Calcium iodate
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Calcium iodate | |
|---|---|
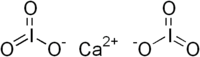 | |
| IUPAC name Calcium diiodate | |
| Other names Lautarite | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 7789-80-2 10031-33-1 (hexahydrate) |
| PubChem | 24619 |
| ChemSpider | 23021 |
| EC-number | 232-191-3 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Ca+2].[O-]I(=O)=O.[O-]I(=O)=O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | Ca(IO3)2 |
| Molar mass | 389.88 g/mol (anhydrous) 407.90 g/mol (monohydrate) |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 4.519 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 540 °C (monohydrate) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| Solubility in water | 0.09 g/100 mL (0 °C) 0.24 g/100 mL (20 °C) 0.67 g/100 mL (90 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in nitric acid insoluble in alcohol |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | monoclinic (anhydrous) cubic (monohydrate) orthorhombic (hexahydrate) |
| Hazards | |
| EU Index | not listed |
| Flash point | non-flammable |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Calcium iodate (also called lautarite) is a compound of calcium and iodate anion. Its formula is Ca(IO3)2. It is used as a dough conditioner. Calcium iodate is an oxidant, hence it is added to lotions and ointments as an antiseptic and deodorant.[1] It can also be used as an iodine supplement in chicken feed. It may be formed by the anodic oxidation of calcium iodide or by passing chlorine into a hot solution of lime in which iodine has been dissolved.
References
- ↑ Calcium iodate from the Online Medical Dictionary
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.