Bufadienolide
| Bufadienolide | ||
|---|---|---|
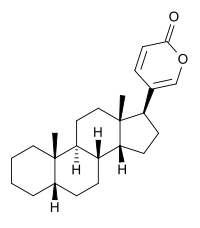 | ||
| IUPAC name 5-[(5R, 8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pyran-2-one | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| PubChem | 3035030 | |
| ChemSpider | 26286947 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C24H34O2 | |
| Molar mass | 354.53 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Bufadienolide is a type of steroid. Its derivatives are collectively known as bufadienolides, including many in the form of bufadienolide glycosides (bufadienolides that contain structural groups derived from sugars). These are a type of cardiac glycoside, the other being the cardenolide glycosides. Both bufadienolides and their glycosides are toxic; specifically, they are heart-arresting.
Etymology
The term derives from the toad genus Bufo that contains bufadienolide glycosides, the suffix -adien- that refers to the two double bonds in the lactone ring, and the ending -olide that denotes the lactone structure. Consequently, related structures with only one double bond are called bufenolides[citation needed], and the saturated equivalent is bufanolide.
Classification
According to MeSH, bufadienolides and bufanolides are classified as follows:
- Bufanolides
- Bufenolides
- Bufadienolides
- Cardenolides
Note that cardenolides have been classified under cardanolides as well as cardiac glycosides in this classification.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||