives of Australia. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ↑ 212.0 212.1 Vaisutis 2009, p. 278.
- ↑ Vaisutis 2009, pp. 283-285.
- ↑ Universal Publishers 2007, pp. 10-12.
- ↑ 215.0 215.1 215.2 "Canberra's international relationships". Chief Minister's Department. Retrieved 13 May 2019.
- ↑ "Festival celebrates Canberra-Nara friendship". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 26 September 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Nara Candle Festival". The Canberra Times. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Nara Park". ACT Government Territory and Municipal Services. 9 October 1999. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ↑ "Speaker archive". National Press Club of Australia. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Bills Digest No. 132 2001-02: Broadcasting Services Amendment (Media Ownership) Bill 2002". Parliament of Australia. 21 March 2002. Archived from the original on 31 January 2013. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ↑ "Subscription television". TransACT. 11 June 2009. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ↑ Wigmore 1971, p. 87.
- ↑ Waterford, Jack (3 March 2013). "History of a paper anniversary". The Canberra Times (Fairfax Media). Archived from the original on 17 September 2013.
- ↑ "BMA comes of age". ABC. 24 March 2013. Archived from the original on 7 October 2013.
- ↑ "Brumbies Crowned Super 12 Champions.". Irish Rugby. 22 May 2004. Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Premiership Records.". Canberra Raiders. Retrieved 22 February 2009.
- ↑ "Canberra Stadium". Australian Institute of Sport. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Sydney 2000:Football". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 1999. Archived from the original on 3 August 2007. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Complete draw for 2003 Rugby World Cup". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 2003. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Caps take WNBL championship". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 17 February 2007. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Canberra downs Roar to clinch W-League title". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 31 January 2012. Retrieved 3 February 2012.
- ↑ Hinds, Richard (1 April 2005). "Kangaroos finding capital gains taxing". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Dogs, Demons to play in Canberra". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 16 August 2006. Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. Retrieved 9 October 2007.
- ↑ "Who Rules, Aussie Rules!". AFL. 15 February 2007. Archived from the original on 5 March 2007. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ Growden 2008, pp. 200-210.
- ↑ "Canberra Marathon". Canberra Marathon. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Title winners head to Canberra". Tennis Australia. 7 January 2006. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ 238.0 238.1 Sparke 1988, p. 304.
- ↑ "History and successes". Australian Institute of Sport. Archived from the original on 18 January 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Boating on Lake Burley Griffin". National Capital Authority. Archived from the original on 23 September 2007. Retrieved 9 October 2007.
- ↑ "Lake Burley Griffin reopens". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 16 November 2007. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Dragway Frequently Asked Questions" (PDF). ACT Government. 21 February 2006. Archived from the original on 10 April 2012. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ "Possum Bourne". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 3 May 2003. Archived from the original on 25 April 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ↑ 244.0 244.1 "Hospitals". ACT Health. Archived from the original on 26 March 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Canberra Hospital". ACT Health. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 246.0 246.1 "Contact Us & Location Map". Calvary Health Care ACT. Archived from the original on 23 March 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Public Hospital". Calvary Health Care ACT. Archived from the original on 18 July 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Cronin, Fiona (12 August 2008). "Chemo crisis to hit ACT patients". The Canberra Times. Archived from the original on 13 November 2011]]. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Welcome to Calvary John James Hospital". Calvary John James Hospital. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "15 years since hospital implosion tragedy". The Canberra Times (Fairfax Media). 13 July 2012. Archived from the original on 14 July 2012. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ↑ Reynolds, Fiona (5 November 1999). "Increasing pressure on ACT Chief Minister". A.M. (Australian Broadcasting Corporation). Archived from the original on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2009.
- ↑ "About Emergency". ACT Government Health Information. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "About Us". ACT Emergency Services Authority. Archived from the original on 22 August 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "What is NETS?". Newborn Emergency Transport Service. Archived from the original on 23 December 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 255.0 255.1 "Canberra's transport system" (PDF). Parliament of Australia. Archived from the original on 7 February 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Penguin Books Australia 2000, pp. 23-25.
- ↑ Penguin Books Australia 2000, pp. 3-6, 32-35, 53-59, 74-77, 90-91, 101-104.
- ↑ "ACT Road Hierarchy". Territory and Municipal Services. 14 April 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Survey shows speeding at disputed camera site". Chief Minister's Department. 17 July 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Speeding". Australian Federal Police. 20 May 2008. Archived from the original on 12 November 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Universal Publishers 2007, pp. 57, 67, 77.
- ↑ Universal Publishers 2007, pp. 1-100.
- ↑ "About Us". ACTION. 18 July 2008. Archived from the original on 31 October 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "About Us". Transborder Express. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "About Us". Deane's Buslines. 4 February 2010. Archived from the original on 18 May 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Taxi company 'not concerned' at losing monopoly". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 3 February 2007. Archived from the original on 18 February 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Timetables". CountryLink. Archived from the original on 26 March 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Travel pass agencies". CountryLink. 14 December 2009. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Shellshear, Walter M. "Railways". Canberra's Engineering Heritage. Engineers Australia. Archived from the original on 23 July 2013. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ "Network map". CountryLink. Archived from the original on 23 April 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ 271.0 271.1 271.2 Penguin Books Australia 2000, pp. 20.
- ↑ Richardson, Michael (19 July 2000). "Sydney to Canberra in 80 Minutes–by High-Speed Train". New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ "Oz HSR Received?". The Australian. 29 October 2002. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ Somer, Belinda (14 June 2001). "Govt considers rail link between eastern cities". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- ↑ Gibbney 1988, pp. 58, 60.
- ↑ 276.0 276.1 Penguin Books Australia 2000, inside cover.
- ↑ "Departures". Canberra International Airport. Archived from the original on 2 September 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ↑ "Designated International Airports in Australia". Australian Government Department of Infrastructure and Regional Development. 27 February 2013. Archived from the original on 10 May 2013.
- ↑ Hogan, Richard (July 2003). "Farewell to Fairbairn". Air Force (Royal Australian Air Force) 45 (12).
- ↑ "Company Profile". ACTEW. Archived from the original on 18 July 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- ↑ "Wastewater Networks". ActewAGL. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Our company". ActewAGL. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Water Catchment". ActewAGL. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "North Canberra Water Reuse Scheme (NCWRS)". ActewAGL. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Lower Molonglo Water Quality Control Centre (LMWQCC) effluent reuse scheme". ActewAGL. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Independent Competition and Regulatory Commission (October 2003). "Review of Contestable Electricity Infrastructure Workshop" (PDF). p. 13. Archived from the original on 20 April 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2010.
- ↑ "ActewAGL". ActewAGL. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "Renewable Gas Sources". ActewAGL. 11 June 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ "The Founding of Canberra". The Sydney Morning Herald. 14 March 1913. p. 5.
- ↑ "1301.0 - Year Book Australia, 2009-10 USE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT)". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 4 June 2010. Archived from the original on 19 November 2013.
References
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (25 January 1963). "The Australian Capital Territory, Canberra the National Capital: Fifty Years of Development". Year Book Australia (Australian Bureau of Statistics). Archived from the original on 4 June 2011
- Lake Burley Griffin, Canberra: Policy Plan. Canberra: National Capital Development Commission. 1988. ISBN 0-642-13957-1.
- The Penguin Australia Road Atlas. Ringwood, Victoria: Penguin Books Australia. 2000. ISBN 0-670-88980-6.
- UBD Canberra. North Ryde, New South Wales: Universal Publishers. 2007. ISBN 0-7319-1882-7.
- Fitzgerald, Alan (1987). Canberra in Two Centuries: A Pictorial History. Torrens, Australian Capital Territory: Clareville Press. ISBN 0-909278-02-4.
- Gibbney, Jim (1988). Canberra 1913–1953. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service. ISBN 0-644-08060-4.
- Gillespie, Lyall (1991). Canberra 1820–1913. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service. ISBN 0-644-08060-4.
- Growden, Greg (2008). Jack Fingleton: The Man Who Stood Up To Bradman. Crows Nest, New South Wales: Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-74175-548-0.
- Sparke, Eric (1988). Canberra 1954–1980. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service. ISBN 0-644-08060-4.
- Vaisutis, Justine (2009). Australia. Footscray, Victoria: Lonely Planet. ISBN 1-74179-160-X.
- Wigmore, Lionel (1971). Canberra: History of Australia's National Capital. Canberra: Dalton Publishing Company. ISBN 0-909906-06-8.
- Williams, Dudley (2006). The Biology of Temporary Waters. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-852811-6.
- Leigh, Andrew (3 October 2010). Canberra is the Best City in Australia (Speech). Festival of Dangerous Ideas. Sydney Opera House. Archived from the original on 13 September 2013. https://web.archive.org/web/20130913160556/http://andrewleigh.com/index.php/speaking2/93-community-home-page/speaking/community/78-canberrabestcity. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
External links
| Wikiquote has a collection of quotations related to: Canberra |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Canberra. |
![]() Canberra travel guide from Wikivoyage
Canberra travel guide from Wikivoyage
- WikiSatellite view of Canberra at WikiMapia
- A general Canberra tourist site
- The ACT Government webpage
- Canberra region map – all districts
- ACT Locate – land and planning maps
- Canberra - Tourism Australia
- Canberra 100 - Celebrating Canberra's 100th anniversary
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||