Calcium iodide
| Calcium iodide | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name calcium iodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 10102-68-8 13640-62-5 (tetrahydrate) |
| PubChem | 66244 |
| ChemSpider | 59629 |
| UNII | 8EKI9QEE2H |
| RTECS number | EV1300000 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Ca+2].[I-].[I-]|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | CaI2 |
| Molar mass | 293.887 g/mol (anhydrous) 365.95 g/mol (tetrahydrate) |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 3.956 g/cm³[1] |
| Melting point | 779 °C (tetrahydrate) with decomposition |
| Boiling point | 1100 °C |
| Solubility in water | 64.6 g/100 mL (0 °C) 66 g/100 mL (20 °C) 81 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in acetone and alcohols |
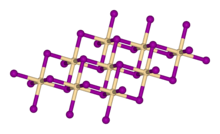
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Rhombohedral, hP3 |
| Space group | P-3m1, No. 164 |
| Coordination geometry |
octahedral |
| Hazards | |
| EU Index | Not listed |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
2
1
|
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | calcium fluoride calcium chloride calcium bromide |
| Other cations | beryllium iodide magnesium iodide strontium iodide barium iodide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Calcium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaI2. This colourless deliquescent solid is highly soluble in water. Its properties are similar to those for related salts, such as calcium chloride. It is used in photography.[1]
Reactions
Henri Moissan first isolated pure calcium in 1898 by reducing calcium iodide with pure sodium metal:[2]
Calcium iodide can be formed by treating calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, or calcium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid:[3]
Calcium iodide slowly reacts with oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air, liberating iodine, which is responsible for the faint yellow color of impure samples.[4]
- 2 CaI2 + 2 CO2 + O2 → 2 CaCO3 + 2 I2
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Turner, Jr., Francis M., ed. (1920), The Condensed Chemical Dictionary (1st ed.), New York: Chemical Catalog Co., p. 127, retrieved 2007-12-08
- ↑ Mellor, Joseph William (1912), Modern Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Longmans, Green, and Co, p. 334, retrieved 2007-12-08
- ↑ Gooch, Frank Austin; Walker, Claude Frederic (1905), Outlines of Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Macmillan, p. 340, retrieved 2007-12-08
- ↑ Jones, Harry Clary (1906), Principles of Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Macmillan, p. 365, retrieved 2007-12-08