Calone
| Calone | |
|---|---|
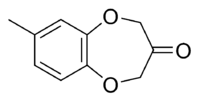 | |
| IUPAC name 7-Methylbenzo[b][1,4]dioxepin-3-one | |
| Other names Calone 1951; Watermelon ketone; Methylbenzodioxepinone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 28940-11-6 |
| ChemSpider | 107218 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C10H10O3 |
| Molar mass | 178.18 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Calone or methylbenzodioxepinone, trade-named Calone 1951, was discovered by Pfizer in 1966. It is used to give the olfactory impression of a fresh seashore through the marine and ozone nuances. Calone is similar in structure of certain alicyclic C11-hydrocarbons like ectocarpene, excreted by some species of brown algae as pheromones.
Calone is an unusual odorant which has an intense "sea-breeze" note with slight floral overtones. It was used as a scent component since the 1980s for its watery, fresh, ozone accords, then as more dominant note in several perfumes of the marine trend, beginning in the 1990s.